
State and explain Biot- savart’s law.
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: The Biot–Savart’s law is an equation describing the magnetic field generated by a constant electric current. It relates the magnetic field to the magnitude, direction, length, and electric current.
Complete step by step answer:
Biot-savart’s law is used to determine the strength of a magnetic field at any point due to a current-carrying conductor.
Consider a very small element AB of the length $dl$ of a conductor carrying current I. The strength of magnetic field $dB$ due to this small current element at a point $P$, distance $r$ from the element is found to depend upon quantities;
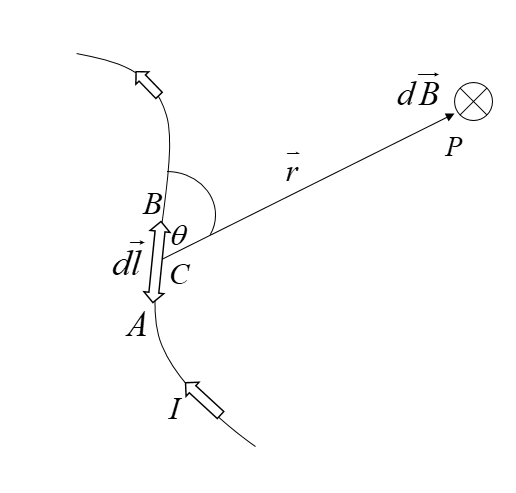
i)${\rm{db}} \propto {\rm{ dl}}$
ii) ${\rm{dB}} \propto {\rm{I}}$
iii) ${\rm{dB}} \propto {\rm{sin}}\theta $, where$\theta $ is the angle between ${\rm{d\vec l}}$ and ${\rm{\vec r}}$ vector
iv) ${\rm{dB}} \propto \dfrac{1}{{{{\rm{r}}^2}}}$
On combining (i) to (iv), we get ${\rm{dB}} \propto \dfrac{{{\rm{Idlsin}}\theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
i.e. ${\rm{dB = }}k\dfrac{{{\rm{Idlsin}}\theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
Where k is the constant of proportionality.
In SI units, ${\rm{k}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}$ where ${\mu _0}$ is called absolute permeability.
Additional information:
Some of the Biot-savart’s law applications are:
- We can use it to calculate magnetic responses even at the atomic or molecular level.
- It is also used in aerodynamic theory to calculate the velocity induced by vortex lines.
Note:
Biot-savart’s law is similar to coulomb’s law in electrostatics. This law is applicable for very small conductors too which vary current. It is also applicable for symmetrical current distribution. Biot–Savart law has evenness with both Ampere's circuital law and Gauss's theorem.
Complete step by step answer:
Biot-savart’s law is used to determine the strength of a magnetic field at any point due to a current-carrying conductor.
Consider a very small element AB of the length $dl$ of a conductor carrying current I. The strength of magnetic field $dB$ due to this small current element at a point $P$, distance $r$ from the element is found to depend upon quantities;

i)${\rm{db}} \propto {\rm{ dl}}$
ii) ${\rm{dB}} \propto {\rm{I}}$
iii) ${\rm{dB}} \propto {\rm{sin}}\theta $, where$\theta $ is the angle between ${\rm{d\vec l}}$ and ${\rm{\vec r}}$ vector
iv) ${\rm{dB}} \propto \dfrac{1}{{{{\rm{r}}^2}}}$
On combining (i) to (iv), we get ${\rm{dB}} \propto \dfrac{{{\rm{Idlsin}}\theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
i.e. ${\rm{dB = }}k\dfrac{{{\rm{Idlsin}}\theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
Where k is the constant of proportionality.
In SI units, ${\rm{k}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}$ where ${\mu _0}$ is called absolute permeability.
Additional information:
Some of the Biot-savart’s law applications are:
- We can use it to calculate magnetic responses even at the atomic or molecular level.
- It is also used in aerodynamic theory to calculate the velocity induced by vortex lines.
Note:
Biot-savart’s law is similar to coulomb’s law in electrostatics. This law is applicable for very small conductors too which vary current. It is also applicable for symmetrical current distribution. Biot–Savart law has evenness with both Ampere's circuital law and Gauss's theorem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




