
Solve this following inequality:
\[\sin x > -\dfrac{1}{2}\]
(a) \[2n\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3} < x < 2n\pi +\dfrac{7\pi }{3};n\in \mathbb{Z}\]
(b) \[2n\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{5} < x < 2n\pi +\dfrac{6\pi }{5};n\in \mathbb{Z}\]
(c) \[2n\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{4} < x < 2n\pi +\dfrac{5\pi }{4};n\in \mathbb{Z}\]
(d) \[2n\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} < x < 2n\pi +\dfrac{7\pi }{6};n\in \mathbb{Z}\]
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: We solve this problem first by finding the exact solution then we can find the general solution.
We use the condition that the period for sine function is \[2\pi \] so that we find the solution in the domain \[\left[ -2\pi, 2\pi \right]\] of one complete curve that satisfies the given inequality then we can find the general solution.
For finding the exact solution we use graph theory that is if \[f\left( x \right) > g\left( x \right)\] then the solution is given by plotting the graph of \[y=f\left( x \right)\] and \[y=g\left( x \right)\] such that the domain above the intersection of both graphs will be the solution.
The general solution for a sine function of one complete curve such that the curve of \[y=\sin x\] is above the line \[y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] is given by adding the \[2n\pi \]where \['n'\] is an integer to exact solution because the period of the sine function is \[2\pi \]
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given with the inequality that is
\[\sin x > -\dfrac{1}{2}\]
We know that the period of sine function is \[2\pi \] so that the exact solution will be in the domain \[\left[ -2\pi ,2\pi \right]\]
Let us use the graph theory to find the exact solution.
We know that if \[f\left( x \right) > g\left( x \right)\] then the solution is given by plotting the graph of \[y=f\left( x \right)\] and \[y=g\left( x \right)\] such that the domain above the intersection of both graphs will be the solution.
Now, let us plot the graphs \[y=\sin x\] and \[y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] then we get
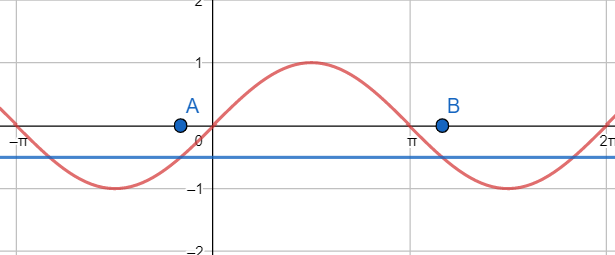
Here we can see that one complete curve of \[y=\sin x\] that is above the line \[y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] is located between that points A and B where the co – ordinates of points are \[A\left( \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{-1}{2} \right),B\left( \dfrac{7\pi }{6},\dfrac{-1}{2} \right)\]
So, we can say that the exact solution lies between these points.
So, by converting the above statement into mathematical inequality we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{-\pi }{6} < x < \dfrac{7\pi }{6}\]
We know that the general solution of sine function is given by adding the \[2n\pi \]where \['n'\] is an integer to exact solution because the period of the sine function is \[2\pi \]
So, by adding the \[2n\pi \] in above equation we get
\[\Rightarrow 2n\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} < x < 2n\pi +\dfrac{7\pi }{6};n\in \mathbb{Z}\]
So, option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: We can find the exact solution without using the graph theory.
We are given the inequality that is
\[\sin x > -\dfrac{1}{2}\]
We know that the sine function is negative in the third and fourth quadrants.
So, we can take one value in this and one value in the fourth quadrant such that \[\sin x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] and then we can change it into inequality by taking the value of \['x'\] between those two values.
We know that if \[\sin x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] then \[x=\dfrac{-\pi }{6}\] is solution in fourth quadrant and \[x=\dfrac{7\pi }{6}\] in third quadrant.
So, we can take the inequality as
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{-\pi }{6} < x < \dfrac{7\pi }{6}\]
So, by adding the \[2n\pi \] in the above equation we get
\[\Rightarrow 2n\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} < x < 2n\pi +\dfrac{7\pi }{6};n\in \mathbb{Z}\]
So, option (d) is the correct answer.
We use the condition that the period for sine function is \[2\pi \] so that we find the solution in the domain \[\left[ -2\pi, 2\pi \right]\] of one complete curve that satisfies the given inequality then we can find the general solution.
For finding the exact solution we use graph theory that is if \[f\left( x \right) > g\left( x \right)\] then the solution is given by plotting the graph of \[y=f\left( x \right)\] and \[y=g\left( x \right)\] such that the domain above the intersection of both graphs will be the solution.
The general solution for a sine function of one complete curve such that the curve of \[y=\sin x\] is above the line \[y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] is given by adding the \[2n\pi \]where \['n'\] is an integer to exact solution because the period of the sine function is \[2\pi \]
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given with the inequality that is
\[\sin x > -\dfrac{1}{2}\]
We know that the period of sine function is \[2\pi \] so that the exact solution will be in the domain \[\left[ -2\pi ,2\pi \right]\]
Let us use the graph theory to find the exact solution.
We know that if \[f\left( x \right) > g\left( x \right)\] then the solution is given by plotting the graph of \[y=f\left( x \right)\] and \[y=g\left( x \right)\] such that the domain above the intersection of both graphs will be the solution.
Now, let us plot the graphs \[y=\sin x\] and \[y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] then we get

Here we can see that one complete curve of \[y=\sin x\] that is above the line \[y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] is located between that points A and B where the co – ordinates of points are \[A\left( \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{-1}{2} \right),B\left( \dfrac{7\pi }{6},\dfrac{-1}{2} \right)\]
So, we can say that the exact solution lies between these points.
So, by converting the above statement into mathematical inequality we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{-\pi }{6} < x < \dfrac{7\pi }{6}\]
We know that the general solution of sine function is given by adding the \[2n\pi \]where \['n'\] is an integer to exact solution because the period of the sine function is \[2\pi \]
So, by adding the \[2n\pi \] in above equation we get
\[\Rightarrow 2n\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} < x < 2n\pi +\dfrac{7\pi }{6};n\in \mathbb{Z}\]
So, option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: We can find the exact solution without using the graph theory.
We are given the inequality that is
\[\sin x > -\dfrac{1}{2}\]
We know that the sine function is negative in the third and fourth quadrants.
So, we can take one value in this and one value in the fourth quadrant such that \[\sin x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] and then we can change it into inequality by taking the value of \['x'\] between those two values.
We know that if \[\sin x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\] then \[x=\dfrac{-\pi }{6}\] is solution in fourth quadrant and \[x=\dfrac{7\pi }{6}\] in third quadrant.
So, we can take the inequality as
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{-\pi }{6} < x < \dfrac{7\pi }{6}\]
So, by adding the \[2n\pi \] in the above equation we get
\[\Rightarrow 2n\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} < x < 2n\pi +\dfrac{7\pi }{6};n\in \mathbb{Z}\]
So, option (d) is the correct answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with the help of class 12 biology CBSE

India is a sovereign socialist secular democratic republic class 12 social science CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




