
When red-flowered plants are crossed with white-flowered plants, the \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation gives a ratio of $3:1$. What do you conclude?
A. That there is a lethal gene
B. That there is independent assortment
C. That white colour is dominant
D. That red colour is dominant
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: In the given cross, red-coloured flowers were seen in more numbers in \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation. This means that allele for red colour if present alone, shows its expression. The white colour expression needs a homologous pairing of alleles for white colour.
Complete answer: The given cross is carried out between one red-coloured flowering plant and one white coloured flowering plant. It means that the red-coloured flowering plant will have a genotype of RR and the white-coloured flowering plant will have genotype rr. R and r are two different alleles determining the red and white colour in flowers respectively.
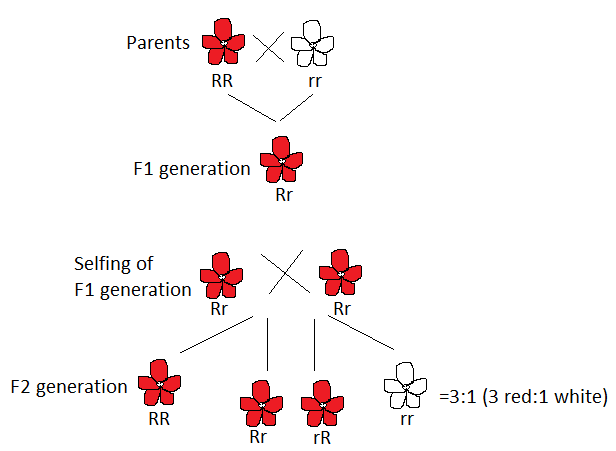
Now, when these pure parents were crossed they produced \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation. The \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation was then self-crossed to produce \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation. The \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation came out of having three red-coloured flowering plants and one white coloured flowering plant. This shows that the red colour is dominant over the white colour. Even a single allele of red colour along with white colour is able to express itself completely. If co-dominance would have occurred then \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation would be showing 1 red, 2 pink, and 1 white-flowered plant. But this did not happen. The above conclusion can be confirmed by a test cross. A test cross is performed between the dominant progeny and its recessive parent. All of the progeny in \[{{F}_{1}}\] will have red-coloured flowers as red is dominant. The genotype of \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation will be Rr if the conclusion is true. The test cross will result in half red and half white flowers which ensures that the \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation will have a heterozygous dominant character.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Note: A test cross is used to check the zygosity of an organism. If an organism is heterozygous dominant, then it will always produce half dominant and half recessive progenies when crossed with its double recessive parent. Thus, the dominance of a trait can be found out with this method.
Complete answer: The given cross is carried out between one red-coloured flowering plant and one white coloured flowering plant. It means that the red-coloured flowering plant will have a genotype of RR and the white-coloured flowering plant will have genotype rr. R and r are two different alleles determining the red and white colour in flowers respectively.

Now, when these pure parents were crossed they produced \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation. The \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation was then self-crossed to produce \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation. The \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation came out of having three red-coloured flowering plants and one white coloured flowering plant. This shows that the red colour is dominant over the white colour. Even a single allele of red colour along with white colour is able to express itself completely. If co-dominance would have occurred then \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation would be showing 1 red, 2 pink, and 1 white-flowered plant. But this did not happen. The above conclusion can be confirmed by a test cross. A test cross is performed between the dominant progeny and its recessive parent. All of the progeny in \[{{F}_{1}}\] will have red-coloured flowers as red is dominant. The genotype of \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation will be Rr if the conclusion is true. The test cross will result in half red and half white flowers which ensures that the \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation will have a heterozygous dominant character.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Note: A test cross is used to check the zygosity of an organism. If an organism is heterozygous dominant, then it will always produce half dominant and half recessive progenies when crossed with its double recessive parent. Thus, the dominance of a trait can be found out with this method.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




