
What is the shape of d-orbital?
A.Spherical
B.Dumb bell
C.Double-dumb bell
D.No definite shape
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is defined as a mathematical function which describes the location and wave-like behaviour of an electron.
These mathematical functions can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in a particular region around the nucleus.
There are four types of atomic orbitals: s (sharp), p (principle), d (diffuse) and f (fundamental).
Complete step by step answer:
Now let us look into the d-orbitals:
The mathematical equation that is used to describe that particular orbital defines the shape of that orbital. d-orbitals have a shape called double dumb bell, as shown in the following diagram:
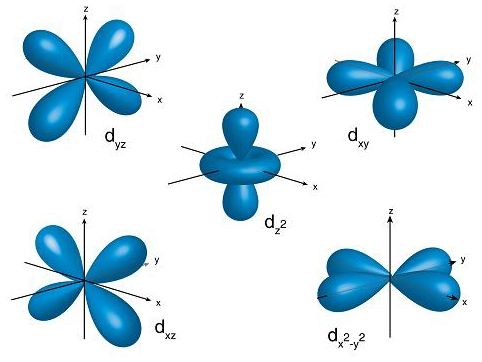
There are five types of d-orbitals namely, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xy}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{yz}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xz}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ and ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$. Each of these have a capacity of 2 electrons each of opposite spin. Thus, d-orbital has a capacity of 10 electrons in total.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Other orbitals are:
s-orbital: it is spherical and has a capacity of 2 electrons.
p-orbital: there are three types of p-orbitals, namely ${{\text{p}}_{\text{x}}}$, ${{\text{p}}_{\text{y}}}$ and ${{\text{p}}_{\text{z}}}$. Each of these has a capacity of 2 electrons and hence p-orbital has a capacity of 6 electrons in total. The shape of p-orbital is called a dumb bell.
d-orbital: discussed above
f-orbital: there are 7 f-orbitals, each having a capacity of 2 electrons so f-orbital has a capacity of 14 electrons in total. The shape of the f-orbital is fairly complicated and very hard to understand.
Please remember that orbitals are a mathematical expression. And are imaginary surfaces where the probability of finding an electron is nearly maximum.
These mathematical functions can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in a particular region around the nucleus.
There are four types of atomic orbitals: s (sharp), p (principle), d (diffuse) and f (fundamental).
Complete step by step answer:
Now let us look into the d-orbitals:
The mathematical equation that is used to describe that particular orbital defines the shape of that orbital. d-orbitals have a shape called double dumb bell, as shown in the following diagram:

There are five types of d-orbitals namely, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xy}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{yz}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xz}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ and ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$. Each of these have a capacity of 2 electrons each of opposite spin. Thus, d-orbital has a capacity of 10 electrons in total.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Other orbitals are:
s-orbital: it is spherical and has a capacity of 2 electrons.
p-orbital: there are three types of p-orbitals, namely ${{\text{p}}_{\text{x}}}$, ${{\text{p}}_{\text{y}}}$ and ${{\text{p}}_{\text{z}}}$. Each of these has a capacity of 2 electrons and hence p-orbital has a capacity of 6 electrons in total. The shape of p-orbital is called a dumb bell.
d-orbital: discussed above
f-orbital: there are 7 f-orbitals, each having a capacity of 2 electrons so f-orbital has a capacity of 14 electrons in total. The shape of the f-orbital is fairly complicated and very hard to understand.
Please remember that orbitals are a mathematical expression. And are imaginary surfaces where the probability of finding an electron is nearly maximum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




