
How will you synthesize benzoic acid from bromobenzene?
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: There are several methods that you can opt for the given conversion. However, you can use the most common one i.e. the use of a Grignard reagent for this. Convert bromobenzene to phenyl bromo bromobenzene and then treat it with carbon dioxide and a dilute acid to get the required mechanism
Complete answer:
We know that the structure of benzoic acid is-
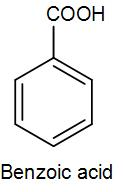
We have to convert bromobenzene to benzoic acid and there are several methods that we can use for this conversion like partial oxidation of toluene, hydration of benzamide. However, here we will discuss the conversion using a Grignard reagent, so let’s discuss the steps involved but before that let’s discuss what Grignard reagent is.
This reagent is magnesium containing a chemical compound with the formula- R-Mg-X. R can be any alkyl group and X stands for halide. The most common example is $C{{H}_{3}}MgCl$. It is partly ionic $\left( \overset{\delta -}{\mathop{R}}\,\cdots \overset{\delta +}{\mathop{Mg}}\,X \right)$ and here the alkyl group bears a partial negative charge. It acts as a strong base and thus reacts with acidic hydrogen to give us alkanes.
In the first step, we have to synthesize the Grignard reagent from bromobenzene which we can do by adding magnesium in a solution of diethyl ether. We can write the reaction as-
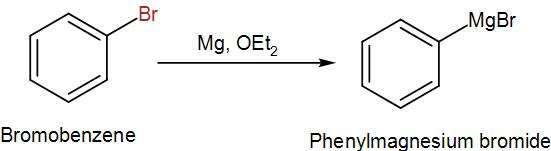
Then, we treat the obtained organometallic reagent by excess dry ice and then add dilute aqueous acid to it. This gives us the required acid. We can write the reaction as-
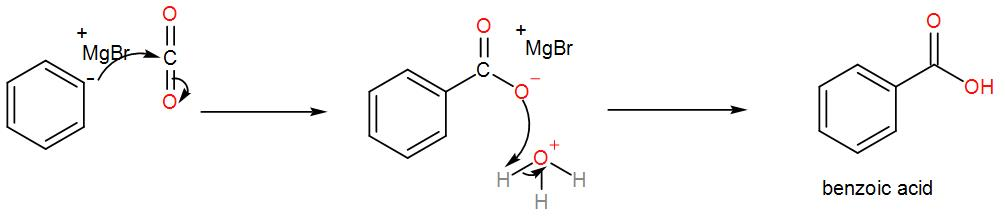
From the above discussion, we can understand the formation of benzoic acid from bromobenzene and this is the required answer.
Note:
Bromobenzene is not available so we have to synthesize it from benzene. Here, for the bromination of benzene we can either use aluminium (III) bromide or iron (III) bromide. Generally we use iron (III) bromide because it is cheaper and readily available. We even use the chloride form of the same reagents for the chlorination of the aromatic benzene ring. Bromine undergoes electrophilic substitution in presence of a catalyst to give us the brominated product.
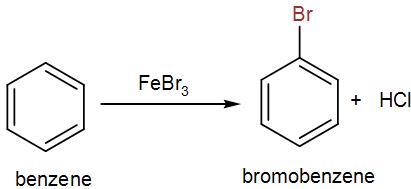
Complete answer:
We know that the structure of benzoic acid is-

We have to convert bromobenzene to benzoic acid and there are several methods that we can use for this conversion like partial oxidation of toluene, hydration of benzamide. However, here we will discuss the conversion using a Grignard reagent, so let’s discuss the steps involved but before that let’s discuss what Grignard reagent is.
This reagent is magnesium containing a chemical compound with the formula- R-Mg-X. R can be any alkyl group and X stands for halide. The most common example is $C{{H}_{3}}MgCl$. It is partly ionic $\left( \overset{\delta -}{\mathop{R}}\,\cdots \overset{\delta +}{\mathop{Mg}}\,X \right)$ and here the alkyl group bears a partial negative charge. It acts as a strong base and thus reacts with acidic hydrogen to give us alkanes.
In the first step, we have to synthesize the Grignard reagent from bromobenzene which we can do by adding magnesium in a solution of diethyl ether. We can write the reaction as-

Then, we treat the obtained organometallic reagent by excess dry ice and then add dilute aqueous acid to it. This gives us the required acid. We can write the reaction as-

From the above discussion, we can understand the formation of benzoic acid from bromobenzene and this is the required answer.
Note:
Bromobenzene is not available so we have to synthesize it from benzene. Here, for the bromination of benzene we can either use aluminium (III) bromide or iron (III) bromide. Generally we use iron (III) bromide because it is cheaper and readily available. We even use the chloride form of the same reagents for the chlorination of the aromatic benzene ring. Bromine undergoes electrophilic substitution in presence of a catalyst to give us the brominated product.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




