
State the properties and uses of a junction transistor.
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: A transistor is a semiconductor electronic device having three terminals used to connect with an external circuit. The main use of a transistor is to amplify the electronic signals. It can also be used for rectification.
Complete step-by-step answer:
There are two types of transistors: Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs).
A junction transistor, also known as bipolar junction transistor, is a semiconductor device which is made of three layers of doped semiconductors such that there are two junctions. It has three terminals to connect with an external circuit.
The three layers are named as emitter, base, and collector.
There are two further types of BJTs: pnp and npn
In a pnp transistor, we have two layers of p-type, one acting as an emitter and other as a collector while one n-type layer is sandwiched between these p-type layers acting as the base.
In a npn transistor, we have two layers of n-type, one acting as an emitter and other as a collector while one p-type layer is sandwiched between these n-type layers acting as the base.
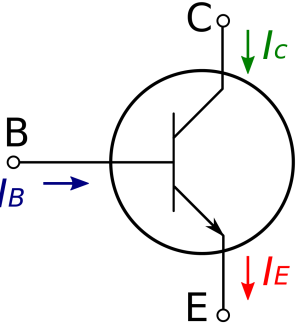
The image shows the symbol of a npn transistor. The two transistors can be differentiated on the basis of an arrow which is always drawn from p-type to n-type.
Applications of junction transistors: It has a wide variety of applications. The main application of the bipolar junction transistor is to amplify the small current signals. It can also be used as a switch in electronic circuits. It is also used for rectification and as an oscillator.
Note: The emitter of a BJT is highly doped, the base is lightly doped while the collector is moderately doped. The current flows from emitter to collector. The purpose of the base is to control the flow of current from emitter to collector.
Complete step-by-step answer:
There are two types of transistors: Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs).
A junction transistor, also known as bipolar junction transistor, is a semiconductor device which is made of three layers of doped semiconductors such that there are two junctions. It has three terminals to connect with an external circuit.
The three layers are named as emitter, base, and collector.
There are two further types of BJTs: pnp and npn
In a pnp transistor, we have two layers of p-type, one acting as an emitter and other as a collector while one n-type layer is sandwiched between these p-type layers acting as the base.
In a npn transistor, we have two layers of n-type, one acting as an emitter and other as a collector while one p-type layer is sandwiched between these n-type layers acting as the base.
The image shows the symbol of a npn transistor. The two transistors can be differentiated on the basis of an arrow which is always drawn from p-type to n-type.

Applications of junction transistors: It has a wide variety of applications. The main application of the bipolar junction transistor is to amplify the small current signals. It can also be used as a switch in electronic circuits. It is also used for rectification and as an oscillator.
Note: The emitter of a BJT is highly doped, the base is lightly doped while the collector is moderately doped. The current flows from emitter to collector. The purpose of the base is to control the flow of current from emitter to collector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




