
Shown in the figure is a post office box. In order to calculate the value of external resistance, it should be connected between:
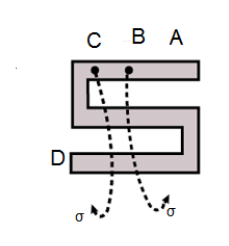
$ \left( A \right)B\,and\,C \\
\left( B \right)A\,and\,D \\
\left( C \right)C\,and\,D \\
\left( D \right)B\,and\,D \\ $

Answer
539.1k+ views
Hint : To solve this question, we are going to first consider a Wheatstone bridge around the post office box taking an external unknown resistance $ S $ , operating on the bridge and writing the conditions, we can calculate the value of the unknown resistance and figure out configuration of $ S $ .
The unknown resistance $ S $ can be calculated as:
$ S = \dfrac{P}{Q}R $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider this post office box acting as a Wheatstone bridge, with three arms $ P,Q\,and\,R $ , the fourth arm is an unknown resistance, $ S $ . This is the circuit diagram for the Wheatstone bridge configuration:
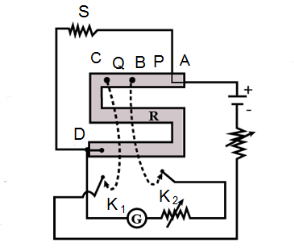
If we define the arms of the Wheatstone bridge, we see that the arms $ P\,and\,Q $ are the known as the ratio arms, while the arm with the resistance, $ R $ is the known as the Rheostat arm.
At the balance point, the condition is like that the current flowing through the Galvanometer $ \left( G \right) $ is zero, also, known as the null point where it is zero and using this balancing condition, we can easily calculate the unknown resistance $ S $ as :
$ S = \dfrac{P}{Q}R $
Hence, as we saw in this configuration that the unknown resistance, i.e., the external resistance has been connected between the points $ A\,and\,D $ , which gives us the perfect configuration of the Wheatstone bridge and also the value of the unknown resistance.
Note :
A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component. The primary benefit of the circuit is its ability to provide extremely accurate measurements. The general configuration of Wheatstone bridge has helped to determine where $ S $ is connected.
The unknown resistance $ S $ can be calculated as:
$ S = \dfrac{P}{Q}R $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider this post office box acting as a Wheatstone bridge, with three arms $ P,Q\,and\,R $ , the fourth arm is an unknown resistance, $ S $ . This is the circuit diagram for the Wheatstone bridge configuration:

If we define the arms of the Wheatstone bridge, we see that the arms $ P\,and\,Q $ are the known as the ratio arms, while the arm with the resistance, $ R $ is the known as the Rheostat arm.
At the balance point, the condition is like that the current flowing through the Galvanometer $ \left( G \right) $ is zero, also, known as the null point where it is zero and using this balancing condition, we can easily calculate the unknown resistance $ S $ as :
$ S = \dfrac{P}{Q}R $
Hence, as we saw in this configuration that the unknown resistance, i.e., the external resistance has been connected between the points $ A\,and\,D $ , which gives us the perfect configuration of the Wheatstone bridge and also the value of the unknown resistance.
Note :
A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component. The primary benefit of the circuit is its ability to provide extremely accurate measurements. The general configuration of Wheatstone bridge has helped to determine where $ S $ is connected.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




