
Solve in positive integers : $5x+2y=53$
(a) $x=1,3,5,7,9;y=24,19,14,9,4$
(b) $x=2,4,6,8,10;y=23,20,13,8,3$
(c) $x=11,13,15,17,19;y=1,3,4,6,9$
(d) None of these
Answer
618.3k+ views
Hint: In these types of questions , choice by elimination is the best approach . Instead of finding the correct option , we will eliminate the wrong answers and the last option remaining is the correct option.
Complete step by step answer:
To solve this question , we must know the following properties of natural numbers :
Product of two odd numbers is always odd.
Sum of two odd numbers is always even.
Sum of two even numbers is always even.
Sum of an odd and an even number is always odd.
Product of an ever or odd number with an even number is always even.
Now , from the question , we can see that the sum in the RHS is an odd number. So , among the two numbers in the LHS , one is even and the other is odd.
Now , the coefficient of $y$ is an even number. So , the value of $2y$ will always be even . It means the value of $5x$ should be odd. Now , we know , product of two odd numbers is always odd and the product of an odd number and an even number is always even . So, the values of $x$ cannot be even. Hence , option(b) is ruled out.
Now , in option (c) , we can see that the first ordered pair is $(11,1)$, i.e. $x=11$ and $y=1$ . On substituting in $5x+2y$ , we get the value of $5x+2y$ as $(5\times 11)+(2\times 1)=57$ , which clearly is not equal to $53$ . So , option (c) is also ruled out.
Now , in option (a) , the first values are $x=1$ and $y=24$ .
On substituting in $5x+2y$ , we get the value of $5x+2y$ as $(5\times 1)+(2\times 24)=5+48=53$.
So , the first ordered pair of option(a) satisfies the equation.
Now , let’s consider the equation $ax+by=c$. Here, the coefficients of $x$ and $y$ are in the ratio $b:a$. Let $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ satisfy the equation of line. So, $a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}=c$. Let’s consider the points $({{x}_{1}}+b,{{y}_{1}}-a)$. On substituting this point in the equation of line , the LHS becomes $a({{x}_{1}}+b)+b({{y}_{1}}-a)$.
$=a{{x}_{1}}+ab+b{{y}_{1}}-ab$
$=a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}$
$=c$ , which is the same as the RHS of the equation of the line.
Hence, the point $({{x}_{1}}+b,{{y}_{1}}-a)$ will also satisfy the equation of the line, or simply we can say that the point $({{x}_{1}}+b,{{y}_{1}}-a)$ will also lie on the line $ax+by=c$.
Now , we can see that the coefficients of $x$ and $y$ are in the ratio $5:2$ . So , if $(a,b)$ satisfies the equation, then $(a+2,b-5)$ will also satisfy the equation.
Now, $(1,24)$ satisfies the equation . So , $(3,19),(5,14),(7,9)$ and $(9,4)$ will also satisfy the equation.
Hence , option(a) is the correct answer.
Note: The question can also be solved graphically. The equation $5x+2y=53$represents a line , which can be shown in a cartesian plane as
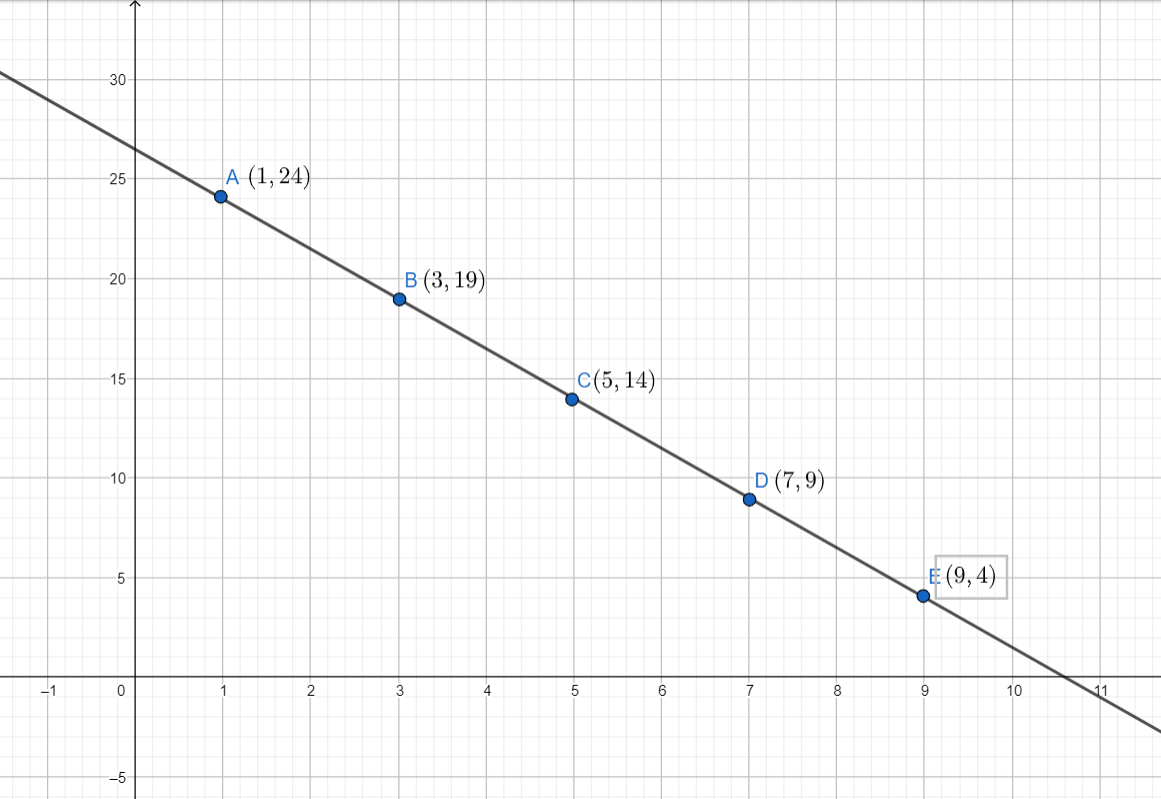
