
Terylene is a polymer obtained from:
a.) Ethylene Glycol and Glycerol
b.) Ethylene Glycol and Glyceraldehyde
c.) Ethylene Glycol and Terephthalic Acid
d.) None of the above.
Answer
601.5k+ views
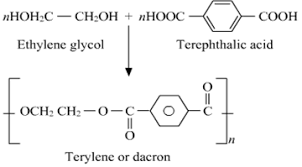
Hint: The structure of Terylene is as follows:
 Monomers are relatively small and simple molecules or units of a large molecule or a polymer. Monomers bond together to form a polymer. With this idea of polymers in mind, think of which of the given options could feasibly polymerise to give Terylene.
Monomers are relatively small and simple molecules or units of a large molecule or a polymer. Monomers bond together to form a polymer. With this idea of polymers in mind, think of which of the given options could feasibly polymerise to give Terylene.
Complete step by step solution:
Before we address this question directly, let us first understand what polymerisation really means.
A polymer is a large molecule/macromolecule which is a combination of many smaller molecules also known as monomers. 103−107u is the range of the molar mass of a polymer.
It is possible to find polymers naturally in plants and animals. These polymers are referred to as natural polymers. The polymers that are man-made however are known as synthetic polymers.
Different polymers have a number of unique physical and chemical properties due to which they find usage in everyday life.
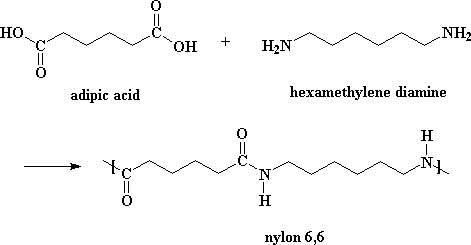
Examples: Nylon 6,6 which is made up of monomers adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine.
Now let us come to the case of Terylene and analyse what its monomers really are.
Terylene is a practical example of a polyester. Like nylon, it is popular for the use in making synthetic textiles from the force constants for bond stretching and valence angle deformation the Young’s modulus E value for the crystal of terylene or fibre can be calculated.
It is made by the condensation polymerization of benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid or we can say terephthalic acid with ethane-1,2-diol in the presence of an acid which works as a catalyst.
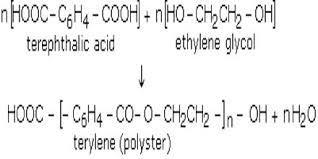 Therefore, we can conclude that the answer to this question is c) Ethylene Glycol and Terephthalic Acid.
Therefore, we can conclude that the answer to this question is c) Ethylene Glycol and Terephthalic Acid.
NOTE: Remember the physical properties of Terylene in that it is a synthetic fibre used for making clothes and that it is elastic, highly durable and wrinkle-free for future reference. It is also very important to have thorough knowledge of the concepts of polymerisation, monomers and polymers for us to be able to answer this question correctly.

Complete step by step solution:
Before we address this question directly, let us first understand what polymerisation really means.
A polymer is a large molecule/macromolecule which is a combination of many smaller molecules also known as monomers. 103−107u is the range of the molar mass of a polymer.
It is possible to find polymers naturally in plants and animals. These polymers are referred to as natural polymers. The polymers that are man-made however are known as synthetic polymers.
Different polymers have a number of unique physical and chemical properties due to which they find usage in everyday life.
Examples: Nylon 6,6 which is made up of monomers adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine.

Now let us come to the case of Terylene and analyse what its monomers really are.
Terylene is a practical example of a polyester. Like nylon, it is popular for the use in making synthetic textiles from the force constants for bond stretching and valence angle deformation the Young’s modulus E value for the crystal of terylene or fibre can be calculated.
It is made by the condensation polymerization of benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid or we can say terephthalic acid with ethane-1,2-diol in the presence of an acid which works as a catalyst.

NOTE: Remember the physical properties of Terylene in that it is a synthetic fibre used for making clothes and that it is elastic, highly durable and wrinkle-free for future reference. It is also very important to have thorough knowledge of the concepts of polymerisation, monomers and polymers for us to be able to answer this question correctly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




