
How can I show the R-configuration of the molecule bromochlorofluoroiodomethane?
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint :The structural isomers are the ones which differ in the structure of the molecule. These are the three carbon molecules. By drawing the structure and replacing the $ Br $ and $ Cl $ with hydrogen, we can get the structural isomers.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First, let us see what structural isomers are. The isomers are those species that contain the same molecular formula. The structural isomers are the ones which differ in the structure of the molecule. It is also called constitutional isomers as it is due to different constitutions of the carbon bonds. The structural isomers are of three different types. The chain isomers in which there is a difference in carbon chains. The other one are the position isomers in which the position of the substituted group is different.
Step1: Draw a $ C $ atom with a wedge, a dash, and two solid bonds.
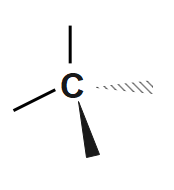
Step2: Add $ F,\text{ }Cl,\text{ }Br $ and $ I $ to the bonds in any order. We have a $ 50:50 $ chance of getting it right. Here's one possibility.
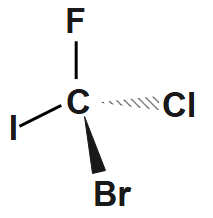
The ethers, carboxylic acids, aldehydes and ketones form functional isomers.
Step3: Assign priorities to the groups; $ I=1;\text{ }Br=2;\text{ }Cl=3;\text{ }F=4. $
Step4: Assign stereochemistry; $ F $ has the lowest priority. In this drawing, it is more convenient to view the molecule from above. Then $ I\text{ }\to \text{ }Br\to \text{ }Cl\text{ }=\text{ }1\text{ }\to \text{ }2\text{ }\to \text{ }3 $ goes in a counterclockwise direction $ \left( S \right). $
If we had gotten it wrong, we would have interchanged any two of the groups. For example, in the diagram below, interchanging the $ Cl $ and $ Br $ atoms converts the R isomer to the $ S $ isomer.
But we are viewing the molecule with our eye closest to the low-priority group. So this is really (R)-bromochlorofluoroiodomethane.
Note :
It must be noted that structural isomers have the same number of atoms of each type. There is a difference in connectivity of atoms. There is another form known as stereoisomers. These molecules have the same molecular formula but differ in arrangement of atoms in three dimensional space.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First, let us see what structural isomers are. The isomers are those species that contain the same molecular formula. The structural isomers are the ones which differ in the structure of the molecule. It is also called constitutional isomers as it is due to different constitutions of the carbon bonds. The structural isomers are of three different types. The chain isomers in which there is a difference in carbon chains. The other one are the position isomers in which the position of the substituted group is different.
Step1: Draw a $ C $ atom with a wedge, a dash, and two solid bonds.

Step2: Add $ F,\text{ }Cl,\text{ }Br $ and $ I $ to the bonds in any order. We have a $ 50:50 $ chance of getting it right. Here's one possibility.

The ethers, carboxylic acids, aldehydes and ketones form functional isomers.
Step3: Assign priorities to the groups; $ I=1;\text{ }Br=2;\text{ }Cl=3;\text{ }F=4. $
Step4: Assign stereochemistry; $ F $ has the lowest priority. In this drawing, it is more convenient to view the molecule from above. Then $ I\text{ }\to \text{ }Br\to \text{ }Cl\text{ }=\text{ }1\text{ }\to \text{ }2\text{ }\to \text{ }3 $ goes in a counterclockwise direction $ \left( S \right). $
If we had gotten it wrong, we would have interchanged any two of the groups. For example, in the diagram below, interchanging the $ Cl $ and $ Br $ atoms converts the R isomer to the $ S $ isomer.
But we are viewing the molecule with our eye closest to the low-priority group. So this is really (R)-bromochlorofluoroiodomethane.
Note :
It must be noted that structural isomers have the same number of atoms of each type. There is a difference in connectivity of atoms. There is another form known as stereoisomers. These molecules have the same molecular formula but differ in arrangement of atoms in three dimensional space.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




