
Suppose two point charges \[100\mu C\]and \[5\mu C\]are placed at point A and B respectively with AB =\[40cm\]. Find the work done by external force in displacing the charge \[5\mu C\] from B to C , Where BC =\[30cm\], angel \[ABC=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and \[\dfrac{1}{4\pi \varepsilon \circ }=9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}/{{C}^{2}}\].
A. \[9J\]
B. \[\dfrac{81}{20}J\]
C. \[\dfrac{9}{25}J\]
D. \[\dfrac{9}{4}J\]
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: Work is a product of measure of energy or charge transfer by an external force in the direction of its placement. We used the formula of work done to solve this question.
Complete step-by-step solution:
As , we know when the charge is moved from one point to another, work is \[W=q(VA-VB)\] , here W= denotes work done.
q= charge
\[VA\]= electric potential at point A
\[VB\]= electric potential at point
Here , work done by external force in displacing the charge \[5\mu C\] from B to C is \[W=5\times {{10}^{-5}}(VC-VB)\]
Let's draw a diagram of this problem to solve this problem easily-
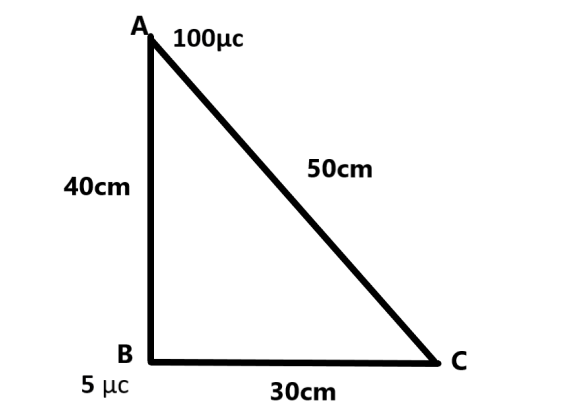
Now we have to calculate the values of \[VA\]and \[VB\] -
\[\begin{align}
& VB\Rightarrow 9\times {{10}^{9}}\times \dfrac{100\times {{10}^{-6}}}{0.4} \\
& VB\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{4}\times {{10}^{6}} \\
\end{align}\]
And
\[\begin{align}
& VC\Rightarrow 9\times {{10}^{9}}\times \dfrac{100\times {{10}^{-6}}}{0.5} \\
& VC\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{5}\times {{10}^{6}} \\
\end{align}\]
So , work done is
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow W=5\times {{10}^{-6}}\times \left( \dfrac{9}{5}\times {{10}^{6}}-\dfrac{9}{4}\times {{10}^{6}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow W=5\times {{10}^{-6}}\times \left( \dfrac{9}{5}-\dfrac{9}{4} \right){{10}^{6}} \\
& \Rightarrow W=5\times {{10}^{-6}}\times \left( \dfrac{9}{20} \right){{10}^{6}} \\
& \Rightarrow W=5\times \dfrac{9}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow W=\dfrac{9}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, correct option is D. \[\dfrac{9}{4}J\]
Note:Note that the work becomes \[(-)ve\] , when the force and displacement are in opposite directions to each other. The work done by force is null when the direction of force and displacement are perpendicular to each other.
Complete step-by-step solution:
As , we know when the charge is moved from one point to another, work is \[W=q(VA-VB)\] , here W= denotes work done.
q= charge
\[VA\]= electric potential at point A
\[VB\]= electric potential at point
Here , work done by external force in displacing the charge \[5\mu C\] from B to C is \[W=5\times {{10}^{-5}}(VC-VB)\]
Let's draw a diagram of this problem to solve this problem easily-

Now we have to calculate the values of \[VA\]and \[VB\] -
\[\begin{align}
& VB\Rightarrow 9\times {{10}^{9}}\times \dfrac{100\times {{10}^{-6}}}{0.4} \\
& VB\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{4}\times {{10}^{6}} \\
\end{align}\]
And
\[\begin{align}
& VC\Rightarrow 9\times {{10}^{9}}\times \dfrac{100\times {{10}^{-6}}}{0.5} \\
& VC\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{5}\times {{10}^{6}} \\
\end{align}\]
So , work done is
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow W=5\times {{10}^{-6}}\times \left( \dfrac{9}{5}\times {{10}^{6}}-\dfrac{9}{4}\times {{10}^{6}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow W=5\times {{10}^{-6}}\times \left( \dfrac{9}{5}-\dfrac{9}{4} \right){{10}^{6}} \\
& \Rightarrow W=5\times {{10}^{-6}}\times \left( \dfrac{9}{20} \right){{10}^{6}} \\
& \Rightarrow W=5\times \dfrac{9}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow W=\dfrac{9}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, correct option is D. \[\dfrac{9}{4}J\]
Note:Note that the work becomes \[(-)ve\] , when the force and displacement are in opposite directions to each other. The work done by force is null when the direction of force and displacement are perpendicular to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




