
What is the source of Electromagnetic Waves?

Answer
487.2k+ views
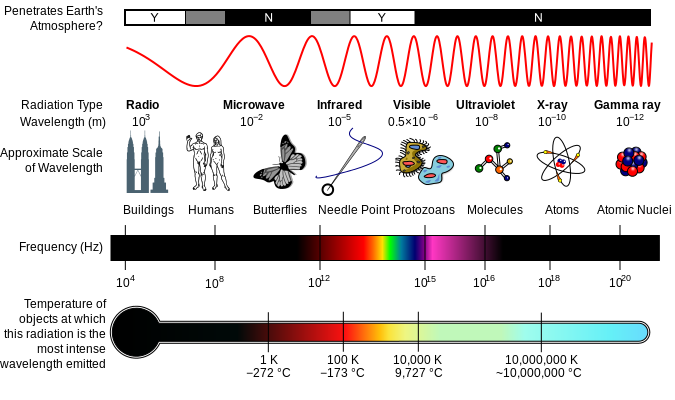
Hint: Electromagnetic radiation is defined as electromagnetic field waves that propagate over space and convey electromagnetic radiant energy. Radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays are all examples of electromagnetic radiation. The electromagnetic spectrum includes all of these wavelengths.
Complete answer:
Electromagnetic radiation is made up of coordinated oscillations of electric and magnetic fields, which are known as electromagnetic waves. The periodic changing of an electric or magnetic field produces electromagnetic radiation or electromagnetic waves. Different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum are created depending on how this periodic shift happens and the power generated. Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, usually abbreviated as c. The oscillations of the two fields create a transverse wave in a homogeneous, isotropic medium because they are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of energy and wave propagation.
Electrically charged particles experiencing acceleration produce electromagnetic waves, which can then interact with other charged particles and exert force on them. EM waves transport energy, momentum, and angular momentum out from their originating particle and can impart these quantities to anything they come into contact with. Because they have gained sufficient distance from the moving charges that created them, electromagnetic radiation is linked with those EM waves that are free to propagate ("radiate") without the ongoing effect of the moving charges that produced them.
As a result, EMR is also known as the far field. The term "near field" refers to electromagnetic fields that are close to the charges and currents that directly created them, such as electromagnetic induction and electrostatic induction.
Note:
According to quantum physics, EMR is made up of photons, which are uncharged elementary particles with zero rest mass and are the quanta of the electromagnetic field, which are responsible for all electromagnetic interactions. Quantum electrodynamics is the theory that describes how electromagnetic radiation interacts with matter at the atomic level. Quantum phenomena, such as the transfer of electrons to lower energy states in an atom and black-body radiation, provide additional sources of EMR. The energy of a single photon is quantized, and higher frequency photons have more energy.
Complete answer:
Electromagnetic radiation is made up of coordinated oscillations of electric and magnetic fields, which are known as electromagnetic waves. The periodic changing of an electric or magnetic field produces electromagnetic radiation or electromagnetic waves. Different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum are created depending on how this periodic shift happens and the power generated. Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, usually abbreviated as c. The oscillations of the two fields create a transverse wave in a homogeneous, isotropic medium because they are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of energy and wave propagation.
Electrically charged particles experiencing acceleration produce electromagnetic waves, which can then interact with other charged particles and exert force on them. EM waves transport energy, momentum, and angular momentum out from their originating particle and can impart these quantities to anything they come into contact with. Because they have gained sufficient distance from the moving charges that created them, electromagnetic radiation is linked with those EM waves that are free to propagate ("radiate") without the ongoing effect of the moving charges that produced them.
As a result, EMR is also known as the far field. The term "near field" refers to electromagnetic fields that are close to the charges and currents that directly created them, such as electromagnetic induction and electrostatic induction.
Note:
According to quantum physics, EMR is made up of photons, which are uncharged elementary particles with zero rest mass and are the quanta of the electromagnetic field, which are responsible for all electromagnetic interactions. Quantum electrodynamics is the theory that describes how electromagnetic radiation interacts with matter at the atomic level. Quantum phenomena, such as the transfer of electrons to lower energy states in an atom and black-body radiation, provide additional sources of EMR. The energy of a single photon is quantized, and higher frequency photons have more energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




