
How many structural isomers are possible for a compound with molecular formula $ {{\text{C}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{7}}}}{\text{Cl}} $ ?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: The chemical compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms in their structure are called structural isomers.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Isomers are molecules having identical molecular but different structural formulae. They are classified as constitutional isomerism and stereoisomerism. Constitutional isomerism is exhibited by compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms whereas stereoisomers have the different arrangement of atoms in space. In other words, the stereoisomers differ in their spatial arrangement of atoms. This difference can lead to the change in physical and chemical properties.
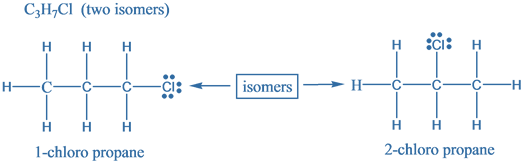
Structural isomers are further classified into following types:
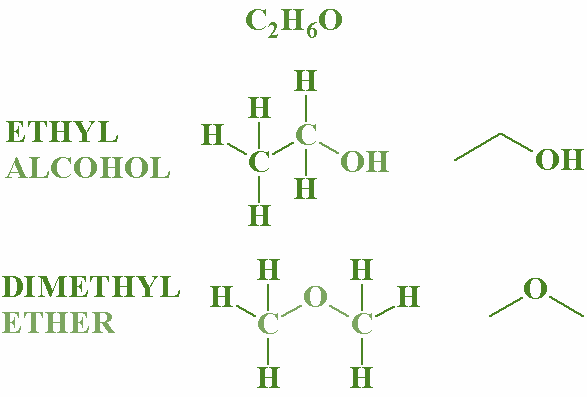
Functional isomers: Where the functional group of the compound differs.
Example- Alcohol and ether
Positional isomers: The position of atoms or functional groups gets different.
Example- Alcohols
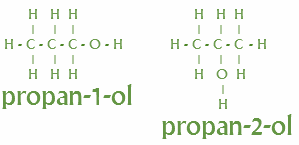
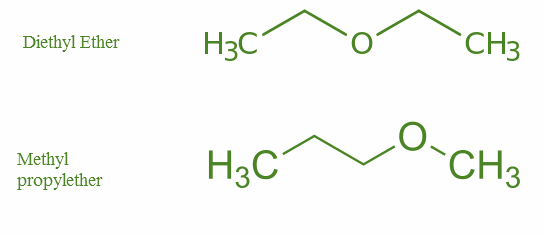
Metamerism: Where the number of atoms in the side chain of the functional group differs.
Example- Ethers
Chain isomerism: Differs in the carbon skeleton
Example-
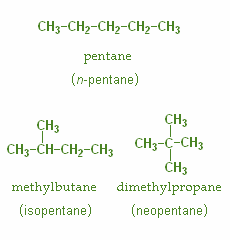
The given molecular formula is $ {{\text{C}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{7}}}}{\text{Cl}} $. Structural isomers are molecules which differ in the arrangement of atoms but have the same molecular formula. These are also known as Constitutional isomers. Following are the structural isomers for the given molecular formula is $ {{\text{C}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{7}}}}{\text{Cl}} $ .
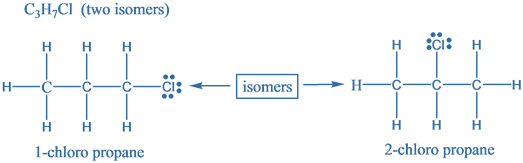
Hence, there are two structural isomers for a compound with molecular formula $ {{\text{C}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{7}}}}{\text{Cl}} $ .
So, the correct option is A.
Note:
The structural isomers can be distinguished by NMR spectroscopy with ease. Due to the different physical and chemical properties these isomers can also be separated easily. The change in name of compounds either in the numbering or functional group reflect structural isomerism.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Isomers are molecules having identical molecular but different structural formulae. They are classified as constitutional isomerism and stereoisomerism. Constitutional isomerism is exhibited by compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms whereas stereoisomers have the different arrangement of atoms in space. In other words, the stereoisomers differ in their spatial arrangement of atoms. This difference can lead to the change in physical and chemical properties.

Structural isomers are further classified into following types:
Functional isomers: Where the functional group of the compound differs.
Example- Alcohol and ether

Positional isomers: The position of atoms or functional groups gets different.
Example- Alcohols
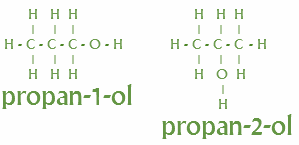
Metamerism: Where the number of atoms in the side chain of the functional group differs.
Example- Ethers

Chain isomerism: Differs in the carbon skeleton
Example-

The given molecular formula is $ {{\text{C}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{7}}}}{\text{Cl}} $. Structural isomers are molecules which differ in the arrangement of atoms but have the same molecular formula. These are also known as Constitutional isomers. Following are the structural isomers for the given molecular formula is $ {{\text{C}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{7}}}}{\text{Cl}} $ .

Hence, there are two structural isomers for a compound with molecular formula $ {{\text{C}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{7}}}}{\text{Cl}} $ .
So, the correct option is A.
Note:
The structural isomers can be distinguished by NMR spectroscopy with ease. Due to the different physical and chemical properties these isomers can also be separated easily. The change in name of compounds either in the numbering or functional group reflect structural isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




