
State Fleming's right-hand rule and give examples. Demonstrate the same with the help of an experiment.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Consider a conductor is moving in a magnetic field. Using Faraday’s law of electromagnetism, find out the direction of current produced. The Fleming's right-hand rule gives the relation between the direction of induced current, direction of the force on the conductor and the direction of the magnetic field in which the conductor is placed.
Complete step by step answer:
Fleming's right rule is an interpretation which gives the direction of induced current in a conductor when the conductor is moved in a magnetic field.
Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction tells us that when we place a moving conductor inside a magnetic field, a current is induced inside the conductor. The fleming's right-hand rule gives us the relation between the direction of induced current in the conductor, the direction of force on the conductor or the direction of motion of the conductor and the direction of the magnetic field in which the conductor is placed.
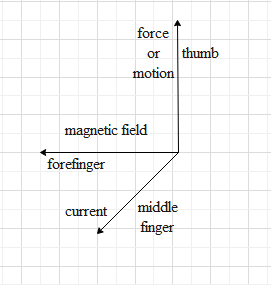
According to the Fleming’s right hand rule, if we hold our right-hand forefinger, middle finger and the thumb at right angle to each other, then, if the forefinger represents the direction of the magnetic field in which the conductor is placed and the thumb represents the direction of motion of the conductor or the direction of applied force, than the direction of the middle finger represents the direction of induced current in the conductor.
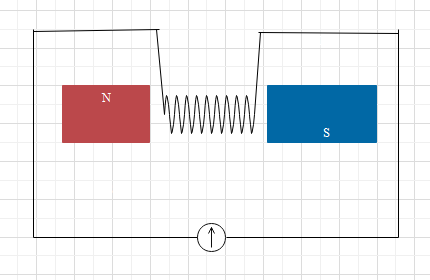
Consider an experiment where we use a stationary magnet and a coil connected to a galvanometer is moved through the magnetic field. When the coil is moved through the magnetic field galvanometer will show deflection due to the induction of current. When we move the coil through the magnetic field in one direction the galvanometer will show deflection. Again, when we move the coil through the magnetic field, the galvanometer will show deflection in the opposite direction i.e. the direction of the current changes. This direction of induced current can be found out from Fleming's right hand rule.
Note:
We also have another interpretation called Fleming's left-hand rule. It gives the direction of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field. If we hold our left-hand forefinger, second finger and the thumb at right angle to each other, then, if the forefinger represents the direction of the magnetic field in which the conductor is placed and the second finger represents the direction of current flow in the conductor, than the direction of the thumb represents the direction of force on the conductor.
Complete step by step answer:
Fleming's right rule is an interpretation which gives the direction of induced current in a conductor when the conductor is moved in a magnetic field.
Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction tells us that when we place a moving conductor inside a magnetic field, a current is induced inside the conductor. The fleming's right-hand rule gives us the relation between the direction of induced current in the conductor, the direction of force on the conductor or the direction of motion of the conductor and the direction of the magnetic field in which the conductor is placed.

According to the Fleming’s right hand rule, if we hold our right-hand forefinger, middle finger and the thumb at right angle to each other, then, if the forefinger represents the direction of the magnetic field in which the conductor is placed and the thumb represents the direction of motion of the conductor or the direction of applied force, than the direction of the middle finger represents the direction of induced current in the conductor.
Consider an experiment where we use a stationary magnet and a coil connected to a galvanometer is moved through the magnetic field. When the coil is moved through the magnetic field galvanometer will show deflection due to the induction of current. When we move the coil through the magnetic field in one direction the galvanometer will show deflection. Again, when we move the coil through the magnetic field, the galvanometer will show deflection in the opposite direction i.e. the direction of the current changes. This direction of induced current can be found out from Fleming's right hand rule.

Note:
We also have another interpretation called Fleming's left-hand rule. It gives the direction of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field. If we hold our left-hand forefinger, second finger and the thumb at right angle to each other, then, if the forefinger represents the direction of the magnetic field in which the conductor is placed and the second finger represents the direction of current flow in the conductor, than the direction of the thumb represents the direction of force on the conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




