
Reaction of R-COOH with ${{N}_{3}}H$ gives $RN{{H}_{2}}$ as the main product. The intermediate(s) involved in this reaction is/are:
(A)- $RNHN{{H}_{2}}$
(B)- $RCO{{N}_{3}}$
(C)- RNCO
(D)- $RCON{{H}_{2}}$
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: An organic reaction in which an azide reacts with a carbonyl derivative which is usually an aldehyde, ketone, or a carboxylic acid under acidic conditions giving an amide or amine with the release of nitrogen is known as Schmidt reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
-Schmidt reaction is named after Karl Friedrich Schmidt who first reported it by successfully converting benzophenone and hydrazoic acid to benzanilide.
-The Schmidt reaction can be employed to get amide by the reaction between an azide and a ketone or to get amine by the reaction between azide with a carboxylic acid.
-Let us now see Schmidt reaction for Carboxylic acids and azide producing amines-
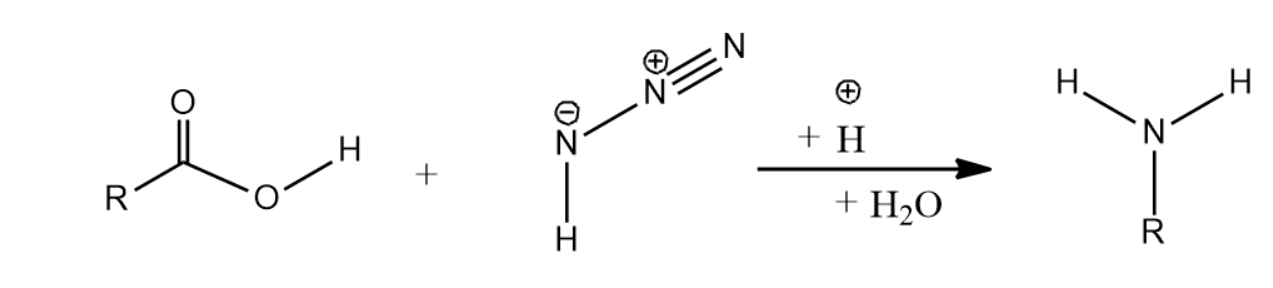
-The mechanism of Schmidt reaction for producing amines is given as below-
(i) The mechanism begins with the formation of an acylium ion produced by the protonation of the carboxylic acid followed by dehydration.
(ii) The acylium ions formed now react with hydrazoic acid leading to the formation of a protonated azido ketone.
(iii) Now, the protonated azido ketone and the alkyl group undergoes a rearrangement reaction, resulting in the migration of the carbon-nitrogen bond and the removal of dinitrogen leading to the formation of a protonated isocyanate.
(iv) When water is introduced to attack the protonated isocyanate, carbamate is formed.
(v) The carbamate on deprotonation and subsequent removal of carbon dioxide yields the required product, which is an amine.
