
Where is the stigma located and what are its functions?
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Stigma is a part of the plant’s reproductive system. It is a part of the pistil where pollen germinates. The main function of it is to attract the pollen grains from the air with its sticky tip for reproduction.
Complete answer:
Stigma is a part of a female flower that forms a specially adapted part of the pistil and is modified for receiving pollens. They are also known as landing zones or landing stages as they trap pollen for fertilization. Stigma has various structures adapted or modified to trap pollen, like hairs, flaps, waxy surface, sticky surface, elongated, etc.
Additional Information:
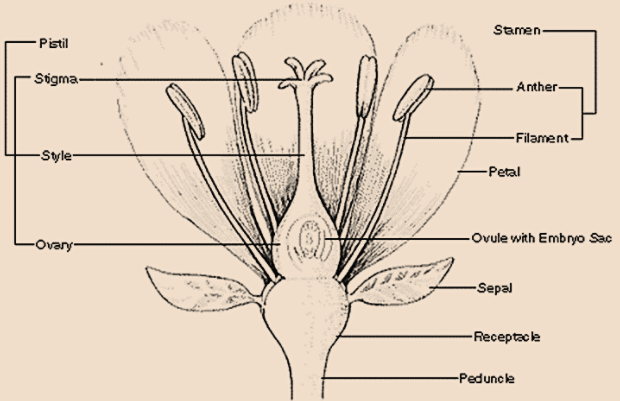
Some of the parts of the flower include (Figure 1):
- Peduncle: The stem or stalk of a flower.
- Receptacle: The part of a flower stalk where the parts of the flower are attached.
- Sepal: The outer parts of the flower (often green and leaf-like) that enclose a developing bud.
- Petal: The parts of a flower that are often conspicuously colored.
- Stamen: The pollen-producing part of a flower, usually with a slender filament supporting the anther.
- Anther: The part of the stamen where pollen is produced.
- Pistil: The ovule producing part of a flower. The ovary often supports a long style, topped by a stigma. The mature ovary is a fruit, and the mature ovule is a seed.
- Ovary: The enlarged basal portion of the pistil where ovules are produced.
Figure 1: Parts of a flower.
Note: Stigma has various modifications according to the demand of pollinators, they can either be long or feathery or branched as in wind pollinating plants (eg. Grasses), or it can be compact with a sticky surface as seen in insect pollinating plants (eg. Sunflower).
Complete answer:
Stigma is a part of a female flower that forms a specially adapted part of the pistil and is modified for receiving pollens. They are also known as landing zones or landing stages as they trap pollen for fertilization. Stigma has various structures adapted or modified to trap pollen, like hairs, flaps, waxy surface, sticky surface, elongated, etc.
Additional Information:
Some of the parts of the flower include (Figure 1):
- Peduncle: The stem or stalk of a flower.
- Receptacle: The part of a flower stalk where the parts of the flower are attached.
- Sepal: The outer parts of the flower (often green and leaf-like) that enclose a developing bud.
- Petal: The parts of a flower that are often conspicuously colored.
- Stamen: The pollen-producing part of a flower, usually with a slender filament supporting the anther.
- Anther: The part of the stamen where pollen is produced.
- Pistil: The ovule producing part of a flower. The ovary often supports a long style, topped by a stigma. The mature ovary is a fruit, and the mature ovule is a seed.
- Ovary: The enlarged basal portion of the pistil where ovules are produced.
Figure 1: Parts of a flower.

Note: Stigma has various modifications according to the demand of pollinators, they can either be long or feathery or branched as in wind pollinating plants (eg. Grasses), or it can be compact with a sticky surface as seen in insect pollinating plants (eg. Sunflower).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




