
Suitable reagent for the following conversion is-
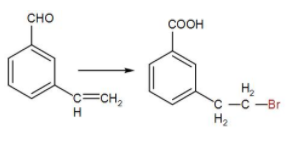
[A] $C{{H}_{3}}MgBr,{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}},{{I}_{2}}/NaOH,H-Br/{{R}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$
[B] $KMn{{O}_{4}},NaOH,HBr/{{R}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$
[C] $C{{H}_{3}}MgBr,KMn{{O}_{4}},HBr$
[D] $C{{H}_{3}}MgBr,{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}},H-Br/NaOH$

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: There are several methods that you can opt for the given conversion. However, you can use the most common one i.e. the use of a Grignard reagent for this. Then, you can use hydrolysis reaction followed by haloform reaction to get the following product by using Anti-Markovnikov's rule.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, we can see that benzaldehyde is converted to benzoic acid and also halogenation of alkane is taking place.
Now let us see the mechanism of the conversion step by step.
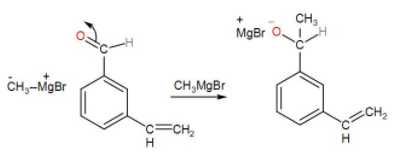
At first, we can use a Grignard reagent for the oxidation. This reagent is magnesium containing a chemical compound with the formula- R-Mg-X. R can be any alkyl group and X stands for halide. It is partly ionic $\left( \overset{\delta -}{\mathop{R}}\,\cdots \overset{\delta +}{\mathop{Mg}}\,X \right)$ and here the alkyl group bears a partial negative charge. It acts as a strong base. Grignard reagent attacks on the carbonyl carbon and the alkyl group is attached to the same carbon. We can write the reaction mechanism as-
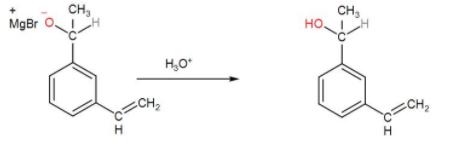
In the next step, hydrolysis of the ${{O}^{-}}$ will take place by ${{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}$ and the O – MgBr bond will cleave and we will get an –OH functional group. We can write the reaction as-
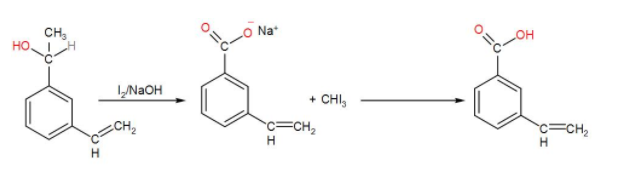
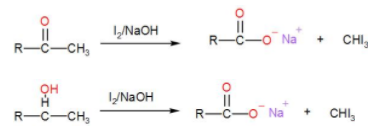
After this, when we add iodine and sodium hydroxide to it, an iodoform reaction takes place. When iodine and sodium hydroxide are added to a compound containing methyl ketone or a secondary alcohol having a methyl group in alpha position, a yellow iodine precipitate is obtained due to formation of triiodomethane and we will get a $CO{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}$ salt which then gives –COOH. We can write the reaction as-
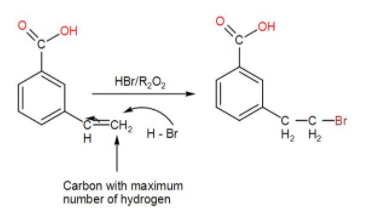
Next, HBr is added in the presence of peroxide. This proceeds via the Anti-Markovnikov pathway.
When HBr is added, it undergoes Markonikov’s addition giving us the above product. According to the Markovnikov’s Rule, bromine will be added to the most substituted carbon, giving us the above product.
If we used HBr + peroxide, we would have got a different product as the addition would be Anti-Markovnikov’s in that case due to the peroxide effect. The bromine would be added to the least substituted carbon, hence giving us a different product.
Thus, the nucleophile will attach to the carbon atom with maximum number of hydrogen. Therefore, here we will obtain the product as-
Therefore, we can understand from the following reactions that the correct answer is option –
[A] $C{{H}_{3}}MgBr,{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}},{{I}_{2}}/NaOH,H-Br/{{R}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$.
Note: Iodoform test is used in laboratories for the detection of aldehydes and ketones containing an alpha methyl group. Compounds containing $C{{H}_{3}}CO\text{ }or\text{ }C{{H}_{3}}CH(OH)$group shows positive result in iodoform test. The reaction is-
Complete step by step solution:
Here, we can see that benzaldehyde is converted to benzoic acid and also halogenation of alkane is taking place.
Now let us see the mechanism of the conversion step by step.
At first, we can use a Grignard reagent for the oxidation. This reagent is magnesium containing a chemical compound with the formula- R-Mg-X. R can be any alkyl group and X stands for halide. It is partly ionic $\left( \overset{\delta -}{\mathop{R}}\,\cdots \overset{\delta +}{\mathop{Mg}}\,X \right)$ and here the alkyl group bears a partial negative charge. It acts as a strong base. Grignard reagent attacks on the carbonyl carbon and the alkyl group is attached to the same carbon. We can write the reaction mechanism as-

In the next step, hydrolysis of the ${{O}^{-}}$ will take place by ${{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}$ and the O – MgBr bond will cleave and we will get an –OH functional group. We can write the reaction as-

After this, when we add iodine and sodium hydroxide to it, an iodoform reaction takes place. When iodine and sodium hydroxide are added to a compound containing methyl ketone or a secondary alcohol having a methyl group in alpha position, a yellow iodine precipitate is obtained due to formation of triiodomethane and we will get a $CO{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}$ salt which then gives –COOH. We can write the reaction as-

Next, HBr is added in the presence of peroxide. This proceeds via the Anti-Markovnikov pathway.
When HBr is added, it undergoes Markonikov’s addition giving us the above product. According to the Markovnikov’s Rule, bromine will be added to the most substituted carbon, giving us the above product.
If we used HBr + peroxide, we would have got a different product as the addition would be Anti-Markovnikov’s in that case due to the peroxide effect. The bromine would be added to the least substituted carbon, hence giving us a different product.
Thus, the nucleophile will attach to the carbon atom with maximum number of hydrogen. Therefore, here we will obtain the product as-

Therefore, we can understand from the following reactions that the correct answer is option –
[A] $C{{H}_{3}}MgBr,{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}},{{I}_{2}}/NaOH,H-Br/{{R}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$.
Note: Iodoform test is used in laboratories for the detection of aldehydes and ketones containing an alpha methyl group. Compounds containing $C{{H}_{3}}CO\text{ }or\text{ }C{{H}_{3}}CH(OH)$group shows positive result in iodoform test. The reaction is-

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




