
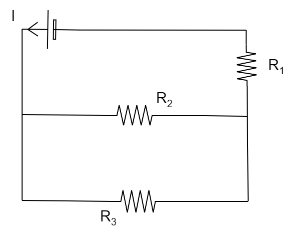
Refer to the circuit shown. What will be the total power dissipation in the circuit if \[P\] is the power dissipated in \[{R_1}\] ? It is given that \[{R_2} = 4{R_1}\] and \[{R_3} = 12{R_1}\]

Answer
495k+ views
Hint:We are asked to find the power dissipation in the given circuit of given current and resistances. We start by finding the equivalent of the three resistances. Two of them are in parallel and the other is in series with the equivalent of the parallel resistors. After this, the answer can be found out pretty quickly as the formula is very direct. After the value of total power dissipation is found, the relation between it and the given power can be found out, giving us the solution.
Formulas used:
The value of equivalent resistance of two resistors in parallel connection is given by,
\[{R_p} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}\]
The value of equivalent resistance of two resistors in series connection is given by,
\[{R_S} = {R_1} + {R_2}\]
Where \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\] are resistances of the individual resistors.
The total power in a circuit can be found out as,
\[P = {I^2}R\]
Where \[I\] is the current through the circuit and \[R\] is the total resistance of the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us start by gathering the given information.
\[{R_2} = 4{R_1}\]
\[\Rightarrow {R_3} = 12{R_1}\]
The resistors \[{R_2}\] and \[{R_3}\] are in parallel, hence their equivalent resistance can be found out using,
\[{R_p} = \dfrac{{{R_3}{R_2}}}{{{R_3} + {R_2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {R_p} = \dfrac{{12{R_1} \times 4{R_1}}}{{12{R_1} + 4{R_1}}} \\
\Rightarrow {R_p} = \dfrac{{48{{\left( {{R_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{16{R_1}}} \\
\Rightarrow {R_p} = 3{R_1}\]
The equivalent parallel resistance is in series with \[{R_1}\] and their equivalent can be found out using,
\[{R_S} = {R_p} + {R_1} \\
\Rightarrow {R_S} = 3{R_1} + {R_1} \\
\Rightarrow {R_S} = 4{R_1}\]
Now that we have the total equivalent resistance of the circuit, we can find the value of total power dissipation using,
\[P_{total} = {I^2}R \\
\Rightarrow P_{total}= {I^2}\left( {4R} \right) \\
\Rightarrow P_{total} = 4{I^2}R\]
But we know that, \[P = {I^2}R\]
Substituting this in the equation we got,
\[\therefore P_{total} = 4P\]
Hence, the total power dissipation will be \[4P\].
Note:The equivalent of the resistors in parallel will be smaller than the smallest value of the two resistors. This can be used to check if we got the correct value for the equivalent resistance in parallel. Power dissipation is the process by which a device produces heat loss as an undesirable byproduct.
Formulas used:
The value of equivalent resistance of two resistors in parallel connection is given by,
\[{R_p} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}\]
The value of equivalent resistance of two resistors in series connection is given by,
\[{R_S} = {R_1} + {R_2}\]
Where \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\] are resistances of the individual resistors.
The total power in a circuit can be found out as,
\[P = {I^2}R\]
Where \[I\] is the current through the circuit and \[R\] is the total resistance of the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us start by gathering the given information.
\[{R_2} = 4{R_1}\]
\[\Rightarrow {R_3} = 12{R_1}\]
The resistors \[{R_2}\] and \[{R_3}\] are in parallel, hence their equivalent resistance can be found out using,
\[{R_p} = \dfrac{{{R_3}{R_2}}}{{{R_3} + {R_2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {R_p} = \dfrac{{12{R_1} \times 4{R_1}}}{{12{R_1} + 4{R_1}}} \\
\Rightarrow {R_p} = \dfrac{{48{{\left( {{R_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{16{R_1}}} \\
\Rightarrow {R_p} = 3{R_1}\]
The equivalent parallel resistance is in series with \[{R_1}\] and their equivalent can be found out using,
\[{R_S} = {R_p} + {R_1} \\
\Rightarrow {R_S} = 3{R_1} + {R_1} \\
\Rightarrow {R_S} = 4{R_1}\]
Now that we have the total equivalent resistance of the circuit, we can find the value of total power dissipation using,
\[P_{total} = {I^2}R \\
\Rightarrow P_{total}= {I^2}\left( {4R} \right) \\
\Rightarrow P_{total} = 4{I^2}R\]
But we know that, \[P = {I^2}R\]
Substituting this in the equation we got,
\[\therefore P_{total} = 4P\]
Hence, the total power dissipation will be \[4P\].
Note:The equivalent of the resistors in parallel will be smaller than the smallest value of the two resistors. This can be used to check if we got the correct value for the equivalent resistance in parallel. Power dissipation is the process by which a device produces heat loss as an undesirable byproduct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




