
Reaction of formaldehyde and ammonia gives:
A. hexamethylenetetramine
B. Bakelite
C. urea
D. triethylenetetramine
Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint: Action of Formaldehyde on Ammonia is an example of hetero condensation polymer. Polymers are large molecules made by the linkage of small units. Condensation polymers are accompanied by loss of substances like water from the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Formaldehyde $\text{HCHO}$ reacts with ammonia $\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}$ in neutral or alkaline solution. Due to the basic medium, neutralisation also takes place when formaldehyde reacts with ammonia by heating up ammonia bicarbonate or ammonium carbonate to generate ammonia vapours. The ammonia vapours formed neutralise the formaldehyde gas which creates a by-product called methenamine. Methenamine is also called hexamine, urotropin and hexamethylenetetramine. The structure of methenamine along with reaction is
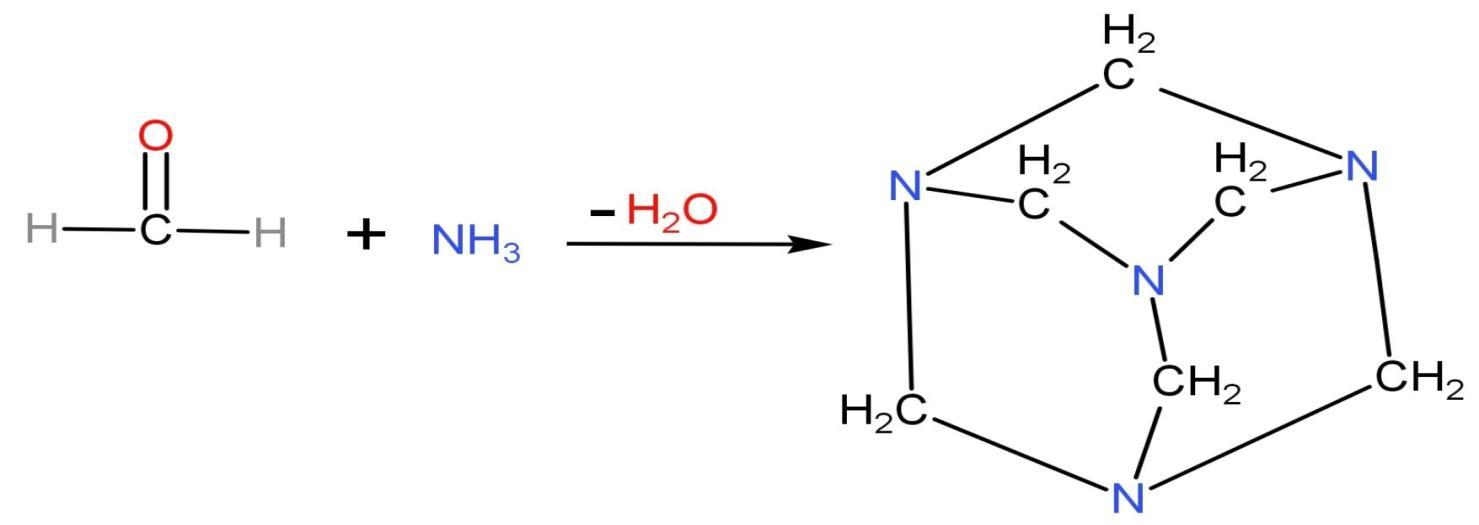
Hexamethylenetetramine is a heterocyclic organic compound which has molecular formula ${{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}} \right)}_{6}}{{\text{N}}_{4}}$. It is a white crystalline compound which is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like structure.
The correct answer is option A.
Additional Information:
Uses of hexamethylenetetramine:
(1) Hexamine is also used as a food additive as a preservative.
(2) Methenamine in the form of cream and spray is used for treatment of excessive sweating and odour.
(3) The use of hexamethylenetetramine is in the production of liquid preparations of phenolic resins and its moulding compounds, where it is used as a hardening component.
Note:
The point to note in this reaction is that this reaction is reversible. It is an interconvertible reaction. By adding $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{-}}$ ions, the reaction will proceed forward and addition of ${{\text{H}}^{+}}$ ions, the reaction will move backward. $\text{6HCHO}+4\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\longrightarrow{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{N}}_{4}}+6{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}$
Complete step by step answer:
Formaldehyde $\text{HCHO}$ reacts with ammonia $\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}$ in neutral or alkaline solution. Due to the basic medium, neutralisation also takes place when formaldehyde reacts with ammonia by heating up ammonia bicarbonate or ammonium carbonate to generate ammonia vapours. The ammonia vapours formed neutralise the formaldehyde gas which creates a by-product called methenamine. Methenamine is also called hexamine, urotropin and hexamethylenetetramine. The structure of methenamine along with reaction is

Hexamethylenetetramine is a heterocyclic organic compound which has molecular formula ${{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}} \right)}_{6}}{{\text{N}}_{4}}$. It is a white crystalline compound which is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like structure.
The correct answer is option A.
Additional Information:
Uses of hexamethylenetetramine:
(1) Hexamine is also used as a food additive as a preservative.
(2) Methenamine in the form of cream and spray is used for treatment of excessive sweating and odour.
(3) The use of hexamethylenetetramine is in the production of liquid preparations of phenolic resins and its moulding compounds, where it is used as a hardening component.
Note:
The point to note in this reaction is that this reaction is reversible. It is an interconvertible reaction. By adding $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{-}}$ ions, the reaction will proceed forward and addition of ${{\text{H}}^{+}}$ ions, the reaction will move backward. $\text{6HCHO}+4\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\longrightarrow{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{N}}_{4}}+6{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}$
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

What is myopia and hypermetropia How are they corrected class 12 physics CBSE




