
Sun rays are incident on a concave mirror parallel to its principal axis. If the image of the sun is formed at $12cm$ distance from the pole of the mirror, find its radius of curvature.
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: Here we need to go through the properties of a concave mirror and see where the image is forming for different object distance. Then we need to apply the concave mirror formula relating the object distance the image distance and the focal length of the mirror. Then we will apply the relation between the focal length and the radius of curvature.
Formula used: $\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$R=2f$
Complete step by step answer:
When rays parallel to the principal axis are incident on a concave mirror, the image is formed at the focus of the mirror. The ray diagram is shown below.
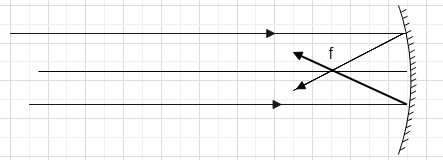
Now if $u$ is the object distance,$v$ is the image distance and $f$ is the focal length, we have
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$. Now for parallel rays $u=\infty $ , so putting the values of all the quantities we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{-12}+\dfrac{1}{\infty }=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& orf=-12cm \\
\end{align}\]
Negative sign indicates the focus lies in front of the mirror.
Now the radius of curvature $R$ is related to $f$ as
$R=2f$ , so putting the value of $f$ we get
$R=2\times (-12)=-24cm$
So the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is $24cm$.
Note: To solve this type of question correctly we need to put the right sign for the different quantities in the formula and then the unknown quantity will come out with the correct sign. For a concave mirror the focal length is negative and for a convex mirror the focal length is positive. We also need to remember that when parallel rays are incident, that means the object is at infinity and theoretically we can say the image will be formed at the focal plane.
Formula used: $\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$R=2f$
Complete step by step answer:
When rays parallel to the principal axis are incident on a concave mirror, the image is formed at the focus of the mirror. The ray diagram is shown below.

Now if $u$ is the object distance,$v$ is the image distance and $f$ is the focal length, we have
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$. Now for parallel rays $u=\infty $ , so putting the values of all the quantities we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{-12}+\dfrac{1}{\infty }=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& orf=-12cm \\
\end{align}\]
Negative sign indicates the focus lies in front of the mirror.
Now the radius of curvature $R$ is related to $f$ as
$R=2f$ , so putting the value of $f$ we get
$R=2\times (-12)=-24cm$
So the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is $24cm$.
Note: To solve this type of question correctly we need to put the right sign for the different quantities in the formula and then the unknown quantity will come out with the correct sign. For a concave mirror the focal length is negative and for a convex mirror the focal length is positive. We also need to remember that when parallel rays are incident, that means the object is at infinity and theoretically we can say the image will be formed at the focal plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




