
State Kirchhoff’s voltage law.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Here, in the question, we need to define and explain the Kirchhoff’s law. Kirchhoff’s law is divided into two sub-parts, i.e., Kirchhoff’s current law and Kirchhoff’s voltage law. We will limit our discussion here to Kirchhoff's voltage law only.
Complete step by step answer:
According to Kirchhoff’s voltage law, the algebraic sum of the voltage drop across all the elements in a closed circuit equals to zero. In other words, Kirchhoff's law is the conservation of energy in a closed circuit. Mathematically $\sum V = 0$.
Let us take an example to better understand the topic.
Consider a closed circuit such that a resistor of resistance R, an inductor of inductance L, and a capacitor of capacitance C are connected in series across an AC voltage source, V. Also, consider a current I flowing in the closed circuit.
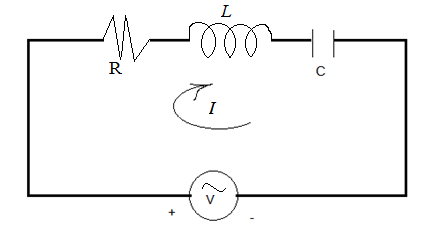
In the shown figure, let us apply the Kirchhoff’s voltage rule as:
$
V - {V_R} - {V_L} - {V_C} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow V - IR - L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} - \dfrac{1}{C}\int {Idt} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow V = IR + L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{1}{C}\int {Idt} \\
$
Hence, we can see that the energy remains conserved in the given circuit.
Note:
It is interesting to note here that the full name of Kirchhoff’s voltage law is Gustav Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law, in which Gustav Kirchhoff is the name of the scientist who discovered this law. Moreover, it is advised to the students to be aware while using the current sign convention and it varies from person-to-person.
Complete step by step answer:
According to Kirchhoff’s voltage law, the algebraic sum of the voltage drop across all the elements in a closed circuit equals to zero. In other words, Kirchhoff's law is the conservation of energy in a closed circuit. Mathematically $\sum V = 0$.
Let us take an example to better understand the topic.
Consider a closed circuit such that a resistor of resistance R, an inductor of inductance L, and a capacitor of capacitance C are connected in series across an AC voltage source, V. Also, consider a current I flowing in the closed circuit.

In the shown figure, let us apply the Kirchhoff’s voltage rule as:
$
V - {V_R} - {V_L} - {V_C} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow V - IR - L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} - \dfrac{1}{C}\int {Idt} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow V = IR + L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{1}{C}\int {Idt} \\
$
Hence, we can see that the energy remains conserved in the given circuit.
Note:
It is interesting to note here that the full name of Kirchhoff’s voltage law is Gustav Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law, in which Gustav Kirchhoff is the name of the scientist who discovered this law. Moreover, it is advised to the students to be aware while using the current sign convention and it varies from person-to-person.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




