
State the correct statement(s) about the cubic structure of diamond.
\[1\] . Effective number of atoms present in a diamond cubic cell is \[8\] .
\[2\] . Each carbon is surrounded by four more carbon atoms.
\[3\] . Atomic radius of carbon is \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times a}}{8}\] , where \[a\] is the edge length of the cube.
\[4\] . Approximate packing fraction of the unit cell is \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times \pi }}{{16}}\].
A. \[1,{\text{ }}2{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}4\]
B. \[2,{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}4\]
C. \[2{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}3\]
D. All \[1,{\text{ }}2{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}4\]
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: The structure of diamond is a crystallographic rearrangement of carbon in three dimensional spaces. Diamonds are also called allotropes of carbon which are held together by covalent bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
Diamond is formed by the chemical bonding of carbon atoms. The carbon atoms in diamond are \[s{p^3}\] hybridized. The carbon atoms are in tetrahedral arrangement over the whole crystal. Due to such a strong arrangement diamond the hardest substance.
Let us check the correctness of the given statements one by one.
\[1\] . Effective number of atoms present in a diamond cubic cell is \[8\] .
In the diamond unit cell the carbon atoms are arranged in face centered cubic crystal. The number of atoms that are contributed by the corner atoms in the unit cell is \[\dfrac{1}{8} \times 8 = 1\] . The number of atoms that are contributed by the face centered atoms in the unit cell is\[\dfrac{1}{2} \times 6 = 3\] . The number of atoms inside the structure of the unit cell =\[4\] . Hence the total number of atoms present in a diamond cubic cell is \[1 + 3 + 4 = 8\] .
\[2\] . Each carbon is surrounded by four more carbon atoms.
Out of eight cube corners in the unit cell, four atoms are bonded to an atom within the cube and the other four are bonded to adjacent cubes of the crystal lattice. Hence each carbon atom present at the centre of the tetrahedron in the crystal and four other carbon atoms are present at the corners of the tetrahedron of the face centered cubic crystal.
\[3\] . Atomic radius of carbon is \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times a}}{8}\] , where \[a\] is the edge length of the cube.
Let us take a cross section of the cube of the FCC lattice where \[a\] is the edge length shared by four atoms.
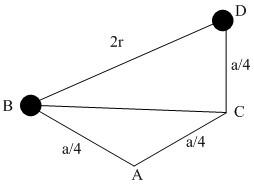
For triangle ABC, \[B{C^2} = {\left[ {\dfrac{a}{4}} \right]^2} + {\left[ {\dfrac{a}{4}} \right]^2} = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{8}\]
For triangle XYZ, $B{D^2} = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{8} + {\left[ {\dfrac{a}{4}} \right]^2} = \dfrac{{3{a^2}}}{{16}}$
As\[BD = 2r\] ,
${[2r]^2} = \dfrac{{3{a^2}}}{{16}}$
$r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times a}}{8}$ . This is the radius of carbon.
\[4\] . Approximate packing fraction of the unit cell is \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times \pi }}{{16}}\].
The packing fraction of the lattice is given as \[\dfrac{{8 \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}}}{{{a^3}}}\].
Inserting the value of radius r in the packing fraction relation,
\[PE = \dfrac{{8 \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {{\left[ {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times a}}{8}} \right]}^3}}}{{{a^3}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times \pi }}{{16}}\] .
Hence, all the four statements about the cubic structure of diamond are correct.
Note: Please note that in the unit cell of diamond, only \[34\% \] of the volume is occupied and \[66\% \] of volume is empty. This is obtained from the packing fraction.
Complete step by step answer:
Diamond is formed by the chemical bonding of carbon atoms. The carbon atoms in diamond are \[s{p^3}\] hybridized. The carbon atoms are in tetrahedral arrangement over the whole crystal. Due to such a strong arrangement diamond the hardest substance.
Let us check the correctness of the given statements one by one.
\[1\] . Effective number of atoms present in a diamond cubic cell is \[8\] .
In the diamond unit cell the carbon atoms are arranged in face centered cubic crystal. The number of atoms that are contributed by the corner atoms in the unit cell is \[\dfrac{1}{8} \times 8 = 1\] . The number of atoms that are contributed by the face centered atoms in the unit cell is\[\dfrac{1}{2} \times 6 = 3\] . The number of atoms inside the structure of the unit cell =\[4\] . Hence the total number of atoms present in a diamond cubic cell is \[1 + 3 + 4 = 8\] .
\[2\] . Each carbon is surrounded by four more carbon atoms.
Out of eight cube corners in the unit cell, four atoms are bonded to an atom within the cube and the other four are bonded to adjacent cubes of the crystal lattice. Hence each carbon atom present at the centre of the tetrahedron in the crystal and four other carbon atoms are present at the corners of the tetrahedron of the face centered cubic crystal.
\[3\] . Atomic radius of carbon is \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times a}}{8}\] , where \[a\] is the edge length of the cube.
Let us take a cross section of the cube of the FCC lattice where \[a\] is the edge length shared by four atoms.

For triangle ABC, \[B{C^2} = {\left[ {\dfrac{a}{4}} \right]^2} + {\left[ {\dfrac{a}{4}} \right]^2} = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{8}\]
For triangle XYZ, $B{D^2} = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{8} + {\left[ {\dfrac{a}{4}} \right]^2} = \dfrac{{3{a^2}}}{{16}}$
As\[BD = 2r\] ,
${[2r]^2} = \dfrac{{3{a^2}}}{{16}}$
$r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times a}}{8}$ . This is the radius of carbon.
\[4\] . Approximate packing fraction of the unit cell is \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times \pi }}{{16}}\].
The packing fraction of the lattice is given as \[\dfrac{{8 \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}}}{{{a^3}}}\].
Inserting the value of radius r in the packing fraction relation,
\[PE = \dfrac{{8 \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {{\left[ {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times a}}{8}} \right]}^3}}}{{{a^3}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \times \pi }}{{16}}\] .
Hence, all the four statements about the cubic structure of diamond are correct.
Note: Please note that in the unit cell of diamond, only \[34\% \] of the volume is occupied and \[66\% \] of volume is empty. This is obtained from the packing fraction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




