
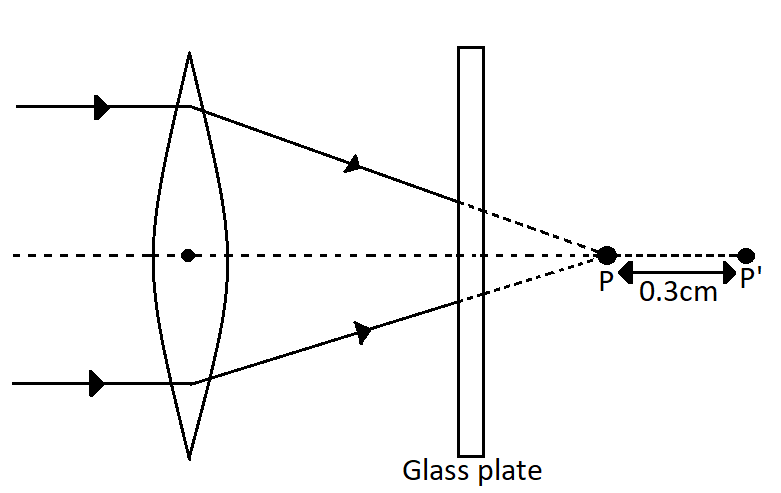
Rays from a lens are converging towards a point P, as shown in figure. How much thick glass plate having refractive index $1.6$ must be located between the lens and point P, so that the image will be formed at P’?
(A) $0.8cm$
(B) $1.6cm$
(C) $5cm$
(D) $2.4cm$

Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint
On placing the glass slab, the image shifts from the point P to the point P’. So we can find the thickness of the slab by using the refractive index of the glass and the distance of the shift of the image from the point P to P’.
In this solution we will be using the formula,
$\Rightarrow x = t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu }} \right)$
where $x$ is the shift in the image.
$t$ is the thickness of the glass slab
and $\mu $ is the refractive index of glass.
Complete step by step answer
In this question, it is said that the image is formed due to the convex lens at the point P. Now when a glass slab is introduced between the point P and the convex lens, we find that the image is formed at the point P’, where the point P’ is at a distance of $0.3cm$ from the point P.
Therefore, the shift of the image is given by the formula,
$\Rightarrow x = t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu }} \right)$
Now in the question we are given the refractive index of glass and the shift. So we can write the equation in terms of the thickness as,
$\Rightarrow x = t\left( {\dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{\mu }} \right)$
So taking all the values except $t$ from RHS to the LHS we get,
$\Rightarrow t = x\left( {\dfrac{\mu }{{\mu - 1}}} \right)$
Therefore on substituting the values of the shift as $x = 0.3cm = 3 \times {10^{ - 3}}m$ and the refractive index as $\mu = 1.6$.
Therefore we get,
$\Rightarrow t = \left( {3 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{1.6}}{{1.6 - 1}}} \right)$
On calculating this gives us,
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{3 \times {{10}^{ - 3}} \times 1.6}}{{0.6}}m$
Hence the thickness of the slab is,
$\Rightarrow t = 8 \times {10^{ - 3}}m$
That is equal to $t = 0.8cm$
So the correct answer is option (A); $0.8cm$.
Note
Due to placing the glass slab in between the convex lens and the image, the image gets shifted from the point P to the point P’. This is because the speed of light is different in the glass slab from the speed of light in air.
On placing the glass slab, the image shifts from the point P to the point P’. So we can find the thickness of the slab by using the refractive index of the glass and the distance of the shift of the image from the point P to P’.
In this solution we will be using the formula,
$\Rightarrow x = t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu }} \right)$
where $x$ is the shift in the image.
$t$ is the thickness of the glass slab
and $\mu $ is the refractive index of glass.
Complete step by step answer
In this question, it is said that the image is formed due to the convex lens at the point P. Now when a glass slab is introduced between the point P and the convex lens, we find that the image is formed at the point P’, where the point P’ is at a distance of $0.3cm$ from the point P.
Therefore, the shift of the image is given by the formula,
$\Rightarrow x = t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu }} \right)$
Now in the question we are given the refractive index of glass and the shift. So we can write the equation in terms of the thickness as,
$\Rightarrow x = t\left( {\dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{\mu }} \right)$
So taking all the values except $t$ from RHS to the LHS we get,
$\Rightarrow t = x\left( {\dfrac{\mu }{{\mu - 1}}} \right)$
Therefore on substituting the values of the shift as $x = 0.3cm = 3 \times {10^{ - 3}}m$ and the refractive index as $\mu = 1.6$.
Therefore we get,
$\Rightarrow t = \left( {3 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{1.6}}{{1.6 - 1}}} \right)$
On calculating this gives us,
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{3 \times {{10}^{ - 3}} \times 1.6}}{{0.6}}m$
Hence the thickness of the slab is,
$\Rightarrow t = 8 \times {10^{ - 3}}m$
That is equal to $t = 0.8cm$
So the correct answer is option (A); $0.8cm$.
Note
Due to placing the glass slab in between the convex lens and the image, the image gets shifted from the point P to the point P’. This is because the speed of light is different in the glass slab from the speed of light in air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




