
Statement ${\rm I}$- Pyrrolidine $\left( {{\rm I}{\rm I}} \right)$ is more basic than pyrrole$\left( {\rm I} \right)$.
Statement ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ -Protonated pyrrole has resonance stabilization of positive charge in aromatic ring.
A.Statement- ${\rm I}$ is true, Statement -${\rm I}{\rm I}$ is true; Statement ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ is a correct explanation for Statement-${\rm I}$
B.Statement- ${\rm I}$ is true, Statement -${\rm I}{\rm I}$ is true; Statement ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ is not a correct explanation for Statement-I
C.Statement- ${\rm I}$ is true, Statement -${\rm I}{\rm I}$ is false
D.Statement- ${\rm I}$ is false, Statement -${\rm I}{\rm I}$ is true
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: The compound which can easily donate its lone pair is more basic. By Huckel‘s rule, we can check an organic compound as aromatic or non-aromatic. The compound having a double bond next to the lone pair has a chance of forming resonating structures in the aromatic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
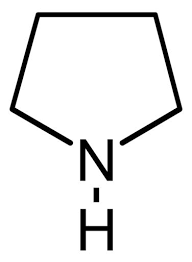
Structure of Pyrrolidine
Structure of Pyrrole
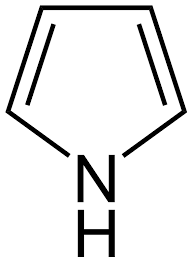
We know that Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons. In pyrrole and pyrrolidine, only 3 valencies are satisfied and there is a lone pair of electrons on the Nitrogen of both the compounds.
In pyrrole structure, Nitrogen has one lone pair of electrons that undergo delocalization with a double bond next to it.
So, the lone pair is less available for donating.
But in the case of pyrrolidine, there is no such double bond present in the structure. So there is no possible movement of the lone pair and it is maximumly available for donating.
From the above, we can conclude that Pyrrolidine is more basic than pyrrole.
Let us look at the resonance structure of pyrrole-
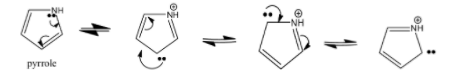
As we can see that there is a transfer of lone pair from nitrogen to its aromatic ring
So, we can say that the protonated pyrrole has resonance stabilization of lone pairs in the aromatic ring which leads to basicity. Resonance stabilization is not of a positive charge. Therefore, the statement ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ is wrong.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
An organic compound is aromatic only when it follows Huckle’s rule.
Huckel’s law states that the number of pi electrons must be equal to $4n + 2$ , where n is any positive real number.
Resonance stabilization can be checked by its central atom whether it has a positive charge, negative charge, or lone pair.
Since nitrogen is considered as the central atom in pyrrole and it has one lone pair hence it shows resonance stabilization of lone pair.
Complete step by step answer:
Structure of Pyrrolidine

Structure of Pyrrole

We know that Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons. In pyrrole and pyrrolidine, only 3 valencies are satisfied and there is a lone pair of electrons on the Nitrogen of both the compounds.
In pyrrole structure, Nitrogen has one lone pair of electrons that undergo delocalization with a double bond next to it.
So, the lone pair is less available for donating.
But in the case of pyrrolidine, there is no such double bond present in the structure. So there is no possible movement of the lone pair and it is maximumly available for donating.
From the above, we can conclude that Pyrrolidine is more basic than pyrrole.
Let us look at the resonance structure of pyrrole-

As we can see that there is a transfer of lone pair from nitrogen to its aromatic ring
So, we can say that the protonated pyrrole has resonance stabilization of lone pairs in the aromatic ring which leads to basicity. Resonance stabilization is not of a positive charge. Therefore, the statement ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ is wrong.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
An organic compound is aromatic only when it follows Huckle’s rule.
Huckel’s law states that the number of pi electrons must be equal to $4n + 2$ , where n is any positive real number.
Resonance stabilization can be checked by its central atom whether it has a positive charge, negative charge, or lone pair.
Since nitrogen is considered as the central atom in pyrrole and it has one lone pair hence it shows resonance stabilization of lone pair.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




