
What is the retention of configuration?
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Retention and inversion are opposite to each other due to their different properties. Retention of configuration can be seen in ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ whereas inverse of the configuration can be seen in ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction.
Complete Solution :
- In the given question we have to explain the term retention of configuration.
- So, firstly we should know what absolute configuration and relative configuration are. In the absolute configuration, the atom does not depend on another atom or molecule.
- Whereas in relative configuration the position of an atom depends or is told concerning the position of another atom or molecule.
- So, in the retention of configuration, both the absolute and relative configuration do not change their structure and the position of the atom after the completion of the reaction.
- Or we can say that the R position remains R and S position remains S after the reaction, they do not convert into each other.
- In R configuration if the priority groups are present in the clockwise direction then are assigned as R configuration whereas if the priority groups are present in the clockwise direction then are assigned as S configuration.
- For example, the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reactions occur through the retention of configuration.
An example is when 2-iodo - 2 phenyl butane i.e. S configuration is hydrolysed by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction through the retention of the configuration then they form one S and one R configuration.
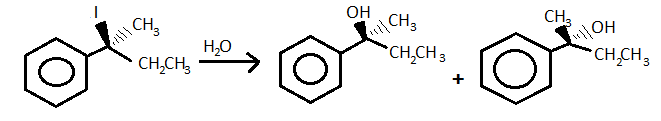
Note: Inverse of the configuration is opposite to retention because in inverse either the absolute or relative atom or molecule changes its position from R to S or from S to R configuration. Also, the inverse of the configuration can be seen in ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction.
Complete Solution :
- In the given question we have to explain the term retention of configuration.
- So, firstly we should know what absolute configuration and relative configuration are. In the absolute configuration, the atom does not depend on another atom or molecule.
- Whereas in relative configuration the position of an atom depends or is told concerning the position of another atom or molecule.
- So, in the retention of configuration, both the absolute and relative configuration do not change their structure and the position of the atom after the completion of the reaction.
- Or we can say that the R position remains R and S position remains S after the reaction, they do not convert into each other.
- In R configuration if the priority groups are present in the clockwise direction then are assigned as R configuration whereas if the priority groups are present in the clockwise direction then are assigned as S configuration.
- For example, the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reactions occur through the retention of configuration.
An example is when 2-iodo - 2 phenyl butane i.e. S configuration is hydrolysed by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction through the retention of the configuration then they form one S and one R configuration.

Note: Inverse of the configuration is opposite to retention because in inverse either the absolute or relative atom or molecule changes its position from R to S or from S to R configuration. Also, the inverse of the configuration can be seen in ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




