
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cells are said to have entered a stage of prophase I, where an exchange of genetic material takes place between homologous chromosomes. The stage is called:
A. Diakinesis
B. Diplotene
C. Pachytene
D. Zygotene
Answer
395.1k+ views
Hint Pachytene, also known as pachynema, derives its name from the Greek word for "thick thread," referring to the fact that at this stage, the homologous chromosomes have been entirely zipped up and are joined from end to end by the synaptonemal complex.
Complete step by step Answer:
Zygotene is distinguished by the onset of the lateral pairing of homologous chromosomes at the chromosomal tips and the creation of synaptonemal complexes down the length of the chromosomes. Pachytene is distinguished by the completion of the lateral pairing of homologous chromosomes over the whole length of the chromosome and cross-over. Diplotene is distinguished by the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex, which keeps the synapsed chromosomes together, resulting in the separation of synapsed chromosomes all along their length except at the moment of crossing over (chiasmata). Diakinesis is also characterized by the separation of homologous chromosomes at chiasmata.
Pachytene is preceded by the zygotene stage, during which synapsis, or the pairing of homologous chromosomes, occurs. The tetrad generated by synapsis becomes apparent in the pachytene stage, and four chromatids are visible. For this reason, the rest of the options are incorrect.
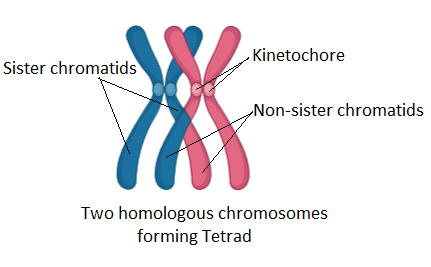
Image: Occurrence of the Chromosomes in the Pachytene stage.
The right answer is option C.
Note: Chromosomes consist of many materials like proteins, nucleic acids, small molecules, and lipids which coexist to maintain the structure. Chromatin undergoes constant change during the cell. The process of chromosome exchange between non-sister chromatids is known as mitosis during which the two strands of sister chromatids separate and exchange genetic material. This process happens in every cell division, but it is especially visible in mitosis.
Complete step by step Answer:
Zygotene is distinguished by the onset of the lateral pairing of homologous chromosomes at the chromosomal tips and the creation of synaptonemal complexes down the length of the chromosomes. Pachytene is distinguished by the completion of the lateral pairing of homologous chromosomes over the whole length of the chromosome and cross-over. Diplotene is distinguished by the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex, which keeps the synapsed chromosomes together, resulting in the separation of synapsed chromosomes all along their length except at the moment of crossing over (chiasmata). Diakinesis is also characterized by the separation of homologous chromosomes at chiasmata.
Pachytene is preceded by the zygotene stage, during which synapsis, or the pairing of homologous chromosomes, occurs. The tetrad generated by synapsis becomes apparent in the pachytene stage, and four chromatids are visible. For this reason, the rest of the options are incorrect.

Image: Occurrence of the Chromosomes in the Pachytene stage.
The right answer is option C.
Note: Chromosomes consist of many materials like proteins, nucleic acids, small molecules, and lipids which coexist to maintain the structure. Chromatin undergoes constant change during the cell. The process of chromosome exchange between non-sister chromatids is known as mitosis during which the two strands of sister chromatids separate and exchange genetic material. This process happens in every cell division, but it is especially visible in mitosis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE




