
Sketch the labelled diagram of Menstrual Cycle.
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: The fertilized egg remains in the fallopian tube for \[3\] to \[4\] days after fertilization. However, it begins rapidly dividing into many cells within \[24\] hours of being fertilized. It continues to divide as it travels via the fallopian tube to the uterus. Its next task is to adhere to the uterine lining.
Complete explanation:
The menstruation cycle describes the growth and shedding of a lining (the endometrium) in a woman's uterus that could enable the development of a fertilized egg. It usually happens in \[28\] days cycles; thus, a woman's period comes after every \[28\] days.
Menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase are the four phases of the menstrual cycle.
On day one, our oestrogen levels are at their lowest, so don't be shocked if you're tired. You may experience period pain or feel weary, achy, or grumpy during the first few days of bleeding.
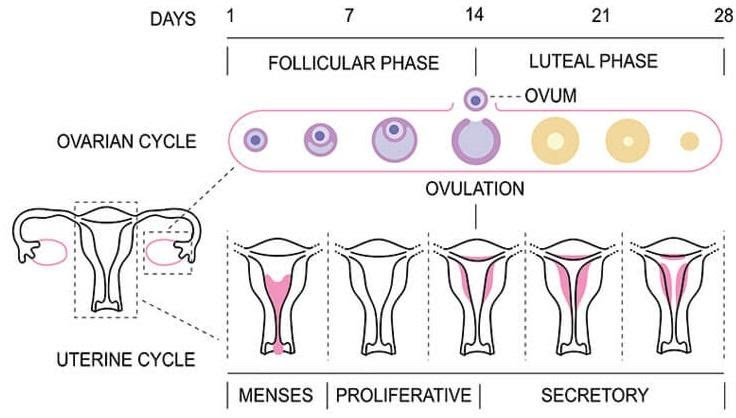
Menstrual cycle
Additional information:
The steps of fertilization are as follows-
1. Sperm Capacitation.
2. Sperm-Zona Pellucida Binding.
3. The Acrosome Reaction.
4. Penetration of the Zona Pellucida.
5. Sperm-Oocyte Binding.
6. Egg Activation and the Cortical Reaction.
7. The Zona Reaction.
8. Post-fertilization Events.
The cycles are driven by naturally existing hormones; the cyclical rise and fall of follicle stimulating hormones triggers the development and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone oestrogen causes the uterine lining to thicken in order to accommodate an embryo in the event of fertilization. A successfully implanted embryo receives nourishment from the blood supply of the thickened lining (endometrium).
Note:
The menstrual cycle is a sequence of natural changes in hormone production and the architecture of the female reproductive system's uterus and ovaries that allow for pregnancy. The ovarian cycle regulates egg production and release, as well as oestrogen and progesterone release. The uterine cycle regulates the preparation and maintenance of the uterine lining (womb) in order to receive a baby.
Complete explanation:
The menstruation cycle describes the growth and shedding of a lining (the endometrium) in a woman's uterus that could enable the development of a fertilized egg. It usually happens in \[28\] days cycles; thus, a woman's period comes after every \[28\] days.
Menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase are the four phases of the menstrual cycle.
On day one, our oestrogen levels are at their lowest, so don't be shocked if you're tired. You may experience period pain or feel weary, achy, or grumpy during the first few days of bleeding.

Menstrual cycle
Additional information:
The steps of fertilization are as follows-
1. Sperm Capacitation.
2. Sperm-Zona Pellucida Binding.
3. The Acrosome Reaction.
4. Penetration of the Zona Pellucida.
5. Sperm-Oocyte Binding.
6. Egg Activation and the Cortical Reaction.
7. The Zona Reaction.
8. Post-fertilization Events.
The cycles are driven by naturally existing hormones; the cyclical rise and fall of follicle stimulating hormones triggers the development and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone oestrogen causes the uterine lining to thicken in order to accommodate an embryo in the event of fertilization. A successfully implanted embryo receives nourishment from the blood supply of the thickened lining (endometrium).
Note:
The menstrual cycle is a sequence of natural changes in hormone production and the architecture of the female reproductive system's uterus and ovaries that allow for pregnancy. The ovarian cycle regulates egg production and release, as well as oestrogen and progesterone release. The uterine cycle regulates the preparation and maintenance of the uterine lining (womb) in order to receive a baby.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




