
What is refraction of light? Draw the diagram of refraction of light in a glass slab. Write the laws of refraction?
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: When we stand at the edge of a swimming pool and observe the depth of the pool, it is always different from the real depth due to bending of light from the bottom of the pool at the boundary between air and water. This is primarily due to refraction of light. Use this concept to explain the refraction of light.
Complete answer:
Refraction of light: When the light travels from one medium to another medium, it bends towards or away from the normal depending upon the refractive index of the second medium. This bending of light due to difference in the refractive index, we call it refraction of light.
When the light ray travels from a rare medium to a denser medium, we can see it bends towards the normal due to higher refractive index of the denser medium relative to the rare medium. Also, when the light ray travels from the denser medium to the rare medium, it bends away from the normal.
We assume the light ray travels from the air incident on the glass slab at an angle \[{\theta _i}\] with the normal (imaginary line perpendicular to the surface of the glass slab).
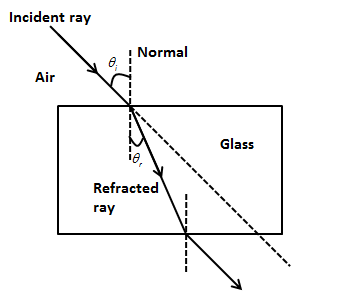
In the above figure, \[{\theta _i}\] is the incident angle and \[{\theta _r}\] is the refracted angle.
We can observe that since the refractive index of the glass is greater than the refractive index of the air, the refracted ray is bent towards the normal.
We will now discuss the laws of refraction: The first law of refraction states that at a point where the refraction has occurred, the incident ray, refracted ray and normal all lie in the same plane. The second law is known as Snell’s law which states that the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is always a constant quantity. That we can write as,
\[\dfrac{{\sin {\theta _i}}}{{\sin {\theta _r}}} = {\text{constant}}\].
Note:
Note that the frequency of the light does not change when it travels from one medium to another medium. The velocity of light depends upon the refractive index of the medium. Therefore, the velocity of light changes medium to medium.
Complete answer:
Refraction of light: When the light travels from one medium to another medium, it bends towards or away from the normal depending upon the refractive index of the second medium. This bending of light due to difference in the refractive index, we call it refraction of light.
When the light ray travels from a rare medium to a denser medium, we can see it bends towards the normal due to higher refractive index of the denser medium relative to the rare medium. Also, when the light ray travels from the denser medium to the rare medium, it bends away from the normal.
We assume the light ray travels from the air incident on the glass slab at an angle \[{\theta _i}\] with the normal (imaginary line perpendicular to the surface of the glass slab).

In the above figure, \[{\theta _i}\] is the incident angle and \[{\theta _r}\] is the refracted angle.
We can observe that since the refractive index of the glass is greater than the refractive index of the air, the refracted ray is bent towards the normal.
We will now discuss the laws of refraction: The first law of refraction states that at a point where the refraction has occurred, the incident ray, refracted ray and normal all lie in the same plane. The second law is known as Snell’s law which states that the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is always a constant quantity. That we can write as,
\[\dfrac{{\sin {\theta _i}}}{{\sin {\theta _r}}} = {\text{constant}}\].
Note:
Note that the frequency of the light does not change when it travels from one medium to another medium. The velocity of light depends upon the refractive index of the medium. Therefore, the velocity of light changes medium to medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




