
How to solve \[3{\tan ^3}x = \tan x\] in the interval where \[x\] belongs to 0 to $2 \pi$?
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: In this type of trigonometric questions we bring all the terms in RHS to LHS and then we try to take out as many terms as are common. Since RHS is zero, after solving we can easily get all the possible values of x that satisfy.
Complete step-by-step solution:
So initially we will take all the terms from RHS to LHS, which will be giving us with,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[3{\tan ^3}x - \tan x = 0\]
Now we will take all common terms out, which will be giving us with,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan x\left( {3{{\tan }^2}x - 1} \right) = 0\]
Now when we equate the above equation to zero, either
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan x\]=\[0\] or \[\left( {3{{\tan }^2}x - 1} \right) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan x\]=\[0\] OR \[\tan x\]=\[ \pm \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
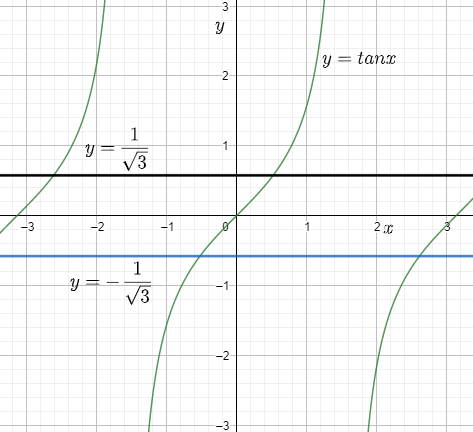
Above given is the graph of tan x and the red line is y=\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] and the grey line below the axis is y=-\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\].
Clearly in the graph we can see that there are 5 points of intersection out of which x=0, \[\pi \] are two.
We know that, in the interval where \[x\] belongs to 0 to $2\pi$
\[\tan x\]=\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] at \[x\]= \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\] , \[\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}\] and \[\tan x\]=-\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] at x= \[\dfrac{{5\pi }}{6}\]
Therefore the 5 solutions to the equation are:-
\[x = 0\] , \[\pi \],\[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\] , \[\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}\], \[\dfrac{{5\pi }}{6}\].
Note: In such types of trigonometric questions, while finding the final solutions we sometimes get confused between angles. That means we sometimes get confused \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\] and \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]. In other words, we sometimes write \[\tan x\]=\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] at \[x\]=\[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] and so on. This should be avoided and taken care of.
Complete step-by-step solution:
So initially we will take all the terms from RHS to LHS, which will be giving us with,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[3{\tan ^3}x - \tan x = 0\]
Now we will take all common terms out, which will be giving us with,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan x\left( {3{{\tan }^2}x - 1} \right) = 0\]
Now when we equate the above equation to zero, either
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan x\]=\[0\] or \[\left( {3{{\tan }^2}x - 1} \right) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\tan x\]=\[0\] OR \[\tan x\]=\[ \pm \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]

Above given is the graph of tan x and the red line is y=\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] and the grey line below the axis is y=-\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\].
Clearly in the graph we can see that there are 5 points of intersection out of which x=0, \[\pi \] are two.
We know that, in the interval where \[x\] belongs to 0 to $2\pi$
\[\tan x\]=\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] at \[x\]= \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\] , \[\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}\] and \[\tan x\]=-\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] at x= \[\dfrac{{5\pi }}{6}\]
Therefore the 5 solutions to the equation are:-
\[x = 0\] , \[\pi \],\[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\] , \[\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}\], \[\dfrac{{5\pi }}{6}\].
Note: In such types of trigonometric questions, while finding the final solutions we sometimes get confused between angles. That means we sometimes get confused \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\] and \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]. In other words, we sometimes write \[\tan x\]=\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] at \[x\]=\[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] and so on. This should be avoided and taken care of.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




