
Show that the derivative of a constant function on an interval is zero.
Answer
519k+ views
Hint: In the given question, we are required to evaluate the derivative of a constant function on an interval. So, we have to show that differentiation of a constant function on an interval yields zero. Now, we first assume a constant function and then try to find its derivative using the basic definition of derivative. Derivative of a function gives the rate of change of that particular function.
Complete step by step answer:
Differentiation provides us with the rate of change of a variable with respect to some other variable. Derivative of a function at a point gives the instantaneous slope of the function at that particular point. The slope of function describes the steepness of a straight line. Slope is also denoted by the symbol ‘$m$’.
Now, we know that a constant function always gives the same output for every input value of a variable. So, there is no change in the slope of a constant function. Hence, the derivative of a constant function on an interval is zero. For example: Let $f\left( x \right) = 5$. Then, as we can see in the graph of the function, for every real value of x, the value of the function remains $5$.
Now, we see that the slope of the constant function $f\left( x \right) = 5$ remains the same throughout the real number line.
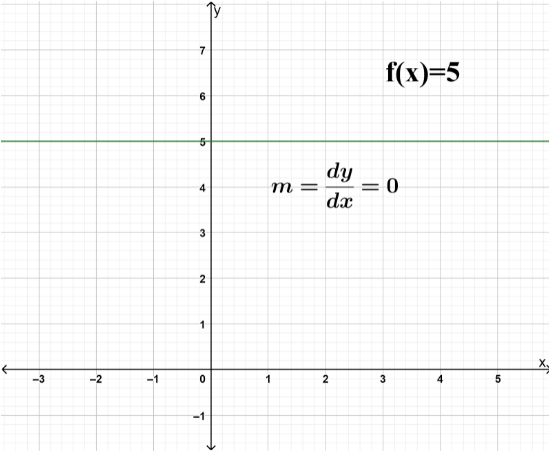
Now, we know that the derivative of a function represents the slope of the function at a particular point. So, the derivative of the constant function over an interval is zero.
Note:We must know the basics of differentiation and limits in order to solve the given question. We can also calculate the derivative of a constant function by using the power rule of differentiation $\dfrac{{d\left( {{x^n}} \right)}}{{dx}} = n{x^{\left( {n - 1} \right)}}$. We should always remember the result of this problem as it can be used in many other complex problems directly.
Complete step by step answer:
Differentiation provides us with the rate of change of a variable with respect to some other variable. Derivative of a function at a point gives the instantaneous slope of the function at that particular point. The slope of function describes the steepness of a straight line. Slope is also denoted by the symbol ‘$m$’.
Now, we know that a constant function always gives the same output for every input value of a variable. So, there is no change in the slope of a constant function. Hence, the derivative of a constant function on an interval is zero. For example: Let $f\left( x \right) = 5$. Then, as we can see in the graph of the function, for every real value of x, the value of the function remains $5$.
Now, we see that the slope of the constant function $f\left( x \right) = 5$ remains the same throughout the real number line.

Now, we know that the derivative of a function represents the slope of the function at a particular point. So, the derivative of the constant function over an interval is zero.
Note:We must know the basics of differentiation and limits in order to solve the given question. We can also calculate the derivative of a constant function by using the power rule of differentiation $\dfrac{{d\left( {{x^n}} \right)}}{{dx}} = n{x^{\left( {n - 1} \right)}}$. We should always remember the result of this problem as it can be used in many other complex problems directly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Prove that a parallelogram circumscribing a circle-class-12-maths-CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




