
Show the mechanism of $\text{KOH}$ and alcohol for forming double bonds in an alkyl halide?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we first need to know what an alkyl halide means. After that, we will find the equilibrium of the given reaction and then find the most favourable reactant. And then, we can easily solve the question. The mechanism followed is E2 and the process is also called dehydrohalogenation.
Complete step-by-step answer:In a solution of alcoholic $\text{KOH}$, we have the equilibrium:
$\text{CH}_{3} \text{CH}_{2} \text{O}-\text{H}+\text{OH} \rightleftharpoons \text{CH}_{3} \text{CH}_{2} \text{O}^{-}+\text{H}_{2} \text{O}$
We can observe that the direction of the equilibrium in the above stated chemical equation is present towards the left hand side. So, we can say that there is very less presence of ethoxide ions.
Also, we know that ethoxide is very much strong when compared to hydroxide. So, ethoxide is a more favoured reactant.
The ethoxide attacks an $\alpha$ -hydrogen atom in an $\text{E} 2$ elimination reaction.
The chemical reaction asked in the question is represented as:
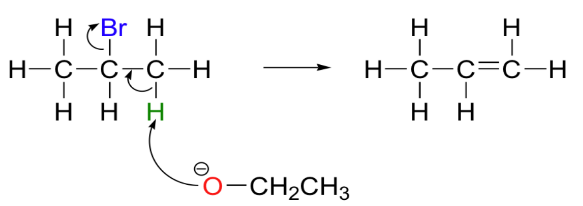
Therefore, the final products formed are ethanol, an alkene, and a halide ion.
Additional Information:
Chemical compounds that are often derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens are alkyl halides, also called haloalkanes or halogenoalkanes. We can also say that alkyl halides are a subset of the halocarbon general class.
Note:Alkyl halides or haloalkanes are formed by substituting halogen atoms for hydrogen atoms in aliphatic hydrocarbons (Fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine). Any organic precursors such as alkanes, alkenes, or alcohols and carboxylic acids can also be produced from them. Alkyl halides generally contain hydrogen atoms attached to the alkyl groups of \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridized carbon atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:In a solution of alcoholic $\text{KOH}$, we have the equilibrium:
$\text{CH}_{3} \text{CH}_{2} \text{O}-\text{H}+\text{OH} \rightleftharpoons \text{CH}_{3} \text{CH}_{2} \text{O}^{-}+\text{H}_{2} \text{O}$
We can observe that the direction of the equilibrium in the above stated chemical equation is present towards the left hand side. So, we can say that there is very less presence of ethoxide ions.
Also, we know that ethoxide is very much strong when compared to hydroxide. So, ethoxide is a more favoured reactant.
The ethoxide attacks an $\alpha$ -hydrogen atom in an $\text{E} 2$ elimination reaction.
The chemical reaction asked in the question is represented as:

Therefore, the final products formed are ethanol, an alkene, and a halide ion.
Additional Information:
Chemical compounds that are often derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens are alkyl halides, also called haloalkanes or halogenoalkanes. We can also say that alkyl halides are a subset of the halocarbon general class.
Note:Alkyl halides or haloalkanes are formed by substituting halogen atoms for hydrogen atoms in aliphatic hydrocarbons (Fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine). Any organic precursors such as alkanes, alkenes, or alcohols and carboxylic acids can also be produced from them. Alkyl halides generally contain hydrogen atoms attached to the alkyl groups of \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridized carbon atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




