
What is rectification? Explain the working of bridge rectifiers. Draw the input and output signals.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Here first we shall understand that the conversion of alternating current to direct current is rectification.
Now let us see what bridge rectifier is-
A bridge rectifier is a type of full wave rectifier using four or more diodes to transform AC to DC effectively.
Complete step by step solution:
Among all the rectifiers the most commonly used is the bridge rectifier.
Construction of a bridge rectifier-
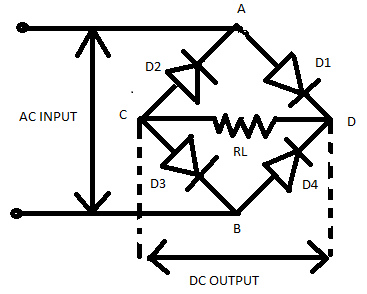
In the figure above the construction of a bridge rectifier is shown. The bridge rectifier consists of four ${D_1},{D_2},{D_3},{D_4}$ diodes and a load resistor ${R_L}$. The diodes form a closed –loop configuration and are connected to transform the AC current into DC current. The input signal is connected across the terminals A and B and the DC output is found across the load resistor ${R_L}$and connected across the terminals C and D. Diodes ${D_1}$ and ${D_3}$ conduct in the positive half cycle and diodes ${D_2}$ and ${D_4}$ conduct in the negative half cycle.
Working of a bridge rectifier circuit
When AC current is supplied to the input during the positive half cycle of the bridge rectifier terminal A becomes positive and terminal B becomes negative. So, diodes ${D_1}$ and ${D_3}$ becomes forward biased and begins to conduct. Diodes ${D_2}$ and ${D_4}$ becomes reverse biased.
When AC current is supplied to the input during the negative half cycle of the bridge rectifier terminal A becomes negative and terminal B becomes positive. So, diodes ${D_2}$ and ${D_4}$ becomes forward biased and begins to conduct. Diodes ${D_1}$ and ${D_3}$ becomes reverse biased.
Thus, during both the positive and negative half periods of the incoming AC signal, a bridge rectifier facilitates electric current.
The AC and DC output is as follows:
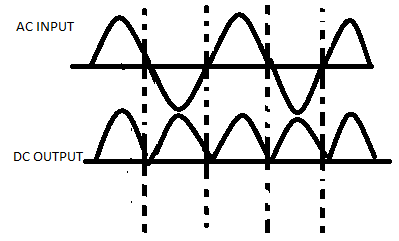
Note: In this solution, during the positive half cycle and the negative half cycles, the current flow through the load resistor ${R_L}$ is the same. The DC signal polarity of the rectifier can be either totally positive or negative.
Now let us see what bridge rectifier is-
A bridge rectifier is a type of full wave rectifier using four or more diodes to transform AC to DC effectively.
Complete step by step solution:
Among all the rectifiers the most commonly used is the bridge rectifier.
Construction of a bridge rectifier-

In the figure above the construction of a bridge rectifier is shown. The bridge rectifier consists of four ${D_1},{D_2},{D_3},{D_4}$ diodes and a load resistor ${R_L}$. The diodes form a closed –loop configuration and are connected to transform the AC current into DC current. The input signal is connected across the terminals A and B and the DC output is found across the load resistor ${R_L}$and connected across the terminals C and D. Diodes ${D_1}$ and ${D_3}$ conduct in the positive half cycle and diodes ${D_2}$ and ${D_4}$ conduct in the negative half cycle.
Working of a bridge rectifier circuit
When AC current is supplied to the input during the positive half cycle of the bridge rectifier terminal A becomes positive and terminal B becomes negative. So, diodes ${D_1}$ and ${D_3}$ becomes forward biased and begins to conduct. Diodes ${D_2}$ and ${D_4}$ becomes reverse biased.
When AC current is supplied to the input during the negative half cycle of the bridge rectifier terminal A becomes negative and terminal B becomes positive. So, diodes ${D_2}$ and ${D_4}$ becomes forward biased and begins to conduct. Diodes ${D_1}$ and ${D_3}$ becomes reverse biased.
Thus, during both the positive and negative half periods of the incoming AC signal, a bridge rectifier facilitates electric current.
The AC and DC output is as follows:

Note: In this solution, during the positive half cycle and the negative half cycles, the current flow through the load resistor ${R_L}$ is the same. The DC signal polarity of the rectifier can be either totally positive or negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




