
What is the relation between
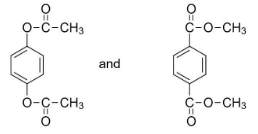
(A) Identical
(B) Position Isomer
(C) Functional Isomer
(D) Metamer

Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: Isomers are those molecules which have the same molecular formula, i.e., the number of atoms in the molecules are the same, but different structures. In the question, both the given molecules have the same molecular formula, ${C_6}{H_4}{{(COOC{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$. Hence these compounds are isomers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have already stated that the given molecules are isomers. Hence, we can eliminate the inference that the two molecules are identical in nature.
Now, position isomers can be defined as molecules which have the same molecular formula, and even the carbon skeleton or carbon chain structure of these molecules are the same, but the position of the functional groups differ in these molecules.
For example, propanol $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ has two isomers, propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol and the position of alcohol functional group (-OH) is different in both the molecules.
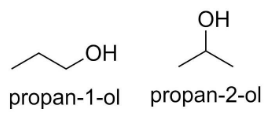
Since in the given question, the functional groups in both the molecules are attached at the same carbon at (1, 4) position, they are not positional isomers.
Functional isomers are molecules which have the same molecular formula, but they differ in their functional groups.
One of the most prominent examples of functional isomers are any molecule having aldehyde and ketone functional groups. Ketone and aldehyde functional groups both have the same molecular formula (=CO) but differ in the way they are attached to the carbon chain.
For example, in propan-2-one, the (=CO) is in the middle of the chain, whereas in acetaldehyde, the (=CO) is at the end of the group.
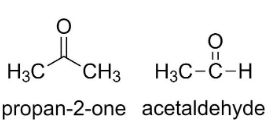
Since in the given question, both the molecules have the same functional group, $(-COOC{{H}_{3}})$, they are not functional isomers.
Metamerism is a phenomenon in organic chemistry in which different molecules or compounds have the same molecular formula, but have different numbers of carbon atoms or alkyl groups on each side of the functional group. These molecules are known as metamers. This type of isomerism is very rare and is usually found in molecules containing a divalent atom like oxygen, O or sulfur, S.
In the given question, the molecules have different numbers of carbon atoms on either side of the (-O-) functional group.
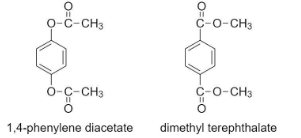
In 1,4-phenylene diacetate, the (-O-) functional group has 2 carbon atoms on its side, whereas in dimethyl terephthalate, the (-O-) functional group only has 1 carbon atom on its side.
Hence the relation between the two given compounds is option (D) Metamers.
Note: It should be noted that some molecules can be both position isomers and metamers simultaneously. For example, propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol are positional isomers as well as metamers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have already stated that the given molecules are isomers. Hence, we can eliminate the inference that the two molecules are identical in nature.
Now, position isomers can be defined as molecules which have the same molecular formula, and even the carbon skeleton or carbon chain structure of these molecules are the same, but the position of the functional groups differ in these molecules.
For example, propanol $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ has two isomers, propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol and the position of alcohol functional group (-OH) is different in both the molecules.

Since in the given question, the functional groups in both the molecules are attached at the same carbon at (1, 4) position, they are not positional isomers.
Functional isomers are molecules which have the same molecular formula, but they differ in their functional groups.
One of the most prominent examples of functional isomers are any molecule having aldehyde and ketone functional groups. Ketone and aldehyde functional groups both have the same molecular formula (=CO) but differ in the way they are attached to the carbon chain.
For example, in propan-2-one, the (=CO) is in the middle of the chain, whereas in acetaldehyde, the (=CO) is at the end of the group.

Since in the given question, both the molecules have the same functional group, $(-COOC{{H}_{3}})$, they are not functional isomers.
Metamerism is a phenomenon in organic chemistry in which different molecules or compounds have the same molecular formula, but have different numbers of carbon atoms or alkyl groups on each side of the functional group. These molecules are known as metamers. This type of isomerism is very rare and is usually found in molecules containing a divalent atom like oxygen, O or sulfur, S.
In the given question, the molecules have different numbers of carbon atoms on either side of the (-O-) functional group.

In 1,4-phenylene diacetate, the (-O-) functional group has 2 carbon atoms on its side, whereas in dimethyl terephthalate, the (-O-) functional group only has 1 carbon atom on its side.
Hence the relation between the two given compounds is option (D) Metamers.
Note: It should be noted that some molecules can be both position isomers and metamers simultaneously. For example, propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol are positional isomers as well as metamers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




