
Solid phosphorus pentachloride has the formula $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$.
a. Draw a diagram to show the shape of each ion.
b. State the bond angles present in each ion.
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: The phosphorus pentachloride is yellowish white-solid and has chemical formula $[PC{l_5}]$. In the solid state, it exists in the ionic form, as a cation and an anion. In solid state, the cationic form of phosphorus pentachloride is $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ and as an anion, it exists as $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$.
Complete step by step answer:
The phosphorus pentachloride is a water sensitive solid which is soluble in many organic solvents. In the solid state, it exists as ionic solid which consists of two ions, cation $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ and anion $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$.
$2PC{l_5} \to {\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }$
The ionic solid phosphorus pentachloride has better crystalline structure than that of covalent solid.
a) The positively charged ion, phosphorus tetrachloride $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ has tetrahedral shape and the negatively charged ion, phosphorus hexachloride, $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ has octahedral shape. The structure of $[PC{l_5}]$ in liquid and gaseous form has trigonal bipyramidal geometry which is asymmetrical in nature. But, the tetrahedral geometry of $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ and the octahedral geometry of $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ are symmetrical in nature. The symmetrical geometry provides more stability than that of unsymmetrical geometry.
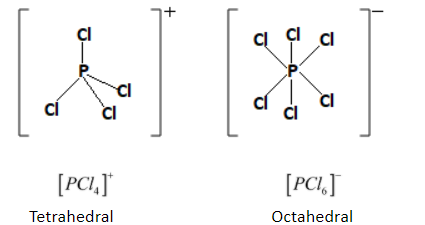
Given below is the shape and structure of cation $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ and anion $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ .
b) The angle formed between three atoms and across two bonds in the structure of a compound or ion is termed as bond angle.
The cation $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ has tetrahedral geometry with no lone pairs. The four chlorine atoms are located at the corners of the tetrahedron around the central phosphorus atom. The bond angle is equal to $109^\circ $.
The geometry of anion $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ is octahedral that means there are six chlorine atoms around the central phosphorus atom. The bond angle for $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ is equal to that of $90^\circ $.
Note: The phosphorus pentachloride, $[PC{l_5}]$ has trigonal bipyramidal geometry in its liquid and gaseous phase. It exists as a covalent solid in the liquid and gaseous phase.
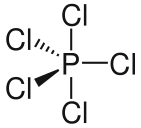
Trigonal bipyramidal structure of $[PC{l_5}]$ in gaseous and liquid phase
Students should remember that in solid state, phosphorus pentachloride exists in ionic form. Hence, it will not retain the same structure in solid state as that of in liquid and gaseous phase.
Complete step by step answer:
The phosphorus pentachloride is a water sensitive solid which is soluble in many organic solvents. In the solid state, it exists as ionic solid which consists of two ions, cation $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ and anion $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$.
$2PC{l_5} \to {\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }$
The ionic solid phosphorus pentachloride has better crystalline structure than that of covalent solid.
a) The positively charged ion, phosphorus tetrachloride $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ has tetrahedral shape and the negatively charged ion, phosphorus hexachloride, $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ has octahedral shape. The structure of $[PC{l_5}]$ in liquid and gaseous form has trigonal bipyramidal geometry which is asymmetrical in nature. But, the tetrahedral geometry of $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ and the octahedral geometry of $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ are symmetrical in nature. The symmetrical geometry provides more stability than that of unsymmetrical geometry.
Given below is the shape and structure of cation $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ and anion $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ .

b) The angle formed between three atoms and across two bonds in the structure of a compound or ion is termed as bond angle.
The cation $[{\left[ {PC{l_4}} \right]^ + }]$ has tetrahedral geometry with no lone pairs. The four chlorine atoms are located at the corners of the tetrahedron around the central phosphorus atom. The bond angle is equal to $109^\circ $.
The geometry of anion $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ is octahedral that means there are six chlorine atoms around the central phosphorus atom. The bond angle for $[{\left[ {PC{l_6}} \right]^ - }]$ is equal to that of $90^\circ $.
Note: The phosphorus pentachloride, $[PC{l_5}]$ has trigonal bipyramidal geometry in its liquid and gaseous phase. It exists as a covalent solid in the liquid and gaseous phase.
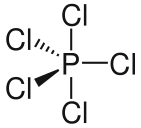
Trigonal bipyramidal structure of $[PC{l_5}]$ in gaseous and liquid phase
Students should remember that in solid state, phosphorus pentachloride exists in ionic form. Hence, it will not retain the same structure in solid state as that of in liquid and gaseous phase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




