
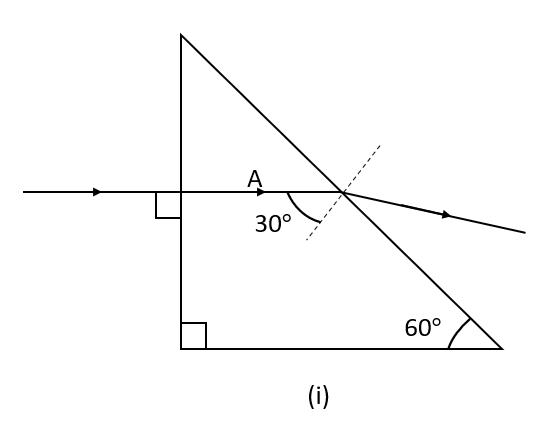
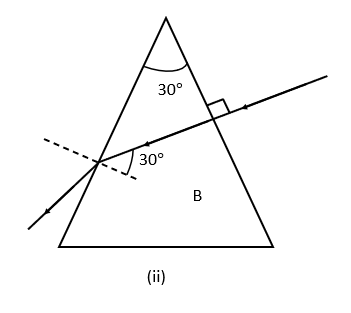
The above figure shows a light ray of single colour incident normally on two prisms A and B. In each case draw the path of the ray of light as it enters and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angle wherever necessary.
Answer
507k+ views
Hint: When a ray of light penetrates the glass prism, it gets diverged two times. First, when it goes inside the glass prism, and second when it appears out of the prism due to the refracting surfaces of the prism are not parallel to each other. Also, when the ray of light moves through the prism, it inclines towards its base.
Complete answer:
The shift in the direction of the path of light, when it moves from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is named the refraction of light.
When a ray of light from the air goes into a denser medium, the ray of light turns towards the normal. As the speed of light drops in the denser medium, it inclines towards the normal.
A glass prism is a transparent material having two triangular edges and three rectangular sides. The refraction of light in a glass prism is distinct from a glass slab. In a glass prism, the incident ray of light is not parallel to an emergent ray of light.
When a light ray crosses from a less dense material (e.g., air) into a denser material (e.g., glass or water), it is bent away from the surface between the two materials. This means that the refraction angle is always less than the angle of incidence in this situation.
When a light ray crosses from a denser material (e.g., water or glass) into a less dense material (e.g., air), it is bent towards the surface between the two materials. This means that the refraction angle is always more significant than the angle of incidence in this situation.
Note: The speed of light drops when it enters from a rarer medium to a denser medium and increases from a denser medium to a rarer medium. Therefore, light rays' speed rises when light rays pass from water to air, and the speed of light decreases when light rays pass from water to glass.
Complete answer:
The shift in the direction of the path of light, when it moves from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is named the refraction of light.
When a ray of light from the air goes into a denser medium, the ray of light turns towards the normal. As the speed of light drops in the denser medium, it inclines towards the normal.
A glass prism is a transparent material having two triangular edges and three rectangular sides. The refraction of light in a glass prism is distinct from a glass slab. In a glass prism, the incident ray of light is not parallel to an emergent ray of light.
When a light ray crosses from a less dense material (e.g., air) into a denser material (e.g., glass or water), it is bent away from the surface between the two materials. This means that the refraction angle is always less than the angle of incidence in this situation.
When a light ray crosses from a denser material (e.g., water or glass) into a less dense material (e.g., air), it is bent towards the surface between the two materials. This means that the refraction angle is always more significant than the angle of incidence in this situation.


Note: The speed of light drops when it enters from a rarer medium to a denser medium and increases from a denser medium to a rarer medium. Therefore, light rays' speed rises when light rays pass from water to air, and the speed of light decreases when light rays pass from water to glass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




