
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Answer
525k+ views
Hint: In this question consider a straight current carrying wire since current is simply flow of electrons and this flow of electrons give rise to a magnetic field thus magnetic fields and also consider an imaginary loop around this conductor as shown also known as imperial loop of radius r, so write the magnetic field at any point on this loop. This will help approaching the problem.
Step By Step Answer:
Ampere’s Circuital law:
It is the relationship between the current and the magnetic field created by the current.
So according to this law the integral of magnetic field density (B) along an imaginary path is equal to the product of the permeability of the free space and the current enclosed by the path.
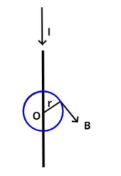
Let us consider an electrical conductor which carries current I in the downward direction as shown in the figure, we also consider an imaginary loop around this conductor as shown also known as amperian loop, so due to this the magnetic field at any point on this loop is given as,
$\oint {\vec B.d\vec l = {\mu _o} \times } I$
Where, ${\mu _o}$ = permeability of the free space = $4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}$H/m.
This law is the basis of the Biot – savart law
Biot – savart law –
The Biot-Savart Law is an equation that describes the magnetic field created by a current-carrying wire and allows you to calculate its strength at various points.
Biot Savart Law
$\left( i \right)$ Directly proportional to current (I)
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Directly proportional to the length of the element (dl)
$\left( {iii} \right)$ Directly proportional to the sine of angle θ between the direction of current and the line joining the element dl.
$\left( {iv} \right)$ Inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) of point A from the element dl.
$\left( v \right)$ $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{Idl\sin \theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
Note: The same role ampere’s circuital law plays in magnetic physics the same is played by Gauss Law in electrostatic physics. The common thing about Gauss law and ampere circuital law is that both are applied to the systems in which the current flowing has symmetrical distribution.
Step By Step Answer:
Ampere’s Circuital law:
It is the relationship between the current and the magnetic field created by the current.
So according to this law the integral of magnetic field density (B) along an imaginary path is equal to the product of the permeability of the free space and the current enclosed by the path.

Let us consider an electrical conductor which carries current I in the downward direction as shown in the figure, we also consider an imaginary loop around this conductor as shown also known as amperian loop, so due to this the magnetic field at any point on this loop is given as,
$\oint {\vec B.d\vec l = {\mu _o} \times } I$
Where, ${\mu _o}$ = permeability of the free space = $4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}$H/m.
This law is the basis of the Biot – savart law
Biot – savart law –
The Biot-Savart Law is an equation that describes the magnetic field created by a current-carrying wire and allows you to calculate its strength at various points.
Biot Savart Law
$\left( i \right)$ Directly proportional to current (I)
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Directly proportional to the length of the element (dl)
$\left( {iii} \right)$ Directly proportional to the sine of angle θ between the direction of current and the line joining the element dl.
$\left( {iv} \right)$ Inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) of point A from the element dl.
$\left( v \right)$ $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{Idl\sin \theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
Note: The same role ampere’s circuital law plays in magnetic physics the same is played by Gauss Law in electrostatic physics. The common thing about Gauss law and ampere circuital law is that both are applied to the systems in which the current flowing has symmetrical distribution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




