
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar due to:
(A) 1-2 linkage
(B) 1-4 linkage
(C) 1-5 linkage
(D) 1-6 linkage
Answer
531.3k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we first need to know what is non-reducing sugar. When a weak oxidizing agent does not reduce the carbohydrate in a basic aqueous solution, the carbohydrate is known as a non-reducing sugar.
Complete answer:
There are no free aldehyde groups or ketone groups in non-reducing sugars. Instead of a hemiacetal group or a hemiketal group, non-reducing sugars contain an acetal group or a ketal group in their place. An acetal group consists of 1 -R group, 1 -H group, and 2 -OR groups.
Now, let us look at the structure of sucrose.
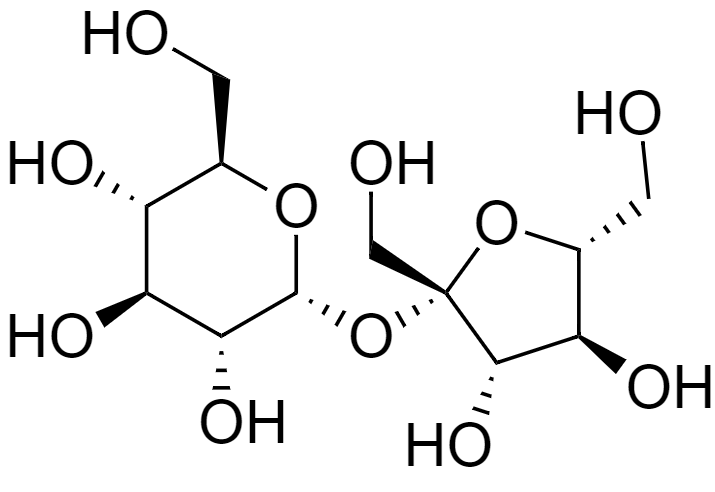
Sucrose is commonly known as table sugar. It is composed of two monosaccharides, glucose, and fructose, and hence is a disaccharide.
In sucrose, the glucose and fructose monomers are bonded by glycosidic linkage i.e., it is linked through an ether bond between C2 of the fructosyl unit and C1of the glucosyl unit.
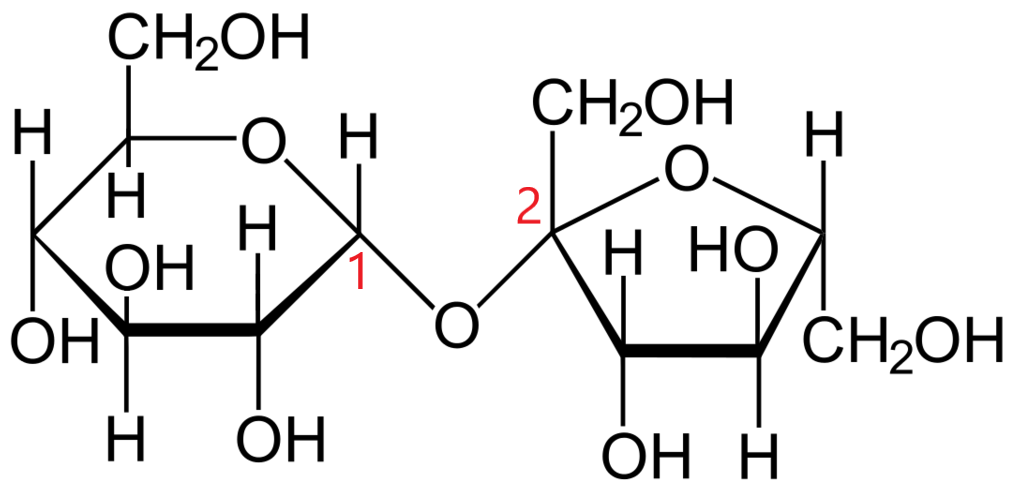
Because of this linkage, the keto group of fructose and the aldehyde group of glucose are not free. It neither contains a hemiketal group or a hemiacetal group and cannot convert from the cyclic form into an aldehyde group-containing open chain.
Hence it is stable in water making it a non-reducing sugar.
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar due to option (A) 1-2 linkage.
Note:
It should be noted that to determine whether sugar is reducing in nature or non-reducing in nature, Benedict's test is used.
When Benedict's solution (clear blue) is added to a reducing sugar (containing free aldehyde and ketone functional groups), a color change is observed (to brick red).
Whereas when Benedict's solution is added to a non-reducing sugar, the solution remains clear blue and no color change is observed.
Complete answer:
There are no free aldehyde groups or ketone groups in non-reducing sugars. Instead of a hemiacetal group or a hemiketal group, non-reducing sugars contain an acetal group or a ketal group in their place. An acetal group consists of 1 -R group, 1 -H group, and 2 -OR groups.
Now, let us look at the structure of sucrose.

Sucrose is commonly known as table sugar. It is composed of two monosaccharides, glucose, and fructose, and hence is a disaccharide.
In sucrose, the glucose and fructose monomers are bonded by glycosidic linkage i.e., it is linked through an ether bond between C2 of the fructosyl unit and C1of the glucosyl unit.

Because of this linkage, the keto group of fructose and the aldehyde group of glucose are not free. It neither contains a hemiketal group or a hemiacetal group and cannot convert from the cyclic form into an aldehyde group-containing open chain.
Hence it is stable in water making it a non-reducing sugar.
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar due to option (A) 1-2 linkage.
Note:
It should be noted that to determine whether sugar is reducing in nature or non-reducing in nature, Benedict's test is used.
When Benedict's solution (clear blue) is added to a reducing sugar (containing free aldehyde and ketone functional groups), a color change is observed (to brick red).
Whereas when Benedict's solution is added to a non-reducing sugar, the solution remains clear blue and no color change is observed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




