
Recall that two circles are congruent if they have the same radii. Prove that equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: To prove that they subtend equal angles it is enough to show that the triangles are congruent to each other by any of the rule examples SAS, AAA, SSS. After proving that congruent then by corresponding parts of congruent triangle theorem the subtend angles are equal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following are the schematic diagram of the two circles having the same radii.
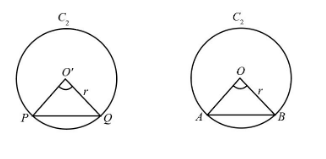
Since, two circles are congruent $ {C_1} $ and $ {C_2} $ .
We know that $ AB $ is the chord of $ {C_1} $ and $ PQ $ is the chord of $ {C_2} $ .
Since, it is given that two chords are equal so $ AB = PQ $ .
The main aim is to prove that angles subtended by chords are equal, that is $ \angle AOB = \angle PXQ $ .
To show that first let us prove that $ \Delta AOB \cong \Delta PO'Q $ .
In the $ \Delta AOB $ and $ \Delta PO'Q $ ,
Since the radius of congruent circles are equal,
So, $ AO = PO' $ ….(1)
Since the radius of congruent circles are equal,
$ BO = QO' $ ……..(2)
It is given that two chords are equal so,
$ AB = PQ $ …….(3)
On equating the equations (1), (2) and (3) we can say by the rule of SSS congruency that,
$ \Delta AOB \cong \Delta PO'Q $
By corresponding parts of congruent triangle theorem that is CPCT rule, we have,
$ \angle AOB = \angle COD $
Hence, equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres.
Note: The corresponding parts of congruent triangle theorem states that if suppose the two or more triangles that are congruent with each other are taken then the corresponding sides and angles of the congruent triangles are also equal to each other. Every time SSS cannot be used depending on the known values we can use different criterion rule.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following are the schematic diagram of the two circles having the same radii.

Since, two circles are congruent $ {C_1} $ and $ {C_2} $ .
We know that $ AB $ is the chord of $ {C_1} $ and $ PQ $ is the chord of $ {C_2} $ .
Since, it is given that two chords are equal so $ AB = PQ $ .
The main aim is to prove that angles subtended by chords are equal, that is $ \angle AOB = \angle PXQ $ .
To show that first let us prove that $ \Delta AOB \cong \Delta PO'Q $ .
In the $ \Delta AOB $ and $ \Delta PO'Q $ ,
Since the radius of congruent circles are equal,
So, $ AO = PO' $ ….(1)
Since the radius of congruent circles are equal,
$ BO = QO' $ ……..(2)
It is given that two chords are equal so,
$ AB = PQ $ …….(3)
On equating the equations (1), (2) and (3) we can say by the rule of SSS congruency that,
$ \Delta AOB \cong \Delta PO'Q $
By corresponding parts of congruent triangle theorem that is CPCT rule, we have,
$ \angle AOB = \angle COD $
Hence, equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres.
Note: The corresponding parts of congruent triangle theorem states that if suppose the two or more triangles that are congruent with each other are taken then the corresponding sides and angles of the congruent triangles are also equal to each other. Every time SSS cannot be used depending on the known values we can use different criterion rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




