
How do you simplify \[\left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\]?
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to simplify the given trigonometric expression.
First we remove the bracket and multiply all the terms with each other. Then we need to simplify each term with the help of trigonometric formulas for the second term .By simplifying the expression we will get the required solution.
Formula used: i)\[\cos ec x = \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}\]
ii)\[\cot x = \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}\]
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that, \[\left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\].
We need to simplify \[\left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\].
To simplify the given expression we need to remove the bracket and multiply all the terms with each other.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 1 \times \cos ec x - 1 \times \cot x + \cos x \times \cos ec x - \cos x \times \cot x\]
Now in the third and fourth term using the trigonometric formula \[\cos ec x = \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}\] and \[\cot x = \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}\]we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos ec x - \cot x + \cos x \times \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}} - \cos x \times \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}\]
Again simplifying with the help of trigonometric formula \[\cot x = \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}\], we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos ec x - \cot x + \cot x - \dfrac{{{{\cos }^2}x}}{{\sin x}}\].
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}} - \dfrac{{{{\cos }^2}x}}{{\sin x}}\]
On using the trigonometric formula \[\cos ec x = \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{1 - {{\cos }^2}x}}{{\sin x}}\]
Also we know that,\[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\], using this we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\sin }^2}x}}{{\sin x}}\]
On cancel the term and we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sin x\]
Hence simplifying \[\left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\], we get \[\sin x\].
Note: Trigonometric expression:
Sin Cos formulas are based on sides of the right-angled triangle. Sin and Cos are basic trigonometric functions along with tan function, in trigonometry. Sine of angle is equal to the ratio of opposite side and hypotenuse whereas cosine of an angle is equal to ratio of adjacent side and hypotenuse.
\[{{sin\theta = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Opposite side}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}\]
\[{{cos\theta = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}\]
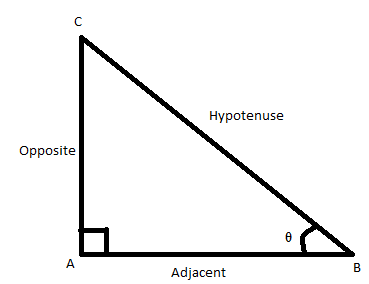
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many others. The most widely used trigonometric functions are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent.
First we remove the bracket and multiply all the terms with each other. Then we need to simplify each term with the help of trigonometric formulas for the second term .By simplifying the expression we will get the required solution.
Formula used: i)\[\cos ec x = \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}\]
ii)\[\cot x = \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}\]
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that, \[\left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\].
We need to simplify \[\left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\].
To simplify the given expression we need to remove the bracket and multiply all the terms with each other.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 1 \times \cos ec x - 1 \times \cot x + \cos x \times \cos ec x - \cos x \times \cot x\]
Now in the third and fourth term using the trigonometric formula \[\cos ec x = \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}\] and \[\cot x = \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}\]we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos ec x - \cot x + \cos x \times \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}} - \cos x \times \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}\]
Again simplifying with the help of trigonometric formula \[\cot x = \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}\], we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos ec x - \cot x + \cot x - \dfrac{{{{\cos }^2}x}}{{\sin x}}\].
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}} - \dfrac{{{{\cos }^2}x}}{{\sin x}}\]
On using the trigonometric formula \[\cos ec x = \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{1 - {{\cos }^2}x}}{{\sin x}}\]
Also we know that,\[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\], using this we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\sin }^2}x}}{{\sin x}}\]
On cancel the term and we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sin x\]
Hence simplifying \[\left( {1 + \cos x} \right)\left( {\cos ec x - \cot x} \right)\], we get \[\sin x\].
Note: Trigonometric expression:
Sin Cos formulas are based on sides of the right-angled triangle. Sin and Cos are basic trigonometric functions along with tan function, in trigonometry. Sine of angle is equal to the ratio of opposite side and hypotenuse whereas cosine of an angle is equal to ratio of adjacent side and hypotenuse.
\[{{sin\theta = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Opposite side}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}\]
\[{{cos\theta = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}\]

In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many others. The most widely used trigonometric functions are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




