
How do you solve and graph the compound inequality $3x - 1 < 8$ or $5x - 5 > 25$?
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint: First, obtain the system of linear inequations. Then, solve each inequation and obtain their solution sets. Also, represent them on a real line. Then, find the intersection of the solutions sets obtained by taking the help of the graphical representation of the solution sets. Thus, the set obtained is the required solution set of the given system of inequations.
Formula used:
In the process of solving an inequation, we use mathematical simplifications which are governed by the following rules:
Rule 1 Same number may be added to (or subtracted from) both sides of an inequation without changing the sign of inequality.
Rule 2 Both sides of an inequation can be multiplied (or divided) by the same positive real number without changing the sign of inequality. However, the sign of inequality is reversed when both sides of an inequation are multiplied or divided by a negative number.
Rule 3 Any term of an inequation may be taken to the other side with its sign changed without affecting the sign of inequality.
Complete step by step answer:
The given system of inequalities is
$3x - 1 < 8$…(i)
$5x - 5 > 25$…(ii)
So, first we will solve inequation (i).
Collect all terms involving the variable on one side of the inequation and the constant terms on the other side and simplify both sides of inequality in their simplest forms to reduce the inequation in the form $ax < b$.
For this, add $1$ to both sides of inequation (i).
So, by rule 1, $3x < 9$…(iii)
Solve the inequation (iii) by dividing both sides of the inequation by the coefficient of the variable.
For this, divide both sides of inequation (iii) by $3$.
So, by rule 2, $x < 3$
Hence, any real number less than $3$ is a solution of inequation (i).
These solutions can be graphed on real line as shown below:
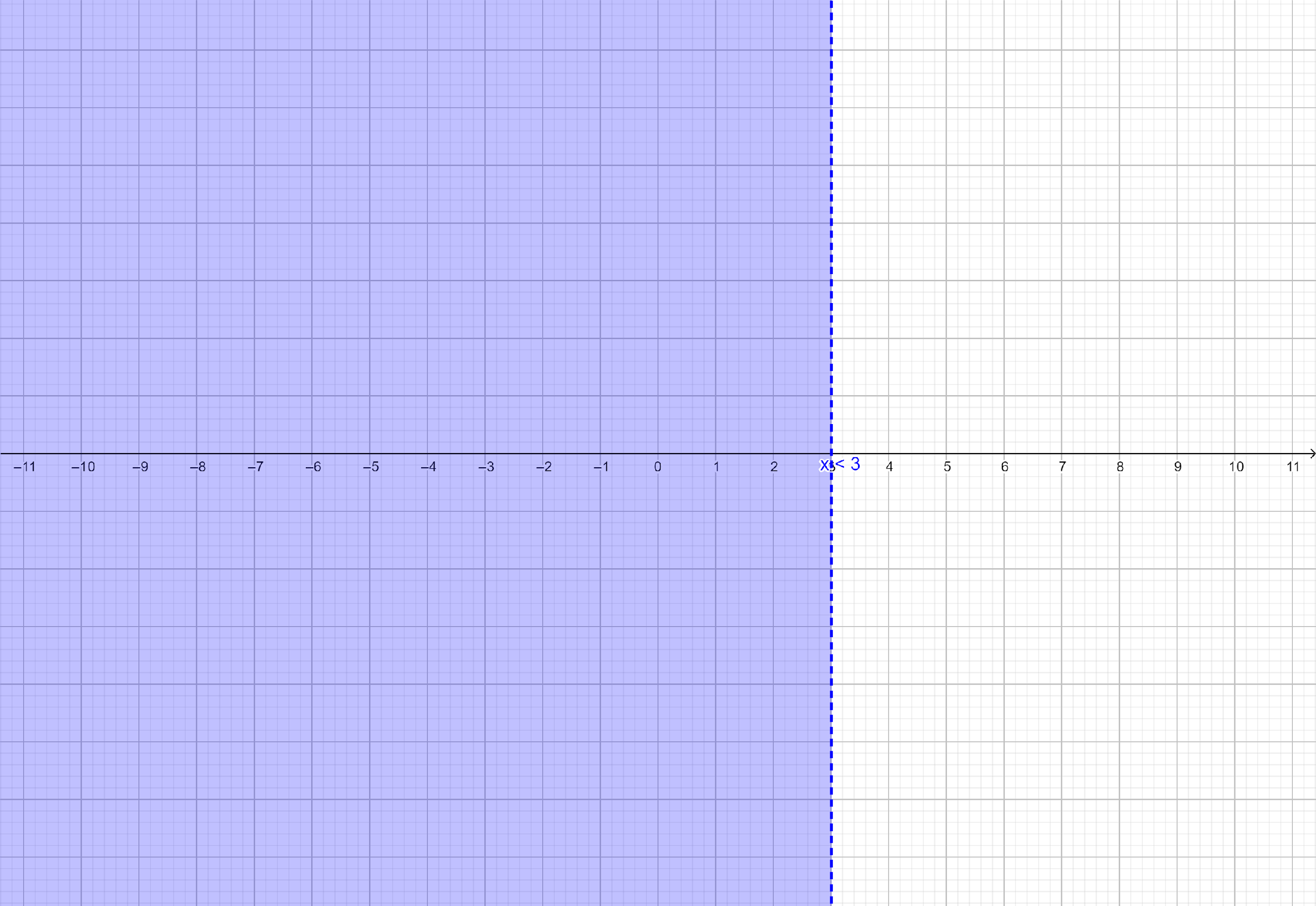 The solution set of inequation (i) is $\left( { - \infty ,3} \right)$.
