
Roshani saw an angle on the top of a tree at an angle of elevation of \[{{61}^{\circ }}\], while she was standing at the door of her house. She went on the terrace of the house so that she could see it clearly. The terrace was at a height of 4 cm. While observing the eagle from the angle of elevation of elevation was \[{{52}^{\circ }}\]. At what height from the ground was the eagle.
Answer
612.6k+ views
Hint: From the given figure consider \[\Delta PRS\] and \[\Delta QRT\]. Take the tangent function from these triangles and frame 2 equations. Equate them together to get the value of y. Thus find the height of eagle from ground i.e. RS.
Complete step-by-step answer:
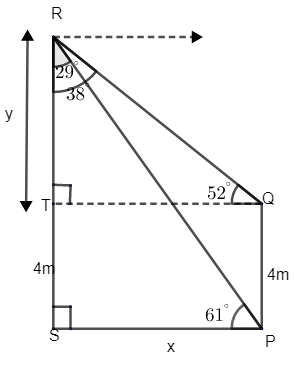
It is said that Roshni saw an angle on top of a tree from the door of her house. Let us consider PQ as her house. The terrace of the house is at point Q. Thus we can say that the height of the building is 4m.
Now let us consider the horizontal distance between the house and tree as x m. Let us consider RS as the tree, from the figure.
Hence from the figure we can say that RT is the height of the eagle from top of terrace. Let us take it as ‘y’.
From the figure we can say that, \[\angle RPS={{61}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle RQT={{52}^{\circ }}\].
First let us consider, \[\Delta RPS\], which is right angled at S.
\[\tan {{61}^{\circ }}\] = opposite side / adjacent side = \[\dfrac{RS}{PS}\].
From trigonometric table we know that, \[\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=1.73\], thus we can take, \[\tan {{61}^{\circ }}=1.8\].
And from figure, RS = RT + TS.
From the figure we can say that PQ is parallel to RS. Thus we can say that PQ = TS = 4cm and PS = x m.
Hence, RS = RT + TS = y + 4.
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore \tan {{61}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{RS}{PS} \\
& 1.8=\dfrac{y+4}{x} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, we have, \[x=\dfrac{y+4}{1.8}-(1)\].
Now let us consider, \[\Delta RQT\], which is right angled at T.
\[\tan {{52}^{\circ }}\] = opposite side / adjacent side = \[\dfrac{RT}{QT}\].
From figure, PS is parallel to QT, hence PS = QT = x.
From the trigonometry table we know that, \[\tan {{52}^{\circ }}=1.28\].
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore \tan {{52}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{RT}{QT} \\
& 1.28=\dfrac{y}{x}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{y}{1.28}-(2) \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us equate equation (1) and (2), we get,
\[\dfrac{y+4}{1.8}=\dfrac{y}{1.28}-(2)\]
Now, applying cross multiplication property, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 1.28\left( y+4 \right)=1.8y \\
& 1.28y+5.12=1.8y \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow 1.8y-1.28y=5.12\]
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore 0.52y=5.12 \\
& y=\dfrac{5.12}{0.52}=9.85m \\
\end{align}\]
Hence we got the length of RT = y = 9.85 m.
The height of the eagle from the ground is RS. From figure we can say that,
RS = TS + RT
RS = 4 + y = 4 + 9.85 = 13.85m
Hence, we got, RS = 13.85m.
Thus the eagle is at a height of 13.85m from the ground.
Note: The values of \[\tan {{61}^{\circ }}\] and \[\tan {{52}^{\circ }}\], will be provided in the question, which you can use directly. But if you try to calculate it using a trigonometric table, you might not get the desired value.

Complete step-by-step answer:
It is said that Roshni saw an angle on top of a tree from the door of her house. Let us consider PQ as her house. The terrace of the house is at point Q. Thus we can say that the height of the building is 4m.
Now let us consider the horizontal distance between the house and tree as x m. Let us consider RS as the tree, from the figure.
Hence from the figure we can say that RT is the height of the eagle from top of terrace. Let us take it as ‘y’.
From the figure we can say that, \[\angle RPS={{61}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle RQT={{52}^{\circ }}\].
First let us consider, \[\Delta RPS\], which is right angled at S.
\[\tan {{61}^{\circ }}\] = opposite side / adjacent side = \[\dfrac{RS}{PS}\].
From trigonometric table we know that, \[\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=1.73\], thus we can take, \[\tan {{61}^{\circ }}=1.8\].
And from figure, RS = RT + TS.
From the figure we can say that PQ is parallel to RS. Thus we can say that PQ = TS = 4cm and PS = x m.
Hence, RS = RT + TS = y + 4.
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore \tan {{61}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{RS}{PS} \\
& 1.8=\dfrac{y+4}{x} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, we have, \[x=\dfrac{y+4}{1.8}-(1)\].
Now let us consider, \[\Delta RQT\], which is right angled at T.
\[\tan {{52}^{\circ }}\] = opposite side / adjacent side = \[\dfrac{RT}{QT}\].
From figure, PS is parallel to QT, hence PS = QT = x.
From the trigonometry table we know that, \[\tan {{52}^{\circ }}=1.28\].
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore \tan {{52}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{RT}{QT} \\
& 1.28=\dfrac{y}{x}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{y}{1.28}-(2) \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us equate equation (1) and (2), we get,
\[\dfrac{y+4}{1.8}=\dfrac{y}{1.28}-(2)\]
Now, applying cross multiplication property, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 1.28\left( y+4 \right)=1.8y \\
& 1.28y+5.12=1.8y \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow 1.8y-1.28y=5.12\]
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore 0.52y=5.12 \\
& y=\dfrac{5.12}{0.52}=9.85m \\
\end{align}\]
Hence we got the length of RT = y = 9.85 m.
The height of the eagle from the ground is RS. From figure we can say that,
RS = TS + RT
RS = 4 + y = 4 + 9.85 = 13.85m
Hence, we got, RS = 13.85m.
Thus the eagle is at a height of 13.85m from the ground.
Note: The values of \[\tan {{61}^{\circ }}\] and \[\tan {{52}^{\circ }}\], will be provided in the question, which you can use directly. But if you try to calculate it using a trigonometric table, you might not get the desired value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




