
Stephen’s reduction converts nitriles into:
(A) aldehydes
(B) ketones
(C) amines
(D) carboxylic acids
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Think about the reagent that is used during this reaction. This will give you an idea about the mechanism of the reaction and how the product is formed. Consider the alternative name for the reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
In this reaction, the reagent that is used is stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid. These reagents reduce the carbon atom that is present in the nitrile group. The first step of this reaction involved the formation of the intermediate compound which is an imine. This amine then undergoes hydrolysis to give us the product.
Nitrile compounds have the structure $R-C\equiv N$. Here, the $R$ represents the alkyl group that is present with the nitrile functional group. The Stephen’s reagent is given by $SnC{{l}_{2}}/HCl$. Using this information, the general reaction is:
\[R-CN+2[H]\xrightarrow{SnC{{l}_{2}}/HCl}R-CH=NHHCl\xrightarrow{{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}}R-CHO+N{{H}_{4}}Cl\]
Here, we can see that an aldehyde is formed, but the detailed mechanism is still not apparent. The mechanism for this reaction is:
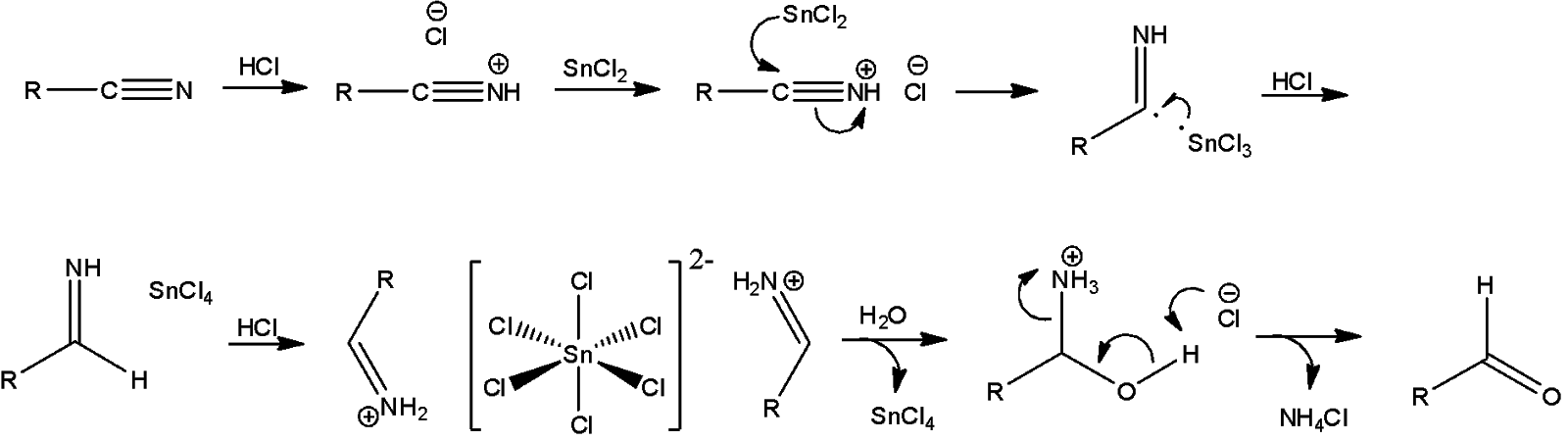
Here, we can see that the alkyl nitrile continuously reacts with stannous chloride and hydrochloric acid to form an imine. This imine is then converted into a tin complex which immediately decomposes to form $SnC{{l}_{4}}$ and the amine is converted into an amide by hydrolysis. Thus, an aldehyde is formed.
Hence, the correct answer to this question is ‘A. aldehydes’
Note: Note that this aldehyde usually further reacts with a hydronium ion and gets oxidized to form a carboxylic acid. But this is not a part of Stephen’s Reduction reaction whose alternative name is Stephen’s Aldehyde Synthesis. So, Stephen’s reduction does not form carboxylic acids.
Complete step by step solution:
In this reaction, the reagent that is used is stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid. These reagents reduce the carbon atom that is present in the nitrile group. The first step of this reaction involved the formation of the intermediate compound which is an imine. This amine then undergoes hydrolysis to give us the product.
Nitrile compounds have the structure $R-C\equiv N$. Here, the $R$ represents the alkyl group that is present with the nitrile functional group. The Stephen’s reagent is given by $SnC{{l}_{2}}/HCl$. Using this information, the general reaction is:
\[R-CN+2[H]\xrightarrow{SnC{{l}_{2}}/HCl}R-CH=NHHCl\xrightarrow{{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}}R-CHO+N{{H}_{4}}Cl\]
Here, we can see that an aldehyde is formed, but the detailed mechanism is still not apparent. The mechanism for this reaction is:

Here, we can see that the alkyl nitrile continuously reacts with stannous chloride and hydrochloric acid to form an imine. This imine is then converted into a tin complex which immediately decomposes to form $SnC{{l}_{4}}$ and the amine is converted into an amide by hydrolysis. Thus, an aldehyde is formed.
Hence, the correct answer to this question is ‘A. aldehydes’
Note: Note that this aldehyde usually further reacts with a hydronium ion and gets oxidized to form a carboxylic acid. But this is not a part of Stephen’s Reduction reaction whose alternative name is Stephen’s Aldehyde Synthesis. So, Stephen’s reduction does not form carboxylic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




