
State and explain the Huygens principle in physics.
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: Huygens Principle is a major law in physics basically in optics. The statement that all points in a wave front of the light in a vacuum or in a transparent medium can be taken as the new sources of wavelets that can expand in each and every direction at a rate which is dependent on their velocities. This theory was given by the Dutch mathematician, and also a physicist as well as an astronomer, Christiaan Huygens in 1690. This is an important and powerful process in order to study different optical phenomena. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A tangent to the surface of the wavelets will include the new wave front. This has been known as the envelope of the wavelets. An extended light source will be included of an infinite number of point sources. This is sometimes thought of as producing a plane wave front. In short, the Huygens principle says that every position on a specific wave front is able to be a source of secondary wavelets which can spread out with the speed of light in that medium and this new wave front will be the three dimensional envelope of the secondary wavelets at that time.
Diffraction is an example which can be explained using Huygens's Principle. The diffraction can be defined as the bending of a wave around the edges of an opening or an obstacle. Hence the question has been answered.
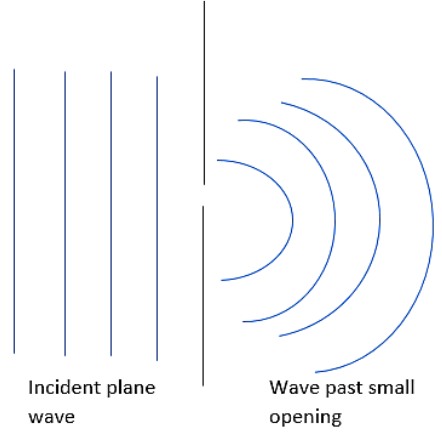
Note: When a medium is found to be homogenous and have similar characteristics throughout, allowing the light to travel with the identical speed without concern about its direction of propagation. This three-dimensional envelope of a point source will be sometimes spherical. Otherwise similar to this case with various crystals, the envelope can be ellipsoidal in shape.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A tangent to the surface of the wavelets will include the new wave front. This has been known as the envelope of the wavelets. An extended light source will be included of an infinite number of point sources. This is sometimes thought of as producing a plane wave front. In short, the Huygens principle says that every position on a specific wave front is able to be a source of secondary wavelets which can spread out with the speed of light in that medium and this new wave front will be the three dimensional envelope of the secondary wavelets at that time.
Diffraction is an example which can be explained using Huygens's Principle. The diffraction can be defined as the bending of a wave around the edges of an opening or an obstacle. Hence the question has been answered.

Note: When a medium is found to be homogenous and have similar characteristics throughout, allowing the light to travel with the identical speed without concern about its direction of propagation. This three-dimensional envelope of a point source will be sometimes spherical. Otherwise similar to this case with various crystals, the envelope can be ellipsoidal in shape.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