From the graph , we can clearly see that the points $(1,24),(3,19),(5,14),(7,9)$ and $(9,4)$lie on the line $5x+2y=53$.
Hence , option(a) is the correct option .
Complete step by step answer:
To solve this question , we must know the following properties of natural numbers :
Product of two odd numbers is always odd.
Sum of two odd numbers is always even.
Sum of two even numbers is always even.
Sum of an odd and an even number is always odd.
Product of an ever or odd number with an even number is always even.
Now , from the question , we can see that the sum in the RHS is an odd number. So , among the two numbers in the LHS , one is even and the other is odd.
Now , the coefficient of $y$ is an even number. So , the value of $2y$ will always be even . It means the value of $5x$ should be odd. Now , we know , product of two odd numbers is always odd and the product of an odd number and an even number is always even . So, the values of $x$ cannot be even. Hence , option(b) is ruled out.
Now , in option (c) , we can see that the first ordered pair is $(11,1)$, i.e. $x=11$ and $y=1$ . On substituting in $5x+2y$ , we get the value of $5x+2y$ as $(5\times 11)+(2\times 1)=57$ , which clearly is not equal to $53$ . So , option (c) is also ruled out.
Now , in option (a) , the first values are $x=1$ and $y=24$ .
On substituting in $5x+2y$ , we get the value of $5x+2y$ as $(5\times 1)+(2\times 24)=5+48=53$.
So , the first ordered pair of option(a) satisfies the equation.
Now , let’s consider the equation $ax+by=c$. Here, the coefficients of $x$ and $y$ are in the ratio $b:a$. Let $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ satisfy the equation of line. So, $a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}=c$. Let’s consider the points $({{x}_{1}}+b,{{y}_{1}}-a)$. On substituting this point in the equation of line , the LHS becomes $a({{x}_{1}}+b)+b({{y}_{1}}-a)$.
$=a{{x}_{1}}+ab+b{{y}_{1}}-ab$
$=a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}$
$=c$ , which is the same as the RHS of the equation of the line.
Hence, the point $({{x}_{1}}+b,{{y}_{1}}-a)$ will also satisfy the equation of the line, or simply we can say that the point $({{x}_{1}}+b,{{y}_{1}}-a)$ will also lie on the line $ax+by=c$.
Now , we can see that the coefficients of $x$ and $y$ are in the ratio $5:2$ . So , if $(a,b)$ satisfies the equation, then $(a+2,b-5)$ will also satisfy the equation.
Now, $(1,24)$ satisfies the equation . So , $(3,19),(5,14),(7,9)$ and $(9,4)$ will also satisfy the equation.
Hence , option(a) is the correct answer.
Note: The question can also be solved graphically. The equation $5x+2y=53$represents a line , which can be shown in a cartesian plane as

From the graph , we can clearly see that the points $(1,24),(3,19),(5,14),(7,9)$ and $(9,4)$lie on the line $5x+2y=53$.
Hence , option(a) is the correct option .
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE

What is the full form of pH?





