
Select the secondary consumer.
a. A fish that feeds on algae.
b. A hawk that feeds on a mouse that feeds on an insect.
c. A plant that is parasitic to another plant.
d. A lion that eats a gazelle that feeds on grass.
e. A beetle that feeds on nectar.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Secondary consumers are the carnivores that depend upon the herbivores for their nutrition. In the trophic level, decomposers and detritivores are placed along the side of the pyramids because they are responsible for the breakdown of dead organisms at all trophic levels.
Complete answer:
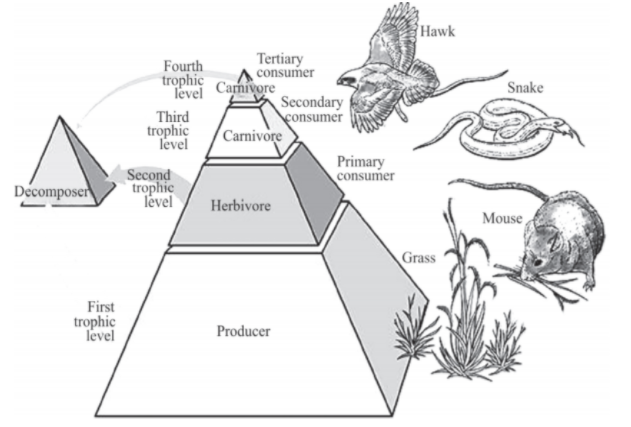
The food chain is a sequential arrangement of organisms of the ecosystem in such a way that food and its contained energy passes from one trophic level to the other.
Trophic level can be defined as any food level of an ecosystem or a food chain.
There are mainly four trophic levels in a food chain which are as follows-
- Producers (T1): It includes the green plants which produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
- Primary consumers (T2): These are the herbivores which depend directly upon the green plants or producers. For example- mouse, rabbit, cow, etc.
- Secondary consumers (T3): These are the carnivores which depend upon the herbivores. For example- snake, fox, etc.
- Tertiary consumers (T4): It includes the organisms which depend upon the carnivores for their food. For example- tigers, lions, etc.
According to the question:
- A fish that feeds on algae (producer) is a primary consumer.
- A hawk that feeds on a mouse (secondary consumer, as it feeds on an insect) is a tertiary consumer.
- A plant that is parasitic to another plant (producer) is a primary consumer.
- A lion that eats a gazelle (primary consumer, as it feeds on grass) is a secondary consumer.
- A beetle that feeds on nectar (producer) is a primary consumer.
Hence, The correct answer is option (D).
Note: Nectar is a sugar rich secretion of the plants, which attracts the birds or insects for the purpose of pollination.
All the green plants are considered as the producers as they are autotrophic in nature.
During the transfer of food from one trophic level to the next, only 10% energy is stored in the flesh, remaining energy is lost during metabolic processes.
Complete answer:
The food chain is a sequential arrangement of organisms of the ecosystem in such a way that food and its contained energy passes from one trophic level to the other.
Trophic level can be defined as any food level of an ecosystem or a food chain.
There are mainly four trophic levels in a food chain which are as follows-
- Producers (T1): It includes the green plants which produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
- Primary consumers (T2): These are the herbivores which depend directly upon the green plants or producers. For example- mouse, rabbit, cow, etc.
- Secondary consumers (T3): These are the carnivores which depend upon the herbivores. For example- snake, fox, etc.
- Tertiary consumers (T4): It includes the organisms which depend upon the carnivores for their food. For example- tigers, lions, etc.

According to the question:
- A fish that feeds on algae (producer) is a primary consumer.
- A hawk that feeds on a mouse (secondary consumer, as it feeds on an insect) is a tertiary consumer.
- A plant that is parasitic to another plant (producer) is a primary consumer.
- A lion that eats a gazelle (primary consumer, as it feeds on grass) is a secondary consumer.
- A beetle that feeds on nectar (producer) is a primary consumer.
Hence, The correct answer is option (D).
Note: Nectar is a sugar rich secretion of the plants, which attracts the birds or insects for the purpose of pollination.
All the green plants are considered as the producers as they are autotrophic in nature.
During the transfer of food from one trophic level to the next, only 10% energy is stored in the flesh, remaining energy is lost during metabolic processes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




