
Seven resistors are connected as shown in the diagram: The equivalent resistance in ohms of this network between $A$ and $B$ is:
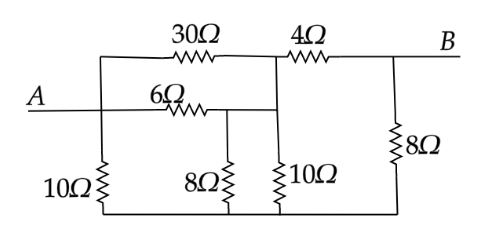
A. $6\Omega $
B. $8\Omega $
C. $12\Omega $
D. $20\Omega $

Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: : Identify the parallel and series connection in the given circuit. First solve for the resistors in parallel connection, then the circuit will become a Wheatstone bridge. Check the condition for a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
Formula used:
Resistors connected in series, equivalence resistance ${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ...$
Resistors connected in parallel, equivalence resistance $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ...$
Complete step by step answer:
First name the resistances and redraw the circuit diagram.
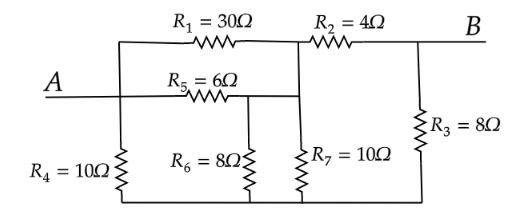
In the above circuit, we have to find the equivalent resistance between the terminal A and B.The resistors ${R_6}$ and ${R_7}$ are connected in parallel.Equivalence of ${R_6}$ and ${R_7}$ is given as
${R_{67}} = \dfrac{{{R_6} \cdot {R_7}}}{{{R_6} + {R_7}}}$
Substitute the values of ${R_6}$ and ${R_7}$ in the above formula.
$ \Rightarrow {R_{67}} = \dfrac{{8 \times 10}}{{8 + 10}}\Omega $
$ \Rightarrow {R_{67}} = \dfrac{{40}}{9}\Omega $
The resistors ${R_1}$ and ${R_5}$ are connected in parallel.
The equivalent resistor of ${R_1}$ and ${R_5}$ is given as
${R_{15}} = \dfrac{{{R_1} \cdot {R_5}}}{{{R_1} + {R_5}}}$
Substitute the values of ${R_1}$ and ${R_5}$ in the above formula.
$ \Rightarrow {R_{15}} = \dfrac{{30 \times 6}}{{30 + 6}}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow{R_{15}} = 5\Omega $
Now the equivalent circuit of above the circuit is as follows
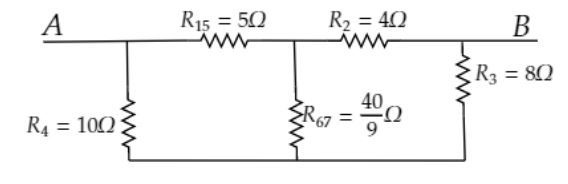
The equivalent circuit of the given circuit is a Wheatstone bridge circuit.
The Wheatstone bridge is balanced because it satisfies the condition $\dfrac{{{R_{15}}}}{{{R_4}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_3}}}$
Therefore, no current flows through the resistor ${R_{67}}$. Remove the ${R_{67}}$ from the Wheatstone bridge. The final circuit is as follows.
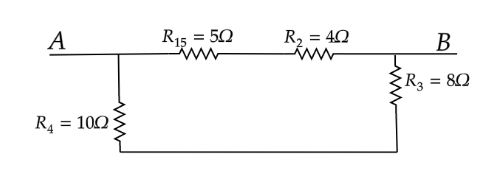
${R_{15}}$ and ${R_2}$ are in series.
The equivalent resistance of ${R_{15}}$ and ${R_2}$ is ${R_{152}} = {R_{15}} + {R_2}$
$ \Rightarrow {R_{152}} = 5\Omega + 4\Omega = 9\Omega $
${R_4}$ and ${R_3}$ are in series connection.
The equivalent resistance of ${R_4}$ and ${R_3}$ is ${R_{45}} = {R_4} + {R_5}$
$ \Rightarrow {R_{45}} = 10\Omega + 8\Omega = 18\Omega $
Now ${R_{152}}$ and ${R_{45}}$ are in parallel connection.
The equivalent resistance of ${R_{152}}$ and ${R_{45}}$ is \[{R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{{R_{152}} \cdot {R_{45}}}}{{{R_{152}} + {R_{45}}}}\].
Substitute the values of ${R_{152}}$ and ${R_{45}}$ in the above formula.
$ \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{9 \times 18}}{{9 + 18}}\Omega $
$\therefore {R_{eq}} = 6\Omega $
The equivalent resistance of the given circuit is $6\Omega $.
Hence the correct option is A.
Note: Alternative method:Alternatively, we can solve the circuit by drawing an equivalent circuit of the given circuit with some extra consideration as follows.
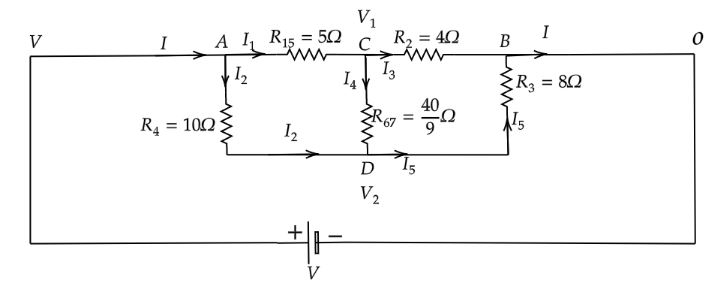
To solve the above equivalence circuit, Let the current $I$ enter junction A and leave junction B. A battery of $V$ voltage is connected across the terminals A and B. For simplification let terminal A is at $V$ voltage and terminal B is at $0$ voltage. Let the junctions C and D are at ${V_1}$ voltage and ${V_2}$ voltage respectively. Now apply Kirchhoff's current law at the junction A in the above equivalence circuit.
$I = {I_1} + {I_2}$
Apply Kirchhoff's current law at the junction C in the above equivalence circuit.
${I_1} = {I_3} + {I_4}$
From the above circuit diagram, ${I_1} = \dfrac{{V - {V_1}}}{5}$
${I_3} = \dfrac{{{V_1} - 0}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow {I_3} = \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow {I_4} = \dfrac{{{V_1} - {V_2}}}{{\dfrac{{40}}{9}}}$
$\Rightarrow {I_4} = \dfrac{9}{{40}}\left( {{V_1} - {V_2}} \right)$
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{{V - {V_1}}}{5} = \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{4} + \dfrac{9}{{40}}\left( {{V_1} - {V_2}} \right)\]
On simplification
$ \Rightarrow 27{V_1} - 9{V_2} = 8V$ …… (1)
Now apply Kirchhoff's current law at junction D in the above equivalence circuit.
${I_2} + {I_4} = {I_5}$
From the above circuit diagram, ${I_2} = \dfrac{{V - {V_2}}}{{10}}$
${I_5} = \dfrac{{{V_2} - 0}}{8}$
$\Rightarrow {I_5} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{8}$
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{{V - {V_2}}}{{10}} + \dfrac{9}{{40}}\left( {{V_1} - {V_2}} \right) = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{8}\]
On simplification
$ \Rightarrow - 9{V_1} + 18{V_2} = 4V$ …… (2)
Now solve the two equations (1) and (2) and find the values of ${V_1}$ and ${V_2}$ in terms of $V$. We got,
${V_1} = \dfrac{{4V}}{9}$,
$\Rightarrow {V_2} = \dfrac{{4V}}{9}$
Now calculate the value of ${I_1} = \dfrac{{V - {V_1}}}{5}$
${I_1} = \dfrac{{V - \dfrac{{4V}}{9}}}{5}$
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{V}{9}$
And calculate the value of ${I_2} = \dfrac{{V - {V_2}}}{{10}}$
${I_2} = \dfrac{{V - \dfrac{{4V}}{9}}}{{10}}$
$\Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{V}{{18}}$
Now we have $I = {I_1} + {I_2}$
Substitute the values of ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ in the above formula for $I$.
$I = \dfrac{V}{9} + \dfrac{V}{{18}}$
Further calculating
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{6}$
The equivalent resistance of the above equivalence circuit between the two terminals A and B is given by
${R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{{V_B} - {V_A}}}{I}$
Substitute all the required values in the above formula
${R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{V - 0}}{{\dfrac{V}{6}}}$
On further simplification
${R_{eq}} = 6\Omega $
Hence the correct option is (A).
Formula used:
Resistors connected in series, equivalence resistance ${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ...$
Resistors connected in parallel, equivalence resistance $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ...$
Complete step by step answer:
First name the resistances and redraw the circuit diagram.

