
State Charle’s law. Also show the graph.
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: The Charle’s law is derived and stated from the ideal gas equation. To solve this we must know the ideal gas law. The ideal gas law states for a given mass of an ideal gas and a constant volume of an ideal gas, the pressure exerted by the molecules of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the expression for the ideal gas law is as follows:
$PV = nRT$
Where, $P$ is the pressure of the gas,
$V$ is the volume of the gas,
$n$ is the number of moles of gas,
$R$ is the universal gas constant,
$T$ is the temperature of the gas.
From the expression for the ideal gas law we can see that the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. The same is stated by Charle’s law.
The Charle’s law states that the volume of any gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale under the same amount of pressure.
The expression for Charle’s law is as follows:
${\text{V}} \propto {\text{T}}$
Where ${\text{V}}$ is the volume of the gas,
${\text{T}}$ is the temperature of the gas.
The Charle’s law states that the volume of any gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale under the same amount of pressure. When we plot volume versus temperature the graph is a straight line passing through origin.
Thus, the graph of Charle’s law is as follows:
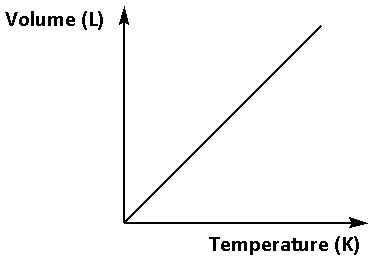
Note:The application of Charle’s law in daily life is the floating hot air balloon in air. The air in the balloon is heated by a torch. This makes the air particles move faster and disperse thus, making the air in the balloon less dense than the air in the surrounding so that the balloon floats.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the expression for the ideal gas law is as follows:
$PV = nRT$
Where, $P$ is the pressure of the gas,
$V$ is the volume of the gas,
$n$ is the number of moles of gas,
$R$ is the universal gas constant,
$T$ is the temperature of the gas.
From the expression for the ideal gas law we can see that the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. The same is stated by Charle’s law.
The Charle’s law states that the volume of any gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale under the same amount of pressure.
The expression for Charle’s law is as follows:
${\text{V}} \propto {\text{T}}$
Where ${\text{V}}$ is the volume of the gas,
${\text{T}}$ is the temperature of the gas.
The Charle’s law states that the volume of any gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale under the same amount of pressure. When we plot volume versus temperature the graph is a straight line passing through origin.
Thus, the graph of Charle’s law is as follows:

Note:The application of Charle’s law in daily life is the floating hot air balloon in air. The air in the balloon is heated by a torch. This makes the air particles move faster and disperse thus, making the air in the balloon less dense than the air in the surrounding so that the balloon floats.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




