
How many stereoisomers of the following molecules are possible?
$HOOC - CH = C = CH - COOH$
(a) Two optical isomers
(b) Two geometrical isomers
(c) Two optical and two geometrical isomers
(d) None of the above
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: When two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in the number of the arrangements of atoms in space are known as stereoisomers and the phenomenon is known as stereoisomerism. It is broadly divided into two types i.e., optical isomerism and geometrical isomerism.
Complete answer:
The compound given in the question is an allene and its structure is drawn as follows:
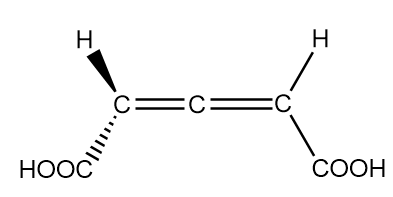
In the structure, the terminal carbons are $s{p^2}$ hybridized and the carbon atom at the centre is $sp$ hybridized. The central atom is bonded via two collinear sigma bonds and two pi bonds which are forming an angle of ${90^o}$ with each other i.e., both the pi bonds are perpendicular to each other. Thus, the groups attached to the terminal carbon atoms do not lie in the same plane and hence do not possess any plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry. The 3D sketch of allenes is as follows:
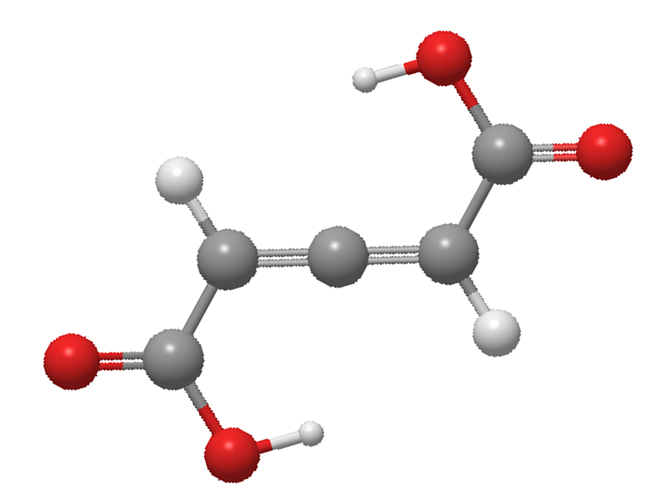
Hence, the molecules exhibit optical isomerism. Total two optical isomers are possible for the given compound i.e., laevorotatory and dextrorotatory.
As the groups on the terminal carbon atoms are not present in the same plane i.e., the molecule is not planar. Therefore, the given compound does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Thus, the total number of stereoisomers of the given molecule $ = $ number of optical isomers $ + $ number of geometrical isomers.
$ \Rightarrow 2 + 0 = 2$ optical isomerism.
Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that geometrical isomerism is exhibited by those molecules only which consist of an odd number of double bonds. If the compound has an even number of double bonds like allenes, then it will not exhibit any geometrical isomerism.
Complete answer:
The compound given in the question is an allene and its structure is drawn as follows:

In the structure, the terminal carbons are $s{p^2}$ hybridized and the carbon atom at the centre is $sp$ hybridized. The central atom is bonded via two collinear sigma bonds and two pi bonds which are forming an angle of ${90^o}$ with each other i.e., both the pi bonds are perpendicular to each other. Thus, the groups attached to the terminal carbon atoms do not lie in the same plane and hence do not possess any plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry. The 3D sketch of allenes is as follows:

Hence, the molecules exhibit optical isomerism. Total two optical isomers are possible for the given compound i.e., laevorotatory and dextrorotatory.
As the groups on the terminal carbon atoms are not present in the same plane i.e., the molecule is not planar. Therefore, the given compound does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Thus, the total number of stereoisomers of the given molecule $ = $ number of optical isomers $ + $ number of geometrical isomers.
$ \Rightarrow 2 + 0 = 2$ optical isomerism.
Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that geometrical isomerism is exhibited by those molecules only which consist of an odd number of double bonds. If the compound has an even number of double bonds like allenes, then it will not exhibit any geometrical isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