In the above circuit, we have to find the equivalent resistance between the terminal A and B.The resistors ${R_6}$ and ${R_7}$ are connected in parallel.Equivalence of ${R_6}$ and ${R_7}$ is given as
${R_{67}} = \dfrac{{{R_6} \cdot {R_7}}}{{{R_6} + {R_7}}}$
Substitute the values of ${R_6}$ and ${R_7}$ in the above formula.
$ \Rightarrow {R_{67}} = \dfrac{{8 \times 10}}{{8 + 10}}\Omega $
$ \Rightarrow {R_{67}} = \dfrac{{40}}{9}\Omega $
The resistors ${R_1}$ and ${R_5}$ are connected in parallel.
The equivalent resistor of ${R_1}$ and ${R_5}$ is given as
${R_{15}} = \dfrac{{{R_1} \cdot {R_5}}}{{{R_1} + {R_5}}}$
Substitute the values of ${R_1}$ and ${R_5}$ in the above formula.
$ \Rightarrow {R_{15}} = \dfrac{{30 \times 6}}{{30 + 6}}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow{R_{15}} = 5\Omega $
Now the equivalent circuit of above the circuit is as follows

The equivalent circuit of the given circuit is a Wheatstone bridge circuit.
The Wheatstone bridge is balanced because it satisfies the condition $\dfrac{{{R_{15}}}}{{{R_4}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_3}}}$
Therefore, no current flows through the resistor ${R_{67}}$. Remove the ${R_{67}}$ from the Wheatstone bridge. The final circuit is as follows.