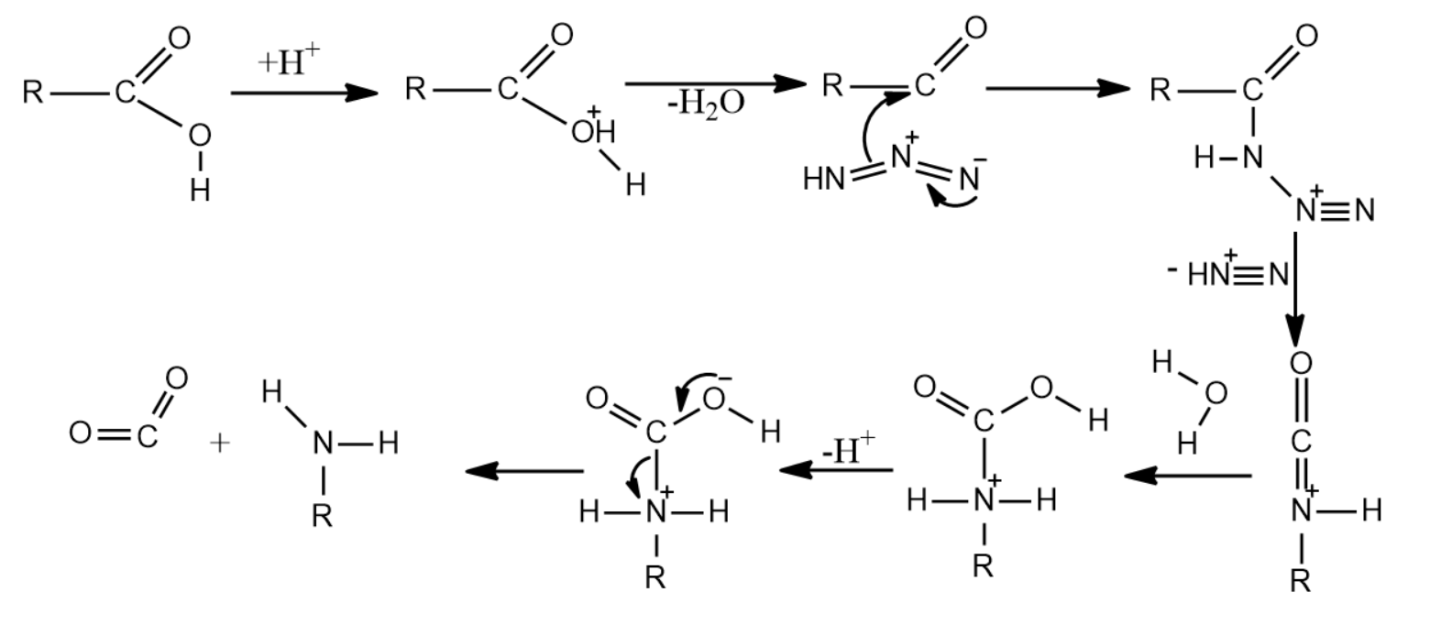
So, the correct answer is “Option B and C”.
Note: You may get confused between Schmidt reaction and Curtius rearrangement. The thermal decomposition of carboxylic azides to produce an isocyanate is known as the Curtius rearrangement. In other words, the reaction sequence including the subsequent reaction with water producing amines is known as the Curtius reaction. Curtius reaction is similar to the Schmidt reaction with acids, differing in that acyl azide which is prepared from the acyl halide and an azide salt.
Complete step by step answer:
-Schmidt reaction is named after Karl Friedrich Schmidt who first reported it by successfully converting benzophenone and hydrazoic acid to benzanilide.
-The Schmidt reaction can be employed to get amide by the reaction between an azide and a ketone or to get amine by the reaction between azide with a carboxylic acid.
-Let us now see Schmidt reaction for Carboxylic acids and azide producing amines-

-The mechanism of Schmidt reaction for producing amines is given as below-
(i) The mechanism begins with the formation of an acylium ion produced by the protonation of the carboxylic acid followed by dehydration.
(ii) The acylium ions formed now react with hydrazoic acid leading to the formation of a protonated azido ketone.
(iii) Now, the protonated azido ketone and the alkyl group undergoes a rearrangement reaction, resulting in the migration of the carbon-nitrogen bond and the removal of dinitrogen leading to the formation of a protonated isocyanate.
(iv) When water is introduced to attack the protonated isocyanate, carbamate is formed.
(v) The carbamate on deprotonation and subsequent removal of carbon dioxide yields the required product, which is an amine.

So, the correct answer is “Option B and C”.
Note: You may get confused between Schmidt reaction and Curtius rearrangement. The thermal decomposition of carboxylic azides to produce an isocyanate is known as the Curtius rearrangement. In other words, the reaction sequence including the subsequent reaction with water producing amines is known as the Curtius reaction. Curtius reaction is similar to the Schmidt reaction with acids, differing in that acyl azide which is prepared from the acyl halide and an azide salt.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




