
Seed coat develops from
A. Nucleus
B. Radicle
C. Plumule
D. Integument
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: Seeds are the result of reproduction in plants. A seed in total is an embryonic plant that is enclosed in a protective layer called the seed coat. Tegmen and testa of a mature ovule form the seed coat.
Complete answer: A seed is the result of sexual reproduction as it develops from the matured ovary. The seed consists of the embryonic plant which stays inside it until favourable conditions arrive for its germination. During germination, the first structure to develop is called the radicle. Radicle is the baby root. The radicle absorbs nutrients and water from the soil and stimulates plumule growth. The plumule is the baby shoot that rises above the ground level. The nucleus is the central part of plant cells that encloses the genetic information for the growing seed. All of the contents of the seed are enclosed in the protective hard covering of the seed called the seed coat. The seed coat arises from the tegmen and testa of integuments of the maturing ovary. The integument reduces in size and thickens to form a protective covering. The inner integument is called tegmen and the outermost seed covering is called testa. In some plants, the seed coat fuses with seed and forms a tissue called the pericarp. This can be seen in tomatoes. The pericarp forms the fleshy and juicy eatable tissue. Some of the plants have their seed coats modified to have certain markings or tufts of hair.
Therefore, the right answer is option D.
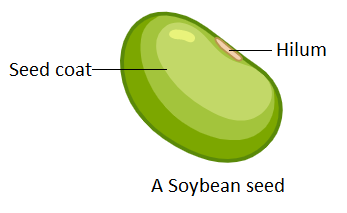
Note: In some seeds, over their seed coats a certain scar or mark can be seen called the hilum. The hilum denotes the prior attachment of the seed to the ovary wall. In a bean seed, a hilum can be commonly seen as a dark spot and is called an eye. In starch grains, the hilum may be the nucleus of the seed.
Complete answer: A seed is the result of sexual reproduction as it develops from the matured ovary. The seed consists of the embryonic plant which stays inside it until favourable conditions arrive for its germination. During germination, the first structure to develop is called the radicle. Radicle is the baby root. The radicle absorbs nutrients and water from the soil and stimulates plumule growth. The plumule is the baby shoot that rises above the ground level. The nucleus is the central part of plant cells that encloses the genetic information for the growing seed. All of the contents of the seed are enclosed in the protective hard covering of the seed called the seed coat. The seed coat arises from the tegmen and testa of integuments of the maturing ovary. The integument reduces in size and thickens to form a protective covering. The inner integument is called tegmen and the outermost seed covering is called testa. In some plants, the seed coat fuses with seed and forms a tissue called the pericarp. This can be seen in tomatoes. The pericarp forms the fleshy and juicy eatable tissue. Some of the plants have their seed coats modified to have certain markings or tufts of hair.
Therefore, the right answer is option D.

Note: In some seeds, over their seed coats a certain scar or mark can be seen called the hilum. The hilum denotes the prior attachment of the seed to the ovary wall. In a bean seed, a hilum can be commonly seen as a dark spot and is called an eye. In starch grains, the hilum may be the nucleus of the seed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