${R_{15}}$ and ${R_2}$ are in series.
The equivalent resistance of ${R_{15}}$ and ${R_2}$ is ${R_{152}} = {R_{15}} + {R_2}$
$ \Rightarrow {R_{152}} = 5\Omega + 4\Omega = 9\Omega $
${R_4}$ and ${R_3}$ are in series connection.
The equivalent resistance of ${R_4}$ and ${R_3}$ is ${R_{45}} = {R_4} + {R_5}$
$ \Rightarrow {R_{45}} = 10\Omega + 8\Omega = 18\Omega $
Now ${R_{152}}$ and ${R_{45}}$ are in parallel connection.
The equivalent resistance of ${R_{152}}$ and ${R_{45}}$ is \[{R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{{R_{152}} \cdot {R_{45}}}}{{{R_{152}} + {R_{45}}}}\].
Substitute the values of ${R_{152}}$ and ${R_{45}}$ in the above formula.
$ \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{9 \times 18}}{{9 + 18}}\Omega $
$\therefore {R_{eq}} = 6\Omega $
The equivalent resistance of the given circuit is $6\Omega $.
Hence the correct option is A.
Note: Alternative method:Alternatively, we can solve the circuit by drawing an equivalent circuit of the given circuit with some extra consideration as follows.

To solve the above equivalence circuit, Let the current $I$ enter junction A and leave junction B. A battery of $V$ voltage is connected across the terminals A and B. For simplification let terminal A is at $V$ voltage and terminal B is at $0$ voltage. Let the junctions C and D are at ${V_1}$ voltage and ${V_2}$ voltage respectively. Now apply Kirchhoff's current law at the junction A in the above equivalence circuit.
$I = {I_1} + {I_2}$
Apply Kirchhoff's current law at the junction C in the above equivalence circuit.
${I_1} = {I_3} + {I_4}$
From the above circuit diagram, ${I_1} = \dfrac{{V - {V_1}}}{5}$
${I_3} = \dfrac{{{V_1} - 0}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow {I_3} = \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow {I_4} = \dfrac{{{V_1} - {V_2}}}{{\dfrac{{40}}{9}}}$
$\Rightarrow {I_4} = \dfrac{9}{{40}}\left( {{V_1} - {V_2}} \right)$
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{{V - {V_1}}}{5} = \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{4} + \dfrac{9}{{40}}\left( {{V_1} - {V_2}} \right)\]
On simplification
$ \Rightarrow 27{V_1} - 9{V_2} = 8V$ …… (1)
Now apply Kirchhoff's current law at junction D in the above equivalence circuit.
${I_2} + {I_4} = {I_5}$
From the above circuit diagram, ${I_2} = \dfrac{{V - {V_2}}}{{10}}$
${I_5} = \dfrac{{{V_2} - 0}}{8}$
$\Rightarrow {I_5} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{8}$
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{{V - {V_2}}}{{10}} + \dfrac{9}{{40}}\left( {{V_1} - {V_2}} \right) = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{8}\]
On simplification
$ \Rightarrow - 9{V_1} + 18{V_2} = 4V$ …… (2)
Now solve the two equations (1) and (2) and find the values of ${V_1}$ and ${V_2}$ in terms of $V$. We got,
${V_1} = \dfrac{{4V}}{9}$,
$\Rightarrow {V_2} = \dfrac{{4V}}{9}$
Now calculate the value of ${I_1} = \dfrac{{V - {V_1}}}{5}$
${I_1} = \dfrac{{V - \dfrac{{4V}}{9}}}{5}$
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{V}{9}$
And calculate the value of ${I_2} = \dfrac{{V - {V_2}}}{{10}}$
${I_2} = \dfrac{{V - \dfrac{{4V}}{9}}}{{10}}$
$\Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{V}{{18}}$
Now we have $I = {I_1} + {I_2}$
Substitute the values of ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ in the above formula for $I$.
$I = \dfrac{V}{9} + \dfrac{V}{{18}}$
Further calculating
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{6}$
The equivalent resistance of the above equivalence circuit between the two terminals A and B is given by
${R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{{V_B} - {V_A}}}{I}$
Substitute all the required values in the above formula
${R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{V - 0}}{{\dfrac{V}{6}}}$
On further simplification
${R_{eq}} = 6\Omega $
Hence the correct option is (A).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




