
State the properties and uses of a junction diode.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: A junction diode is a semiconductor device which is made by just using the n-type semiconductor and p-type semiconductor together, which leads to formation of a depletion layer or region which is depleted of charge carriers (holes and electrons) resulting in allowing current to flow in one direction only.
Complete step by step answer:
Some of the properties of a p-n junction diode are following:
1. Diode is made by joining a n-type semiconductor to a p-type semiconductor. N-type (charge carriers are electrons) and p-type (charge carriers are holes) semiconductors are relatively conductive whereas a diode due to formation of depletion region (no charge carriers) is nonconductive.
2. In a diode there is a voltage barrier created due to depletion region. The movement of charge carriers across junctions only happens when this barrier has been overcome.
3. The thickness of the depletion region varies with the applied voltage. When a diode is zero biased i.e. no external voltage is applied to it, there is still a natural potential barrier developed across the depletion region which is approximately equal to 0.7V for silicon diodes and 0.3V for germanium diodes.
4. When a diode is operated under forward bias (voltage applied from p to n) the thickness of the depletion region decreases and as the potential barrier is overcome there is a sudden exponential increase in current. The diode acts like a short circuit (zero resistance) allowing all the circuit current to flow.
5. When a diode is operated under reverse bias (voltage applied from n to p) the thickness of the depletion region increases and the diode acts like an open circuit (infinite resistance), blocking any circuit current flow through it. Only a very little leakage current flows under reverse bias.
6. Hence, diode is a semiconductor device which allows current to flow only in one direction (forward bias) and the current flowing through it doesn’t follow a linear relationship (ohm’s law) like a resistor. The current in forward bias increases exponentially.
Some of the uses of junction diode are:
1.) Diode is used in the rectification of the part of DC Power Supplies.
2.) Diode is used in detector circuits.
3.) They are used in bracing systems as dc restorers.
4.) They are used in cut-out circuits for waveform era.
5.) They are used in switches in advanced rational circuits.
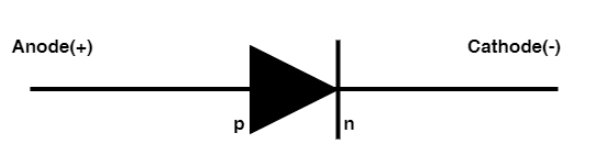
Note: Most of the students get confused about which end of the diode is connected to anode or cathode, so here we mention in the diagram about it that the anode (+) is connected to the p side and the cathode (-) is connected to the n side.
Complete step by step answer:
Some of the properties of a p-n junction diode are following:
1. Diode is made by joining a n-type semiconductor to a p-type semiconductor. N-type (charge carriers are electrons) and p-type (charge carriers are holes) semiconductors are relatively conductive whereas a diode due to formation of depletion region (no charge carriers) is nonconductive.
2. In a diode there is a voltage barrier created due to depletion region. The movement of charge carriers across junctions only happens when this barrier has been overcome.
3. The thickness of the depletion region varies with the applied voltage. When a diode is zero biased i.e. no external voltage is applied to it, there is still a natural potential barrier developed across the depletion region which is approximately equal to 0.7V for silicon diodes and 0.3V for germanium diodes.
4. When a diode is operated under forward bias (voltage applied from p to n) the thickness of the depletion region decreases and as the potential barrier is overcome there is a sudden exponential increase in current. The diode acts like a short circuit (zero resistance) allowing all the circuit current to flow.
5. When a diode is operated under reverse bias (voltage applied from n to p) the thickness of the depletion region increases and the diode acts like an open circuit (infinite resistance), blocking any circuit current flow through it. Only a very little leakage current flows under reverse bias.
6. Hence, diode is a semiconductor device which allows current to flow only in one direction (forward bias) and the current flowing through it doesn’t follow a linear relationship (ohm’s law) like a resistor. The current in forward bias increases exponentially.
Some of the uses of junction diode are:
1.) Diode is used in the rectification of the part of DC Power Supplies.
2.) Diode is used in detector circuits.
3.) They are used in bracing systems as dc restorers.
4.) They are used in cut-out circuits for waveform era.
5.) They are used in switches in advanced rational circuits.
Note: Most of the students get confused about which end of the diode is connected to anode or cathode, so here we mention in the diagram about it that the anode (+) is connected to the p side and the cathode (-) is connected to the n side.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