The solution set of inequation (i) is $\left( { - \infty ,3} \right)$.
Now, we will solve inequation (ii).
Collect all terms involving the variable on one side of the inequation and the constant terms on the other side and simplify both sides of inequality in their simplest forms to reduce the inequation in the form $ax > b$.
For this, add $5$ to both sides of inequation (ii).
So, by rule 1, $5x > 30$…(iv)
Solve the inequation (iv) by dividing both sides of the inequation by the coefficient of the variable.
For this, divide both sides of inequation (iv) by $5$.
So, by rule 2, $x > 6$
Hence, any real number less than $3$ is a solution of inequation (ii).
These solutions can be graphed on real line as shown below:
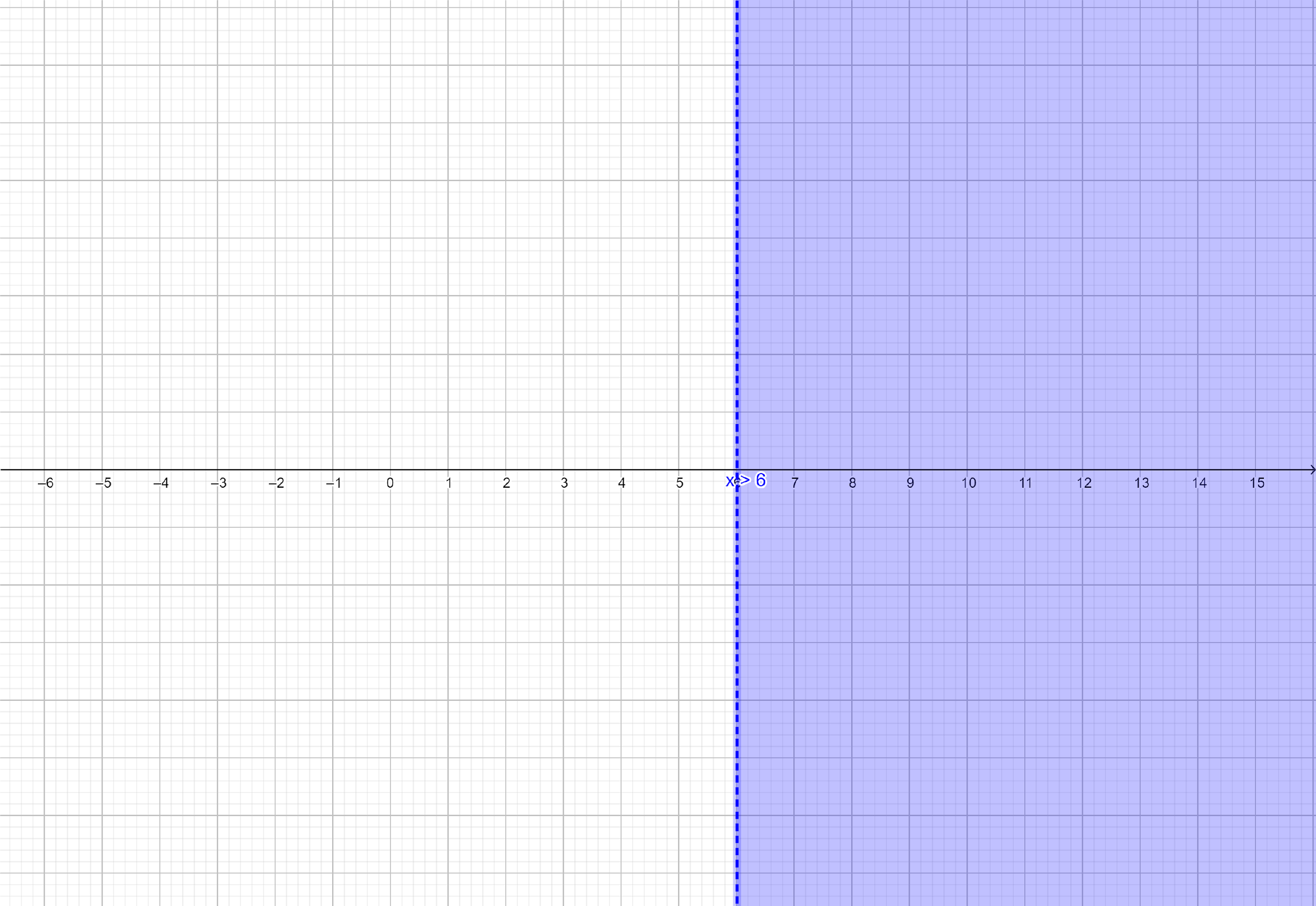 The solution set of inequation (ii) is $\left( {6,\infty } \right)$.
