
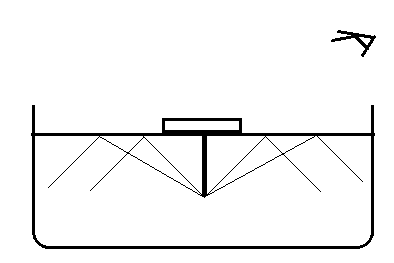
Take a thin thermocol sheet. Cut it in circular discs of different radii like \[2cm,3cm,4cm,4.5cm,5cm\] etc and mark centres with a sketch pen. Now take needles of length nearly \[6cm\]. Pin a needle to each disc at its centre vertically. Take water in a large opaque tray and place the disc with \[2cm\] radius in such a way that the needle is inside the water as shown in the figure. Now try to view the free end (head) of the needle from the surface of the water.
Are you able to see the head of the needle?

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: We know that light undergoes refraction when it travels from one medium to another. From Snell’s law we also know that the angle of the refracted light also depends on the medium i.e. the refractive index of the medium.
Complete answer:
We know that the light has the ability to bend or bounce back when it interacts with a medium. This is given as the reflection and refraction of light.
Here since the light rays travel from the water to air they undergo refraction. Then we can talk about the refractive index of water and air, which describes how fast or slow the light travels in the given medium.
We also know that the light rays undergo total internal reflection. Here, the air-water medium acts as a mirror, causing the incident light to reflect back into the water medium. This occurs when the refracted light makes an angle $90^{\circ}$ with the medium, then the corresponding angle of incidence is called the critical angle.
For water the critical angle is \[{{48.5}^{\circ }}\].
Then, we can say that to observe the needle in the water, the light from the needle must reach the air medium and must avoid total internal reflection. Thus for the needle to be visible it must be viewed at an angle less than \[{{48.5}^{\circ }}\]
Note:
From Snell’s law, we can say that $\mu_{w} sin( i)=\mu_{a} sin( r)$ where $i$ is the angle of incidence of the light ray from the water medium whose refractive index is given as $\mu_{w}$ and $r$ is the angle of refraction of the light ray at the air medium whose refractive index is given as $\mu_{a}$ .
Complete answer:
We know that the light has the ability to bend or bounce back when it interacts with a medium. This is given as the reflection and refraction of light.
Here since the light rays travel from the water to air they undergo refraction. Then we can talk about the refractive index of water and air, which describes how fast or slow the light travels in the given medium.
We also know that the light rays undergo total internal reflection. Here, the air-water medium acts as a mirror, causing the incident light to reflect back into the water medium. This occurs when the refracted light makes an angle $90^{\circ}$ with the medium, then the corresponding angle of incidence is called the critical angle.
For water the critical angle is \[{{48.5}^{\circ }}\].
Then, we can say that to observe the needle in the water, the light from the needle must reach the air medium and must avoid total internal reflection. Thus for the needle to be visible it must be viewed at an angle less than \[{{48.5}^{\circ }}\]
Note:
From Snell’s law, we can say that $\mu_{w} sin( i)=\mu_{a} sin( r)$ where $i$ is the angle of incidence of the light ray from the water medium whose refractive index is given as $\mu_{w}$ and $r$ is the angle of refraction of the light ray at the air medium whose refractive index is given as $\mu_{a}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