The solution set of inequation (ii) is $\left( {6,\infty } \right)$.
We observe that there is no common solution of the two inequalities.
Final solution: Thus, the given system of inequalities has no solution.
Note: We follow the following algorithm to solve a linear inequation in one variable.
Algorithm:
Step I Obtain the linear inequation.
Step II Collect all terms involving the variable on one side of the inequation and the constant terms on the other side.
Step III Simplify both sides of inequality in their simplest forms to reduce the inequation in the form $ax < b$, or $ax \leqslant b$, or $ax > b$, or $ax \geqslant b$
Step IV Solve the inequation obtained in step III by dividing both sides of the inequation by the coefficient of the variable.
Step V Write the solution set obtained in step IV in the form of an interval on the real line.
In order to solve a system of linear inequalities in one variable, we follow the following algorithm.
Algorithm:
Step I Obtain the system of linear inequations.
Step II Solve each inequation and obtain their solution sets. Also, represent them on a real line.
Step III Find the intersection of the solution sets obtained in step II by taking the help of the graphical representation of the solution sets in step II.
Step IV The set obtained in step III is the required solution set of the given system of inequations.
Formula used:
In the process of solving an inequation, we use mathematical simplifications which are governed by the following rules:
Rule 1 Same number may be added to (or subtracted from) both sides of an inequation without changing the sign of inequality.
Rule 2 Both sides of an inequation can be multiplied (or divided) by the same positive real number without changing the sign of inequality. However, the sign of inequality is reversed when both sides of an inequation are multiplied or divided by a negative number.
Rule 3 Any term of an inequation may be taken to the other side with its sign changed without affecting the sign of inequality.
Complete step by step answer:
The given system of inequalities is
$3x - 1 < 8$…(i)
$5x - 5 > 25$…(ii)
So, first we will solve inequation (i).
Collect all terms involving the variable on one side of the inequation and the constant terms on the other side and simplify both sides of inequality in their simplest forms to reduce the inequation in the form $ax < b$.
For this, add $1$ to both sides of inequation (i).
So, by rule 1, $3x < 9$…(iii)
Solve the inequation (iii) by dividing both sides of the inequation by the coefficient of the variable.
For this, divide both sides of inequation (iii) by $3$.
So, by rule 2, $x < 3$
Hence, any real number less than $3$ is a solution of inequation (i).
These solutions can be graphed on real line as shown below:

Now, we will solve inequation (ii).
Collect all terms involving the variable on one side of the inequation and the constant terms on the other side and simplify both sides of inequality in their simplest forms to reduce the inequation in the form $ax > b$.
For this, add $5$ to both sides of inequation (ii).
So, by rule 1, $5x > 30$…(iv)
Solve the inequation (iv) by dividing both sides of the inequation by the coefficient of the variable.
For this, divide both sides of inequation (iv) by $5$.
So, by rule 2, $x > 6$
Hence, any real number less than $3$ is a solution of inequation (ii).
These solutions can be graphed on real line as shown below:

We observe that there is no common solution of the two inequalities.
Final solution: Thus, the given system of inequalities has no solution.
Note: We follow the following algorithm to solve a linear inequation in one variable.
Algorithm:
Step I Obtain the linear inequation.
Step II Collect all terms involving the variable on one side of the inequation and the constant terms on the other side.
Step III Simplify both sides of inequality in their simplest forms to reduce the inequation in the form $ax < b$, or $ax \leqslant b$, or $ax > b$, or $ax \geqslant b$
Step IV Solve the inequation obtained in step III by dividing both sides of the inequation by the coefficient of the variable.
Step V Write the solution set obtained in step IV in the form of an interval on the real line.
In order to solve a system of linear inequalities in one variable, we follow the following algorithm.
Algorithm:
Step I Obtain the system of linear inequations.
Step II Solve each inequation and obtain their solution sets. Also, represent them on a real line.
Step III Find the intersection of the solution sets obtained in step II by taking the help of the graphical representation of the solution sets in step II.
Step IV The set obtained in step III is the required solution set of the given system of inequations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




